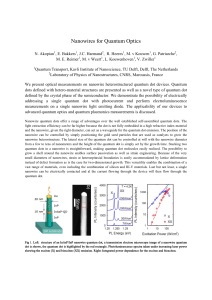
Experimental Optimal Cloning of Four
... Classical information can be freely measured, perfectly copied on demand, and broadcast without fundamental limitations. The handling of quantum information, which is encoded in the quantum states of physical systems, is instead subject to several fundamental restrictions. For example, an unknown qu ...
... Classical information can be freely measured, perfectly copied on demand, and broadcast without fundamental limitations. The handling of quantum information, which is encoded in the quantum states of physical systems, is instead subject to several fundamental restrictions. For example, an unknown qu ...
Measuring the quantum mechanical wave function
... classical statistics. For example, if you sum over Nn /M, or integrate over w (x) 2 , you must get unity. In light of this, it is probably more clear to say that you have `inferred’ or `determined’ w (x) 2 rather than `measured’ it, since a single observation of a particle tells virtually nothing ab ...
... classical statistics. For example, if you sum over Nn /M, or integrate over w (x) 2 , you must get unity. In light of this, it is probably more clear to say that you have `inferred’ or `determined’ w (x) 2 rather than `measured’ it, since a single observation of a particle tells virtually nothing ab ...
Do dispositions and propensities have a role in the
... classical language, they can be attributed to the same system at the same time only via a contradiction. In fact, complementary properties cannot be simultaneously revealed by the same experiment, given that any apparatus obeys classical physics. • On the other hand, if we refer to a quantum system ...
... classical language, they can be attributed to the same system at the same time only via a contradiction. In fact, complementary properties cannot be simultaneously revealed by the same experiment, given that any apparatus obeys classical physics. • On the other hand, if we refer to a quantum system ...
A critique of recent semi-classical spin-half quantum plasma theories
... constraints and FD statistics are essential. Thus, we must distinguish between T ≤ T F ‘quantum plasmas’, which must be described according to quantum many-body theory [and shown to be fully consistent with FD statistics, Fermi liquid theory, quantum Master equations etc.] and ‘fully ionized classic ...
... constraints and FD statistics are essential. Thus, we must distinguish between T ≤ T F ‘quantum plasmas’, which must be described according to quantum many-body theory [and shown to be fully consistent with FD statistics, Fermi liquid theory, quantum Master equations etc.] and ‘fully ionized classic ...
physics and narrative - Rutgers Philosophy Department
... theory aren’t going to be narratable. Suppose (for example) that the momentum of a free particle is measured along the hypersurface marked t=0 in figure 5, and that later on a collapse leaves the particle localized at P. Then the projection-postulate that Aharonov and I proposed is going to stipulat ...
... theory aren’t going to be narratable. Suppose (for example) that the momentum of a free particle is measured along the hypersurface marked t=0 in figure 5, and that later on a collapse leaves the particle localized at P. Then the projection-postulate that Aharonov and I proposed is going to stipulat ...
From Path Integrals to Fractional Quantum Statistics
... in three-dimensional space, moving from the configuration C at time ti to the same configuration C at time tf . Figure ?? showed two disconnected histories between these configurations, one which left each particle where it started, and the other which swapped their positions. It is not completely o ...
... in three-dimensional space, moving from the configuration C at time ti to the same configuration C at time tf . Figure ?? showed two disconnected histories between these configurations, one which left each particle where it started, and the other which swapped their positions. It is not completely o ...
Quantum computation, non-demolition measurements, and reflective
... becomes close to absolute zero. Under these conditions, internal fluctuations in the measuring device will not mask the action of weak force being detected, and specific high-frequency vibrations will be induced in the device. This is possible if the relaxation of macromolecular device keeps coheren ...
... becomes close to absolute zero. Under these conditions, internal fluctuations in the measuring device will not mask the action of weak force being detected, and specific high-frequency vibrations will be induced in the device. This is possible if the relaxation of macromolecular device keeps coheren ...
Controlled Hawking Process by Quantum Information
... view. This implies that the classical black holes do no remember the detailed information of falling matters. However, the black holes still remember what they swallowed in a quantum mechanical way. Via the QET protocol, we can extract energy from the black holes by using correct measurement results ...
... view. This implies that the classical black holes do no remember the detailed information of falling matters. However, the black holes still remember what they swallowed in a quantum mechanical way. Via the QET protocol, we can extract energy from the black holes by using correct measurement results ...
Monday, Nov. 14, 2016
... • Particles that have the same masses as particles but with opposite charges and quantum numbers ...
... • Particles that have the same masses as particles but with opposite charges and quantum numbers ...
Document
... (and why must we detect) highly-entangled qubit states? • What is quantum entanglement? • How to detect it? the complete way: quantum state tomography the scalable way: entanglement witnesses ...
... (and why must we detect) highly-entangled qubit states? • What is quantum entanglement? • How to detect it? the complete way: quantum state tomography the scalable way: entanglement witnesses ...
- 1 - THE NATURE AND SPEED OF LIGHT Peter Kohut Maly Saris
... A photon can oscillate in all possible directions perpendicular to the direction of its flight. If it oscillates in only one direction, it is polarized. Then we say that the vector of intensity of its electric (or magnetic) field oscillates in one direction. Oscillation or rotation of a quantum dipo ...
... A photon can oscillate in all possible directions perpendicular to the direction of its flight. If it oscillates in only one direction, it is polarized. Then we say that the vector of intensity of its electric (or magnetic) field oscillates in one direction. Oscillation or rotation of a quantum dipo ...
Bell's theorem
Bell's theorem is a ‘no-go theorem’ that draws an important distinction between quantum mechanics (QM) and the world as described by classical mechanics. This theorem is named after John Stewart Bell.In its simplest form, Bell's theorem states:Cornell solid-state physicist David Mermin has described the appraisals of the importance of Bell's theorem in the physics community as ranging from ""indifference"" to ""wild extravagance"". Lawrence Berkeley particle physicist Henry Stapp declared: ""Bell's theorem is the most profound discovery of science.""Bell's theorem rules out local hidden variables as a viable explanation of quantum mechanics (though it still leaves the door open for non-local hidden variables). Bell concluded:Bell summarized one of the least popular ways to address the theorem, superdeterminism, in a 1985 BBC Radio interview: