Recombinant DNA and the Production of Insulin
... Diabetes is a condition where a person has too much sugar in their blood. Insulin, which is a hormone created by the pancreas, normally helps lower the level of sugar in a person’s blood. But people who are diabetics do not produce enough insulin to properly lower their blood sugar. Too much sugar i ...
... Diabetes is a condition where a person has too much sugar in their blood. Insulin, which is a hormone created by the pancreas, normally helps lower the level of sugar in a person’s blood. But people who are diabetics do not produce enough insulin to properly lower their blood sugar. Too much sugar i ...
Electrophoretic stretching of DNA molecules using microscale T
... Controlled trapping and stretching of DNA molecules are critical for single molecule genomic and polymer physics studies. The authors present a microfabricated T junction which can trap and stretch single free DNA molecules using electrophoretic forces. The device does not require special end functi ...
... Controlled trapping and stretching of DNA molecules are critical for single molecule genomic and polymer physics studies. The authors present a microfabricated T junction which can trap and stretch single free DNA molecules using electrophoretic forces. The device does not require special end functi ...
PowerPoint Presentation - LSU Museum of Natural Science
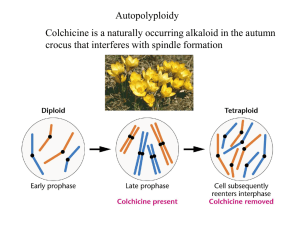
... 7 chromosomes, whereas the normal 2N number is 8. A karyotype revealed that a nonreciprocal translocation had occurred so that one copy of chromosome 4 had attached to the end of chromosome 2. It lost its centromere. Diagram all members of chromosomes II and IV during synapsis in Meiosis I -chromoso ...
... 7 chromosomes, whereas the normal 2N number is 8. A karyotype revealed that a nonreciprocal translocation had occurred so that one copy of chromosome 4 had attached to the end of chromosome 2. It lost its centromere. Diagram all members of chromosomes II and IV during synapsis in Meiosis I -chromoso ...
Chapter 16 - Molecular Basis of Inheritance DNA as the Genetic
... Base composition of DNA varies from one species to another Amounts of bases are not equal, but are present in a characteristic ratio Chargaff’s Rule %A = %T and %G = %C % Purine = % Pyrimidine (A + G = C + T) developed before double helix structure known In human DNA: A & T = ~30% for each C & G = ~ ...
... Base composition of DNA varies from one species to another Amounts of bases are not equal, but are present in a characteristic ratio Chargaff’s Rule %A = %T and %G = %C % Purine = % Pyrimidine (A + G = C + T) developed before double helix structure known In human DNA: A & T = ~30% for each C & G = ~ ...
DNA Translocation Through Nanopores
... dsDNA revealed a strong increase of the threading force upon decreasing the diameter of the pore. This can be attributed to a reduction of the electroosmotic flow in smaller pores, which always opposes the electrostatic force acting on the DNA molecule. Coating the nanopore walls with an electricall ...
... dsDNA revealed a strong increase of the threading force upon decreasing the diameter of the pore. This can be attributed to a reduction of the electroosmotic flow in smaller pores, which always opposes the electrostatic force acting on the DNA molecule. Coating the nanopore walls with an electricall ...
Chlamydia NAATs: update in the clinical and laboratory setting
... • Urine samples submitted for routine testing • Sample anonymised and divided in 4 aliquots • Samples sent overnight to other labs for testing • Each site - 510 neg and 170 pos (M/F) • Total 1530 neg and 510 pos tested by 3 methods • Aim to detect difference in sensitivity of 5% ...
... • Urine samples submitted for routine testing • Sample anonymised and divided in 4 aliquots • Samples sent overnight to other labs for testing • Each site - 510 neg and 170 pos (M/F) • Total 1530 neg and 510 pos tested by 3 methods • Aim to detect difference in sensitivity of 5% ...
L.R. Huang, J.O. Tegenfeldt, J.J. Kraeft, J.C. Sturm, R.H. Austin, E.C. Cox, "Generation of large-area tunable uniform electric fields in microfluid arrays for rapid DNA separation," Tech. Dig. Int. Elect. Dev. Mtg., pp. 363-366 (2001).
... molecules in microfluidic systems. In this paper we present a novel method for generating tunable uniform electric fields over large microfluidic arrays in two dimensions, and its application to a microfabricated device that separates genomic DNA. The device fractionates large DNA molecules over thr ...
... molecules in microfluidic systems. In this paper we present a novel method for generating tunable uniform electric fields over large microfluidic arrays in two dimensions, and its application to a microfabricated device that separates genomic DNA. The device fractionates large DNA molecules over thr ...
Genetic Technology
... Diagnosis of genetic disorders • The DNA of people with and without a genetic disorder is compared to find differences that are associated with the disorder. Once it is clearly understood where a gene is located and that a mutation in the gene causes the disorder, a diagnosis can be made for an ind ...
... Diagnosis of genetic disorders • The DNA of people with and without a genetic disorder is compared to find differences that are associated with the disorder. Once it is clearly understood where a gene is located and that a mutation in the gene causes the disorder, a diagnosis can be made for an ind ...
Genetics 3 – Aneuploidies and Other Chromosome
... These do not normally cause any negative effect if any, because all the DNA of both chromosomes is present. They can however be associated with cancer if they occur in haploid cells. ...
... These do not normally cause any negative effect if any, because all the DNA of both chromosomes is present. They can however be associated with cancer if they occur in haploid cells. ...
HBV Quantitative Real Time PCR Kit User Manual For In
... the centrifuge before use. It’s better to use commercial kits for nucleic acid extraction. 1) Take 50ul serum or plasma, add 50µl DNA extraction buffer, and close the tube then vortex for 10 seconds. Spin down briefly in a table centrifuge. 2) Incubate the tube for 10 minutes at 100°C. 3) Centrifuge ...
... the centrifuge before use. It’s better to use commercial kits for nucleic acid extraction. 1) Take 50ul serum or plasma, add 50µl DNA extraction buffer, and close the tube then vortex for 10 seconds. Spin down briefly in a table centrifuge. 2) Incubate the tube for 10 minutes at 100°C. 3) Centrifuge ...
DNA notes
... DNA degraded to fragments only a few hundred base pairs in length can serve as effective templates for amplification. Large numbers of copies of specific DNA sequences can be amplified simultaneously with multiplex PCR reactions. Commercial kits are now available for easy PCR reaction setup an ...
... DNA degraded to fragments only a few hundred base pairs in length can serve as effective templates for amplification. Large numbers of copies of specific DNA sequences can be amplified simultaneously with multiplex PCR reactions. Commercial kits are now available for easy PCR reaction setup an ...
Chapter 2 Chemistry of nucleic acid
... absorption value at 260nm would increased sharply,which indicates that the double strand helix DNA was separated into single strand. ...
... absorption value at 260nm would increased sharply,which indicates that the double strand helix DNA was separated into single strand. ...
Practical Guide: Selecting the Optimal Resins for Removal of DNA
... DNA. The contaminating DNA leads to increased viscosity of the feedstream and can interfere with subsequent purification steps such as anion exchange chromatography. In addition, contamination with cellular DNA creates a therapeutic risk. Regulatory authorities require that DNA levels in all therape ...
... DNA. The contaminating DNA leads to increased viscosity of the feedstream and can interfere with subsequent purification steps such as anion exchange chromatography. In addition, contamination with cellular DNA creates a therapeutic risk. Regulatory authorities require that DNA levels in all therape ...
Chapter 12: DNA & RNA
... • Mutations – heritable changes in genetic information (changes to the DNA sequence) • Two types - gene and chromosomal mutations • Mutations can be caused by chemical or physical agents (mutagens) – Chemical – pesticides, tobacco smoke, environmental pollutants – Physical – X-rays and ultraviolet l ...
... • Mutations – heritable changes in genetic information (changes to the DNA sequence) • Two types - gene and chromosomal mutations • Mutations can be caused by chemical or physical agents (mutagens) – Chemical – pesticides, tobacco smoke, environmental pollutants – Physical – X-rays and ultraviolet l ...
View PDF
... bands on a gel. Together, the separated DNA bands look like a ladder on the gel. DNA ladders are used in gel electrophoresis to determine the size and quantity of DNA fragments. DNA ligase: An enzyme that catalyzes the formation of covalent chemical bonds in the sugar-phosphate backbone, thereby bin ...
... bands on a gel. Together, the separated DNA bands look like a ladder on the gel. DNA ladders are used in gel electrophoresis to determine the size and quantity of DNA fragments. DNA ligase: An enzyme that catalyzes the formation of covalent chemical bonds in the sugar-phosphate backbone, thereby bin ...
Information S1.
... numbered vials consisting of the dilutions in triplicates for each cell line DNA and 12 aliquots of SW46 DNA. A total of 3600 samples were sent to 40 laboratories. Extraction, dilution and distribution were centralized in one laboratory (UMR775, INSERM, Pr P. Laurent-Puig). The p.G12R cell line obta ...
... numbered vials consisting of the dilutions in triplicates for each cell line DNA and 12 aliquots of SW46 DNA. A total of 3600 samples were sent to 40 laboratories. Extraction, dilution and distribution were centralized in one laboratory (UMR775, INSERM, Pr P. Laurent-Puig). The p.G12R cell line obta ...
DNA Analysis
... • This is important for 2 reasons: – It is a standard or control (i.e. important for Daubert challenges) – one needs to argue that the same amount of DNA is used in each lab, by each lab technician and every time sample is processed – The amount has been optimized for subsequent reactions – so it en ...
... • This is important for 2 reasons: – It is a standard or control (i.e. important for Daubert challenges) – one needs to argue that the same amount of DNA is used in each lab, by each lab technician and every time sample is processed – The amount has been optimized for subsequent reactions – so it en ...
SC.7.L.16.1 - Understand and explain that every organism requires
... In this video module, students learn how scientists use genetic information from dogs to find out which gene (out of all 20,000 dog genes) is associated with any specific trait or disease of interest. This method involves comparing hundreds of dogs with the trait to hundreds of dogs not displaying t ...
... In this video module, students learn how scientists use genetic information from dogs to find out which gene (out of all 20,000 dog genes) is associated with any specific trait or disease of interest. This method involves comparing hundreds of dogs with the trait to hundreds of dogs not displaying t ...
Blueprint for life - Siemens Science Day
... Tell students that they are going to decode the DNA of some plant seeds to predict what the plants will look like after they have grown. Explain that the activity is only a simulation to show how a code can work. DNA uses a code that is different than the code students will use in the simulation. 2. ...
... Tell students that they are going to decode the DNA of some plant seeds to predict what the plants will look like after they have grown. Explain that the activity is only a simulation to show how a code can work. DNA uses a code that is different than the code students will use in the simulation. 2. ...
Comparative genomic hybridization

Comparative genomic hybridization is a molecular cytogenetic method for analysing copy number variations (CNVs) relative to ploidy level in the DNA of a test sample compared to a reference sample, without the need for culturing cells. The aim of this technique is to quickly and efficiently compare two genomic DNA samples arising from two sources, which are most often closely related, because it is suspected that they contain differences in terms of either gains or losses of either whole chromosomes or subchromosomal regions (a portion of a whole chromosome). This technique was originally developed for the evaluation of the differences between the chromosomal complements of solid tumor and normal tissue, and has an improved resoIution of 5-10 megabases compared to the more traditional cytogenetic analysis techniques of giemsa banding and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) which are limited by the resolution of the microscope utilized.This is achieved through the use of competitive fluorescence in situ hybridization. In short, this involves the isolation of DNA from the two sources to be compared, most commonly a test and reference source, independent labelling of each DNA sample with a different fluorophores (fluorescent molecules) of different colours (usually red and green), denaturation of the DNA so that it is single stranded, and the hybridization of the two resultant samples in a 1:1 ratio to a normal metaphase spread of chromosomes, to which the labelled DNA samples will bind at their locus of origin. Using a fluorescence microscope and computer software, the differentially coloured fluorescent signals are then compared along the length of each chromosome for identification of chromosomal differences between the two sources. A higher intensity of the test sample colour in a specific region of a chromosome indicates the gain of material of that region in the corresponding source sample, while a higher intensity of the reference sample colour indicates the loss of material in the test sample in that specific region. A neutral colour (yellow when the fluorophore labels are red and green) indicates no difference between the two samples in that location.CGH is only able to detect unbalanced chromosomal abnormalities. This is because balanced chromosomal abnormalities such as reciprocal translocations, inversions or ring chromosomes do not affect copy number, which is what is detected by CGH technologies. CGH does, however, allow for the exploration of all 46 human chromosomes in single test and the discovery of deletions and duplications, even on the microscopic scale which may lead to the identification of candidate genes to be further explored by other cytological techniques.Through the use of DNA microarrays in conjunction with CGH techniques, the more specific form of array CGH (aCGH) has been developed, allowing for a locus-by-locus measure of CNV with increased resolution as low as 100 kilobases. This improved technique allows for the aetiology of known and unknown conditions to be discovered.