Lecture 4
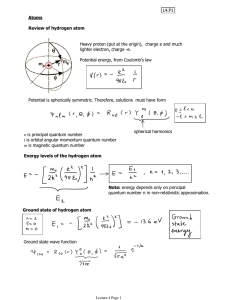
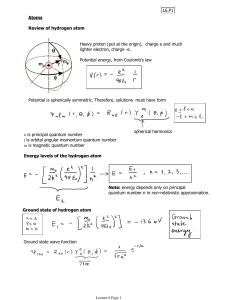
... Review: hydrogenic atoms (these are called ions since they are charged). A hydrogenic (or hydrogen-like) atom consists of a single electron orbiting a nucleus with Z protons. What are the corresponding energies? ...
... Review: hydrogenic atoms (these are called ions since they are charged). A hydrogenic (or hydrogen-like) atom consists of a single electron orbiting a nucleus with Z protons. What are the corresponding energies? ...
Chemistry 871/671/495, Structure and Bonding
... followed by analytical solutions of the Schrödinger equation for simple systems, such as the particle in a box, harmonic oscillator, and rigid rotor. These examples not only illustrate energy quantization of microscopic systems, but also have important practical significance as discussed later. We w ...
... followed by analytical solutions of the Schrödinger equation for simple systems, such as the particle in a box, harmonic oscillator, and rigid rotor. These examples not only illustrate energy quantization of microscopic systems, but also have important practical significance as discussed later. We w ...
The Future of Computer Science
... The radiation seems thermal (uncorrelated with whatever fell in). But if quantum mechanics is true, then it can’t be! Susskind, ‘t Hooft 1990s: “Black-hole complementarity.” Idea that quantum states emerging from black hole are somehow “the same states” as the ones trapped inside, just measured in a ...
... The radiation seems thermal (uncorrelated with whatever fell in). But if quantum mechanics is true, then it can’t be! Susskind, ‘t Hooft 1990s: “Black-hole complementarity.” Idea that quantum states emerging from black hole are somehow “the same states” as the ones trapped inside, just measured in a ...
Lecture 29B - UCSD Department of Physics
... Problems with Bohr’s Model Bohr’s explanation of atomic spectra includes some features of the currently accepted theory. Bohr’s model includes both classical and nonclassical ideas. He applied Planck’s ideas of quantized energy levels to orbiting electrons and Einstein’s concept of the photon to de ...
... Problems with Bohr’s Model Bohr’s explanation of atomic spectra includes some features of the currently accepted theory. Bohr’s model includes both classical and nonclassical ideas. He applied Planck’s ideas of quantized energy levels to orbiting electrons and Einstein’s concept of the photon to de ...
PHYS 1311: Advanced Intro. Physics I
... teacher.pas.rochester.edu/phy_labs/appendixe/appendixe.html) ...
... teacher.pas.rochester.edu/phy_labs/appendixe/appendixe.html) ...
quantum - Academia Sinica
... (1) One of the founders of the quantum concept (2) A first, thought there must be something wrong with the quantum theory. (3) After much debate with Bohr, he finally was convinced that QM gives correct results, but it could not be the final theory. It is incomplete! ...
... (1) One of the founders of the quantum concept (2) A first, thought there must be something wrong with the quantum theory. (3) After much debate with Bohr, he finally was convinced that QM gives correct results, but it could not be the final theory. It is incomplete! ...
Quantum Physics 2005 Notes-6 Solving the Time Independent Schrodinger Equation
... If we know the values of ! j and ! j #1 near some point, we can solve for ! j+1. We can usually get ! j and ! j #1 from the continuity or symmetry conditions at a point. The only parameter with which to achieve agreement of the wavefunction with expected behavior is % . Notes 6 ...
... If we know the values of ! j and ! j #1 near some point, we can solve for ! j+1. We can usually get ! j and ! j #1 from the continuity or symmetry conditions at a point. The only parameter with which to achieve agreement of the wavefunction with expected behavior is % . Notes 6 ...
Field extension of real values of physical observables in classical
... Bell inequality is a mathematical inequality involving certain averages of correlations of measure- ...
... Bell inequality is a mathematical inequality involving certain averages of correlations of measure- ...
BCK0103-15 Quantum physics (3-0-4) - nuvem
... BCK0103-15 Quantum physics (3-0-4) General goals: The main goal of this course is to present to the student the main concepts of the quantum theory, with the perspective of comprehending the basic phenomena which originate at the atomic scale, their effects and technological applications. ...
... BCK0103-15 Quantum physics (3-0-4) General goals: The main goal of this course is to present to the student the main concepts of the quantum theory, with the perspective of comprehending the basic phenomena which originate at the atomic scale, their effects and technological applications. ...
Another version - Scott Aaronson
... Intuition: If Range(f) and Range(g) are disjoint, then the H register decoheres all entanglement between R and B, leaving only classical correlation If, on the other hand, Range(f)=Range(g), then there’s some permutation of the |x,1R states that puts the last qubit of R into an EPR pair with B Thus ...
... Intuition: If Range(f) and Range(g) are disjoint, then the H register decoheres all entanglement between R and B, leaving only classical correlation If, on the other hand, Range(f)=Range(g), then there’s some permutation of the |x,1R states that puts the last qubit of R into an EPR pair with B Thus ...
Lecture notes for FYS610 Many particle Quantum Mechanics
... best for unconstrained systems defined in Cartesian coordinates in Newtonian or specialrelativistic space-time. It is much harder, or impossible, to apply for constrained systems, including gauge field theories and systems defined in a curved space-time. Canonical quantization is not the only quanti ...
... best for unconstrained systems defined in Cartesian coordinates in Newtonian or specialrelativistic space-time. It is much harder, or impossible, to apply for constrained systems, including gauge field theories and systems defined in a curved space-time. Canonical quantization is not the only quanti ...
The Quantum Spin Hall Effect
... of HgTe/CdTe quantum wells have been fabricated. • Because of the small band gap, about several meV, one can gate dope this system from n to p doped regimes. • Two tuning parameters, the thickness d of the quantum well, and the gate voltage. ...
... of HgTe/CdTe quantum wells have been fabricated. • Because of the small band gap, about several meV, one can gate dope this system from n to p doped regimes. • Two tuning parameters, the thickness d of the quantum well, and the gate voltage. ...
Quantum Correlations, Information and Entropy
... known forces between them, and …… separate again, then they can no longer be described in the same way as before, viz. by endowing each of them with a representative of its own. I would not call that one but rather the characteristic trait of quantum mechanics, the one that enforces its entire depar ...
... known forces between them, and …… separate again, then they can no longer be described in the same way as before, viz. by endowing each of them with a representative of its own. I would not call that one but rather the characteristic trait of quantum mechanics, the one that enforces its entire depar ...
Using Boolean Logic to Research Quantum Field Theory
... The Stanford Encyclopedia of philosophy recognizes Quantum Field Theory as mathematical and conceptual framework that implements elementary particles in particle physics. This also acquired the theory as a sub subject of both Quantum Physics and Particle Physics. Stanford University uses those facts ...
... The Stanford Encyclopedia of philosophy recognizes Quantum Field Theory as mathematical and conceptual framework that implements elementary particles in particle physics. This also acquired the theory as a sub subject of both Quantum Physics and Particle Physics. Stanford University uses those facts ...
Bell's theorem
Bell's theorem is a ‘no-go theorem’ that draws an important distinction between quantum mechanics (QM) and the world as described by classical mechanics. This theorem is named after John Stewart Bell.In its simplest form, Bell's theorem states:Cornell solid-state physicist David Mermin has described the appraisals of the importance of Bell's theorem in the physics community as ranging from ""indifference"" to ""wild extravagance"". Lawrence Berkeley particle physicist Henry Stapp declared: ""Bell's theorem is the most profound discovery of science.""Bell's theorem rules out local hidden variables as a viable explanation of quantum mechanics (though it still leaves the door open for non-local hidden variables). Bell concluded:Bell summarized one of the least popular ways to address the theorem, superdeterminism, in a 1985 BBC Radio interview: