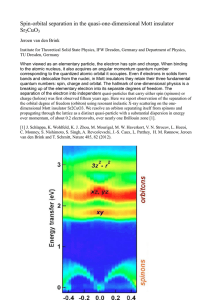
Spin-orbital separation in the quasi-one
... When viewed as an elementary particle, the electron has spin and charge. When binding to the atomic nucleus, it also acquires an angular momentum quantum number corresponding to the quantized atomic orbital it occupies. Even if electrons in solids form bands and delocalize from the nuclei, in Mott i ...
... When viewed as an elementary particle, the electron has spin and charge. When binding to the atomic nucleus, it also acquires an angular momentum quantum number corresponding to the quantized atomic orbital it occupies. Even if electrons in solids form bands and delocalize from the nuclei, in Mott i ...
Riemannian method in quantum field theory about curved space-time
... Starting from a given Lorentz metric g~k on a space-time manifold M and a tube T of world lines along which observers may move, we describe an algorithm to obtain the quantum theory of scalar particles of mass m. Let ei denote the 4-velocities of the world lines, and let V~, s real, be a family o f ...
... Starting from a given Lorentz metric g~k on a space-time manifold M and a tube T of world lines along which observers may move, we describe an algorithm to obtain the quantum theory of scalar particles of mass m. Let ei denote the 4-velocities of the world lines, and let V~, s real, be a family o f ...
Detection of entanglement and of features of quantum evolution with
... We will give an overview of several recent results concerning the detection of properties of composite states and of quantum evolutions by employing measurements of complementary properties. Two properties of a quantum systems are called complementary if they are such that, if one knows the value of ...
... We will give an overview of several recent results concerning the detection of properties of composite states and of quantum evolutions by employing measurements of complementary properties. Two properties of a quantum systems are called complementary if they are such that, if one knows the value of ...
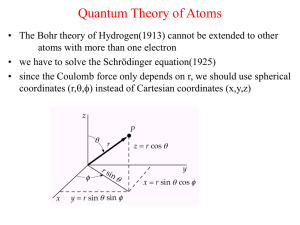
Document
... We cannot solve this Schrödinger equation analytically. (Two electrons are not separable nor independent any more.) A series of approximations will be introduced. ...
... We cannot solve this Schrödinger equation analytically. (Two electrons are not separable nor independent any more.) A series of approximations will be introduced. ...
1 PHY4605–Introduction to Quantum Mechanics II Spring 2004 Test 1 Solutions
... (a) Explain the Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen ”paradox”. How does the Copenhagen school of quantum mechanics escape the apparent violation of causality? Simplest example: spin 0 particle decays in lab frame into two spin–1/2 particles which recoil in opposite directions. Quantum Mechanics says spin state ...
... (a) Explain the Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen ”paradox”. How does the Copenhagen school of quantum mechanics escape the apparent violation of causality? Simplest example: spin 0 particle decays in lab frame into two spin–1/2 particles which recoil in opposite directions. Quantum Mechanics says spin state ...
3.4 Quantum Numbers
... The Spin Quantum Number (ms) • Gives the spin state of the electron • Describes the direction in which the electron is spinning (identifies the electron within an orbital) • Goudsmit and Uhlenbeck noticed that an atom has a magnetic moment when it is placed in an external magnetic field • ms can ha ...
... The Spin Quantum Number (ms) • Gives the spin state of the electron • Describes the direction in which the electron is spinning (identifies the electron within an orbital) • Goudsmit and Uhlenbeck noticed that an atom has a magnetic moment when it is placed in an external magnetic field • ms can ha ...
Physics 451 - BYU Physics and Astronomy
... I have noticed in recent homeworks that more students quit to do entire problem(s). They are either short in time or overwhelmed by the length of the problems. It is understandable that this is an intense course, and the homework is time consuming. And as it is approaching the middle of the semester ...
... I have noticed in recent homeworks that more students quit to do entire problem(s). They are either short in time or overwhelmed by the length of the problems. It is understandable that this is an intense course, and the homework is time consuming. And as it is approaching the middle of the semester ...
Quantum Mechanics in the Early Universe
... • Simply a universe where Bell inequalities can be tested with primordial fluctuations. ...
... • Simply a universe where Bell inequalities can be tested with primordial fluctuations. ...
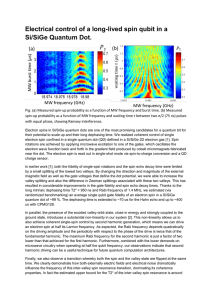
Electrical control of a long-lived spin qubit in a
... ground state, introduces a substantial non-linearity in our system [2]. This non-linearity allows us to also achieve coherent single-spin control by second harmonic generation, which means we can drive an electron spin at half its Larmor frequency. As expected, the Rabi frequency depends quadratical ...
... ground state, introduces a substantial non-linearity in our system [2]. This non-linearity allows us to also achieve coherent single-spin control by second harmonic generation, which means we can drive an electron spin at half its Larmor frequency. As expected, the Rabi frequency depends quadratical ...
Asymptotic Freedom: From Paradox to Paradigm
... Screening by virtual particles wipes out interactions The demise of quantum field theory was widely proclaimed - and welcomed! ...
... Screening by virtual particles wipes out interactions The demise of quantum field theory was widely proclaimed - and welcomed! ...
THE UNCERTAINTY PRINCIPLE The uncertainty principle states
... The uncertainty principle states that a function f on Rn and its Fourier transform fˆ can not both be too highly localized. In the Schrödinger formulation of quantum mechanics, this becomes the statement that both the position and the momentum of a quantum particle cannot be prescribed too accurate ...
... The uncertainty principle states that a function f on Rn and its Fourier transform fˆ can not both be too highly localized. In the Schrödinger formulation of quantum mechanics, this becomes the statement that both the position and the momentum of a quantum particle cannot be prescribed too accurate ...
A quantum point contact for ultra cold Fermions
... constrictions are imprinted on a quasi two-dimensional ballistic channel connecting two adjustable reservoirs of quantum degenerate fermionic lithium atoms. By tuning either a gate potential or the transverse confinements of the constrictions, we observe distinct plateaus in the conductance for matt ...
... constrictions are imprinted on a quasi two-dimensional ballistic channel connecting two adjustable reservoirs of quantum degenerate fermionic lithium atoms. By tuning either a gate potential or the transverse confinements of the constrictions, we observe distinct plateaus in the conductance for matt ...
The Search for QIMDS - University of Illinois Urbana
... 1. If we interpret raw data in QM terms, then can conclude we have a quantum superposition rather than a mixture of meso/macroscopically distinct states. However, “only 1 degree of freedom involved.” 2. Do data exclude general hypothesis of macrorealism? NO ...
... 1. If we interpret raw data in QM terms, then can conclude we have a quantum superposition rather than a mixture of meso/macroscopically distinct states. However, “only 1 degree of freedom involved.” 2. Do data exclude general hypothesis of macrorealism? NO ...
Bell's theorem
Bell's theorem is a ‘no-go theorem’ that draws an important distinction between quantum mechanics (QM) and the world as described by classical mechanics. This theorem is named after John Stewart Bell.In its simplest form, Bell's theorem states:Cornell solid-state physicist David Mermin has described the appraisals of the importance of Bell's theorem in the physics community as ranging from ""indifference"" to ""wild extravagance"". Lawrence Berkeley particle physicist Henry Stapp declared: ""Bell's theorem is the most profound discovery of science.""Bell's theorem rules out local hidden variables as a viable explanation of quantum mechanics (though it still leaves the door open for non-local hidden variables). Bell concluded:Bell summarized one of the least popular ways to address the theorem, superdeterminism, in a 1985 BBC Radio interview: