Internal Structure of the Earth File
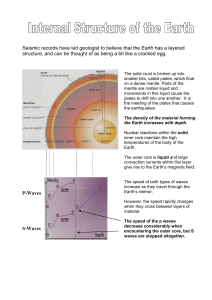
... Point B - At certain points the refraction becomes more pronounced as the waves meet a definite boundary between layers. No S waves can travel through angles greater than 1030 hence the boundary at B must separate solid from liquid. This is the evidence that the outer core is made of a dense liquid. ...
... Point B - At certain points the refraction becomes more pronounced as the waves meet a definite boundary between layers. No S waves can travel through angles greater than 1030 hence the boundary at B must separate solid from liquid. This is the evidence that the outer core is made of a dense liquid. ...
Main Idea 2
... to make one rotation, or complete spin on its axis. • As Earth spins, different parts of the planet face the sun, thus causing the changes from day to ...
... to make one rotation, or complete spin on its axis. • As Earth spins, different parts of the planet face the sun, thus causing the changes from day to ...
Handout
... earthquake is a vibration. This vibrational energy moves as seismic waves through the solid earth, the oceans, and on the surface. Earthquakes can produce a new fracture in the earth’s crust or can cause sliding or movement on an existing fracture or can occur on a “blind fault” (an old fracture tha ...
... earthquake is a vibration. This vibrational energy moves as seismic waves through the solid earth, the oceans, and on the surface. Earthquakes can produce a new fracture in the earth’s crust or can cause sliding or movement on an existing fracture or can occur on a “blind fault” (an old fracture tha ...
Chapter205.ppt
... earthquake is a vibration. This vibrational energy moves as seismic waves through the solid earth, the oceans, and on the surface. Earthquakes can produce a new fracture in the earth’s crust or can cause sliding or movement on an existing fracture or can occur on a “blind fault” (an old fracture tha ...
... earthquake is a vibration. This vibrational energy moves as seismic waves through the solid earth, the oceans, and on the surface. Earthquakes can produce a new fracture in the earth’s crust or can cause sliding or movement on an existing fracture or can occur on a “blind fault” (an old fracture tha ...
The Layer`s Of The Earth!
... • The Earth is divided into four main layers. Crust Mantle Outer Core Inner Core ...
... • The Earth is divided into four main layers. Crust Mantle Outer Core Inner Core ...
Document
... 2. Armed with a spray paint can, stranded outside the shuttle, what do you do to ensure getting back? throw can toward shuttle throw can away from shuttle ...
... 2. Armed with a spray paint can, stranded outside the shuttle, what do you do to ensure getting back? throw can toward shuttle throw can away from shuttle ...
BlackBubbles2011
... • That mg and mi were directly proportional was evidence for a basic connection between them • No mechanical experiment could distinguish between the two • He extended the idea to no experiment of any type could distinguish the two masses ...
... • That mg and mi were directly proportional was evidence for a basic connection between them • No mechanical experiment could distinguish between the two • He extended the idea to no experiment of any type could distinguish the two masses ...
Open Ended Questions OEQ 1 The car manufacturer SATSUMA
... ODU 8 A 500g ice hockey puck moves across a frictionless surface at 8m/s, and collides with an identical puck moving at 4m/s in the opposite direction. The first puck then stops completely. After the collision: (a) Using the principal of conservation of momentum, show by calculation whether the col ...
... ODU 8 A 500g ice hockey puck moves across a frictionless surface at 8m/s, and collides with an identical puck moving at 4m/s in the opposite direction. The first puck then stops completely. After the collision: (a) Using the principal of conservation of momentum, show by calculation whether the col ...
High School Science Proficiency Review #3 Earth Science
... stone A had dates cut into the rock in 1922. A. Water enters and leaves Earth during evaporation and precipi‐ Tombstone B had dates cut into the rock in 1892. tation cycles. B. The water present on Earth today is made of the same atoms but the molecules have been recycled through biologic act ...
... stone A had dates cut into the rock in 1922. A. Water enters and leaves Earth during evaporation and precipi‐ Tombstone B had dates cut into the rock in 1892. tation cycles. B. The water present on Earth today is made of the same atoms but the molecules have been recycled through biologic act ...
Chapter 21- Planet Earth
... ____________________________ can determine a more exact, or _____________, age of rocks. • The radioactive elements that make up minerals in rocks _____________ over billions of years. ...
... ____________________________ can determine a more exact, or _____________, age of rocks. • The radioactive elements that make up minerals in rocks _____________ over billions of years. ...
Earth Science Chapter 5
... • Curve like seams through Earth’s oceans • Most mountains are under water, except Iceland! ...
... • Curve like seams through Earth’s oceans • Most mountains are under water, except Iceland! ...
2010 - The Physics Teacher
... In an experiment to measure the specific latent heat of vaporisation of water, a student used a copper calorimeter containing water and a sensitive thermometer. The water was cooled below room temperature before adding dry steam to it. The following measurements were recorded. Mass of copper calorim ...
... In an experiment to measure the specific latent heat of vaporisation of water, a student used a copper calorimeter containing water and a sensitive thermometer. The water was cooled below room temperature before adding dry steam to it. The following measurements were recorded. Mass of copper calorim ...
Plate Tectonics
... • Each person will focus on one type of boundary – divergent (Column A) – convergent (Column B) – transform (Column C) ...
... • Each person will focus on one type of boundary – divergent (Column A) – convergent (Column B) – transform (Column C) ...
Schiehallion experiment

The Schiehallion experiment was an 18th-century experiment to determine the mean density of the Earth. Funded by a grant from the Royal Society, it was conducted in the summer of 1774 around the Scottish mountain of Schiehallion, Perthshire. The experiment involved measuring the tiny deflection of a pendulum due to the gravitational attraction of a nearby mountain. Schiehallion was considered the ideal location after a search for candidate mountains, thanks to its isolation and almost symmetrical shape. One of the triggers for the experiment were anomalies noted during the survey of the Mason–Dixon Line.The experiment had previously been considered, but rejected, by Isaac Newton as a practical demonstration of his theory of gravitation. However, a team of scientists, notably Nevil Maskelyne, the Astronomer Royal, were convinced that the effect would be detectable and undertook to conduct the experiment. The deflection angle depended on the relative densities and volumes of the Earth and the mountain: if the density and volume of Schiehallion could be ascertained, then so could the density of the Earth. Once this was known, then this would in turn yield approximate values for those of the other planets, their moons, and the Sun, previously known only in terms of their relative ratios. As an additional benefit, the concept of contour lines, devised to simplify the process of surveying the mountain, later became a standard technique in cartography.























