Chapter 26 Photons
... filament in order to get an electron beam. It was the thermal energy that allowed electrons to escape from the filament. We now want to know whether the oscillating electric force of the light wave can supply enough energy to an electron for the electron to escape. There are two obvious conclusions ...
... filament in order to get an electron beam. It was the thermal energy that allowed electrons to escape from the filament. We now want to know whether the oscillating electric force of the light wave can supply enough energy to an electron for the electron to escape. There are two obvious conclusions ...
Preparation and Properties of an Aqueous Ferrofluid
... description of ferrofluid spiking is given in the Results and Discussion section). If the fluid does not spike, or the spikes are small, remove the cow magnet, add one drop of distilled water, stir well with the glass rod, and again check for spiking with the cow magnet. If spikes are still not seen ...
... description of ferrofluid spiking is given in the Results and Discussion section). If the fluid does not spike, or the spikes are small, remove the cow magnet, add one drop of distilled water, stir well with the glass rod, and again check for spiking with the cow magnet. If spikes are still not seen ...
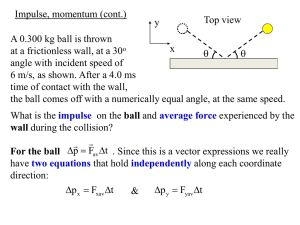
A 0.300 kg ball is thrown at a frictionless wall, at a 30o angle with
... Maria wins, even if she merely holds on with one hand and Arnold does all the pulling. No matter how hard one or the other (or both) pull, they will meet at their center of mass. We’ll soon see why this happens. For now we just want to define the center of mass and learn how to calculated it in var ...
... Maria wins, even if she merely holds on with one hand and Arnold does all the pulling. No matter how hard one or the other (or both) pull, they will meet at their center of mass. We’ll soon see why this happens. For now we just want to define the center of mass and learn how to calculated it in var ...
- RZ User
... same kind, although it requires more, namely the identity of states resulting from particle permutations. Such an identity is in conflict with the concept of particles with their individual trajectories, while a field with two bumps at points x and y would trivially be the same as one with bumps at ...
... same kind, although it requires more, namely the identity of states resulting from particle permutations. Such an identity is in conflict with the concept of particles with their individual trajectories, while a field with two bumps at points x and y would trivially be the same as one with bumps at ...
CHAPTER 14 :OSCILLATIONS One mark
... a simple pendulum on the surface of moon if its time period on the surface of earth is 1.5s. 8. A particle describes SHM with amplitude of 5 cm and a period of 0.2 s. Find the acceleration and velocity of the particle when the displacement is (a) 5cm, (b) 3 cm and (c) 0 cm. 9. A block of mass is 1 k ...
... a simple pendulum on the surface of moon if its time period on the surface of earth is 1.5s. 8. A particle describes SHM with amplitude of 5 cm and a period of 0.2 s. Find the acceleration and velocity of the particle when the displacement is (a) 5cm, (b) 3 cm and (c) 0 cm. 9. A block of mass is 1 k ...
Brief review: Force and Electric Field for point charges
... All objects have a charge! If there is an equal amount of each type, the object is neutral. ...
... All objects have a charge! If there is an equal amount of each type, the object is neutral. ...
Classical Mechanics - UC Riverside (Math)
... the result may already be helpful for people interested in the mathematics of classical mechanics. The chapters in this LATEX version are in the same order as the weekly lectures, but I’ve merged weeks together, and sometimes split them over chapter, to obtain a more textbook feel to these notes. Fo ...
... the result may already be helpful for people interested in the mathematics of classical mechanics. The chapters in this LATEX version are in the same order as the weekly lectures, but I’ve merged weeks together, and sometimes split them over chapter, to obtain a more textbook feel to these notes. Fo ...
+1 +2 d
... The four E field vectors all point outwards from the center of the square toward their respective charges. Because they are all equal, the net E field is zero at the center!! Follow-up: What if the upper two charges were +2 C? What if the right-hand charges were +2 C? ...
... The four E field vectors all point outwards from the center of the square toward their respective charges. Because they are all equal, the net E field is zero at the center!! Follow-up: What if the upper two charges were +2 C? What if the right-hand charges were +2 C? ...
Q1. This question is about the structure of atoms. (a) Choose words
... Complete the four spaces in the passage. The chemical formula of ammonia is NH3. This shows that there is one atom of .......................................... and three atoms of .................................. in each ......................................... of ammonia. These atoms are joined ...
... Complete the four spaces in the passage. The chemical formula of ammonia is NH3. This shows that there is one atom of .......................................... and three atoms of .................................. in each ......................................... of ammonia. These atoms are joined ...
eXtremely Fast Tr
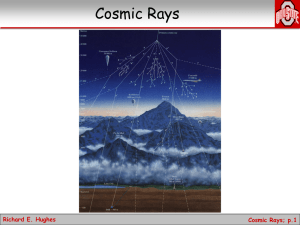
... the passage of an extensive air shower: one can look for the particles in the pancake directly, or one can look for the Cherenkov light generated by the particles in the atmosphere. The figure below illustrates both techniques. On the left is an air Cherenkov telescope (ACT). These are large mirrors ...
... the passage of an extensive air shower: one can look for the particles in the pancake directly, or one can look for the Cherenkov light generated by the particles in the atmosphere. The figure below illustrates both techniques. On the left is an air Cherenkov telescope (ACT). These are large mirrors ...
Generalized Curvilinear Coordinates in Hybrid and Electromagnetic Codes Daniel W. Swift
... the current on cell faces where it is needed in the field equations. The scheme is illustrated schematically in Fig. 2. As mentioned previously, the grid is topologically equivalent to a square or cubic lattice. Each particle carries with it a square or cubic charge element, and the particle transpo ...
... the current on cell faces where it is needed in the field equations. The scheme is illustrated schematically in Fig. 2. As mentioned previously, the grid is topologically equivalent to a square or cubic lattice. Each particle carries with it a square or cubic charge element, and the particle transpo ...
Variational Monte Carlo studies of Atoms - DUO
... is a technique for simulating physical systems numerically, and is used to perform ab initio calculations on the system. The term “ab initio” means that the method is based on first principle calculations with strictly controlled approximations being made (e.g. the Born-Oppenheimer approximation, se ...
... is a technique for simulating physical systems numerically, and is used to perform ab initio calculations on the system. The term “ab initio” means that the method is based on first principle calculations with strictly controlled approximations being made (e.g. the Born-Oppenheimer approximation, se ...
x - 東海大學
... q2 = +2μ C .With V = 0 at infinity, what is the electric potential at (a) corner A and (b) corner B? (c) How much work is required to move a charge q3 = +3μ C from B to A along a diagonal of the rectangle? (d) Does this work increase or decrease the electric potential energy of the three-charge syst ...
... q2 = +2μ C .With V = 0 at infinity, what is the electric potential at (a) corner A and (b) corner B? (c) How much work is required to move a charge q3 = +3μ C from B to A along a diagonal of the rectangle? (d) Does this work increase or decrease the electric potential energy of the three-charge syst ...
A relativistic beam-plasma system with electromagnetic waves
... Condition 共14兲 is necessary for neglecting the nonlinear response of the background plasma on the short plasma oscillation time scale. There are additional restrictions that apply when slower time scale effects are considered. For example, since we consider only long laser pulses, the ponderomotive ...
... Condition 共14兲 is necessary for neglecting the nonlinear response of the background plasma on the short plasma oscillation time scale. There are additional restrictions that apply when slower time scale effects are considered. For example, since we consider only long laser pulses, the ponderomotive ...
Department of Physics, Chemistry and Biology Master’s Thesis
... In order to explore a quantum version of a discrete nonlinear Schrödinger equation (DNLS), we quantize one nonlinear Schrödinger model, which is used to study different physical systems, e.g. coupled Bose-Einstein condensates. We will focus on small systems, like Dimer and Trimer. In our efforts to ...
... In order to explore a quantum version of a discrete nonlinear Schrödinger equation (DNLS), we quantize one nonlinear Schrödinger model, which is used to study different physical systems, e.g. coupled Bose-Einstein condensates. We will focus on small systems, like Dimer and Trimer. In our efforts to ...
CONCEPTUAL FOUNDATIONS OF THE UNI- FIED THEORY OF WEAK AND ELECTROMAG-
... There was actually an exception to this proof, pointed out soon afterwards by Higgs, Kibble, and others. [9] They showed that if the broken symmetry is a local, gauge symmetry, like electromagnetic gauge invariance, then although the Goldstone bosons exist formally, and are in some sense real, they ...
... There was actually an exception to this proof, pointed out soon afterwards by Higgs, Kibble, and others. [9] They showed that if the broken symmetry is a local, gauge symmetry, like electromagnetic gauge invariance, then although the Goldstone bosons exist formally, and are in some sense real, they ...
Elementary particle
In particle physics, an elementary particle or fundamental particle is a particle whose substructure is unknown, thus it is unknown whether it is composed of other particles. Known elementary particles include the fundamental fermions (quarks, leptons, antiquarks, and antileptons), which generally are ""matter particles"" and ""antimatter particles"", as well as the fundamental bosons (gauge bosons and Higgs boson), which generally are ""force particles"" that mediate interactions among fermions. A particle containing two or more elementary particles is a composite particle.Everyday matter is composed of atoms, once presumed to be matter's elementary particles—atom meaning ""indivisible"" in Greek—although the atom's existence remained controversial until about 1910, as some leading physicists regarded molecules as mathematical illusions, and matter as ultimately composed of energy. Soon, subatomic constituents of the atom were identified. As the 1930s opened, the electron and the proton had been observed, along with the photon, the particle of electromagnetic radiation. At that time, the recent advent of quantum mechanics was radically altering the conception of particles, as a single particle could seemingly span a field as would a wave, a paradox still eluding satisfactory explanation.Via quantum theory, protons and neutrons were found to contain quarks—up quarks and down quarks—now considered elementary particles. And within a molecule, the electron's three degrees of freedom (charge, spin, orbital) can separate via wavefunction into three quasiparticles (holon, spinon, orbiton). Yet a free electron—which, not orbiting an atomic nucleus, lacks orbital motion—appears unsplittable and remains regarded as an elementary particle.Around 1980, an elementary particle's status as indeed elementary—an ultimate constituent of substance—was mostly discarded for a more practical outlook, embodied in particle physics' Standard Model, science's most experimentally successful theory. Many elaborations upon and theories beyond the Standard Model, including the extremely popular supersymmetry, double the number of elementary particles by hypothesizing that each known particle associates with a ""shadow"" partner far more massive, although all such superpartners remain undiscovered. Meanwhile, an elementary boson mediating gravitation—the graviton—remains hypothetical.