Dr.Eman Zakaria Hegazy Quantum Mechanics and Statistical
... Hydrogen atomic spectrum consists of several series of lines ...
... Hydrogen atomic spectrum consists of several series of lines ...
Chapter 30 - Planet Holloway
... Is responsible for the binding of atoms and molecules About 10-2 times the strength of the strong force A long-range force that decreases in strength as the inverse square of the separation between interacting particles ...
... Is responsible for the binding of atoms and molecules About 10-2 times the strength of the strong force A long-range force that decreases in strength as the inverse square of the separation between interacting particles ...
Wave Particle Duality
... the atom. He used much of de Broglie’s work on the wavelike properties of particles in the creation of this model. Because of Heisenberg’s Principle of Uncertainty, we cannot know both the position and the momentum of an electron at a given time. Rather than give exact location of an electron, the q ...
... the atom. He used much of de Broglie’s work on the wavelike properties of particles in the creation of this model. Because of Heisenberg’s Principle of Uncertainty, we cannot know both the position and the momentum of an electron at a given time. Rather than give exact location of an electron, the q ...
2_Quantum theory_ techniques and applications
... Ingenious devices exploit the quantum effects of miniature structures to control electrical current. These devices operate by single electron control, and they require that electron movement be confined to two (quantum well), one (quantum wire), or zero (quantum dot) dimensions. In these devices sma ...
... Ingenious devices exploit the quantum effects of miniature structures to control electrical current. These devices operate by single electron control, and they require that electron movement be confined to two (quantum well), one (quantum wire), or zero (quantum dot) dimensions. In these devices sma ...
File
... • Performed with electrons (C Jönsson 1961 Zeitschrift für Physik 161 454474, translated 1974 American Journal of Physics 42 4-11) • Performed with single electrons (A Tonomura et al. 1989 American Journal of Physics 57 117-120) • Performed with neutrons (A Zeilinger et al. 1988 Reviews of Modern Ph ...
... • Performed with electrons (C Jönsson 1961 Zeitschrift für Physik 161 454474, translated 1974 American Journal of Physics 42 4-11) • Performed with single electrons (A Tonomura et al. 1989 American Journal of Physics 57 117-120) • Performed with neutrons (A Zeilinger et al. 1988 Reviews of Modern Ph ...
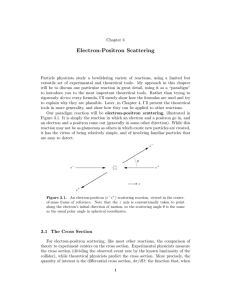
On classical and quantum effects at scattering of fast charged
... turnover upside down that is connected with the change of sign of the particle charge. We can see that entire scattering picture for PCP even changes its entire angular dimensions at first half-periods of oscillations, while in the case of NCP it quickly reaches its maximal value and then only chang ...
... turnover upside down that is connected with the change of sign of the particle charge. We can see that entire scattering picture for PCP even changes its entire angular dimensions at first half-periods of oscillations, while in the case of NCP it quickly reaches its maximal value and then only chang ...
PHYS1220 - s3.amazonaws.com
... position and momentum of an electron as precisely as possible with a powerful light microscope In order to determine the electron’s location (ie making x small ~ l) at least one photon of light (with momentum h/l must be scattered (as in (a)) But the photon imparts an unknown amount of its momentum ...
... position and momentum of an electron as precisely as possible with a powerful light microscope In order to determine the electron’s location (ie making x small ~ l) at least one photon of light (with momentum h/l must be scattered (as in (a)) But the photon imparts an unknown amount of its momentum ...
Uncertainty Relations for Quantum Mechanical Observables
... To gain a solid uncertainty, we specify the experiment and especially the measuring process more: Let ψ, ξ be two states (representing particles). We first want to measure A on ψ. We assume that every meaurement includes interaction with another particle (cf. measurement of car speed with radar gun) ...
... To gain a solid uncertainty, we specify the experiment and especially the measuring process more: Let ψ, ξ be two states (representing particles). We first want to measure A on ψ. We assume that every meaurement includes interaction with another particle (cf. measurement of car speed with radar gun) ...