Planet Earth in a Nutshell
... million and 4,600 million years ago. As the cloud contracted under force of gravity, the atoms got closer together and became denser. The spinning cloud eventually flattened out, with a bulge in the middle from which the Sun was born. Over time, materials in the disc around the Sun turned into solid ...
... million and 4,600 million years ago. As the cloud contracted under force of gravity, the atoms got closer together and became denser. The spinning cloud eventually flattened out, with a bulge in the middle from which the Sun was born. Over time, materials in the disc around the Sun turned into solid ...
worksheets extreme earth
... - Shame!! Superman is saving people from an earthquake. - Our second option is SuperBoy he’s slower but he can do it! - SuperBoy digs holes at the speed of 200 km/s. - He’s flying over the sea, 8km over the upper mantle. How long would it take him to get to the core and come back? ...
... - Shame!! Superman is saving people from an earthquake. - Our second option is SuperBoy he’s slower but he can do it! - SuperBoy digs holes at the speed of 200 km/s. - He’s flying over the sea, 8km over the upper mantle. How long would it take him to get to the core and come back? ...
Lectures on Astronomy, Astrophysics, and
... regular elliptical shapes and seem to be a great distance beyond the Galaxy. Kant seems to have been the first to suggest that these latter might be circular discs, but appear elliptical because we see them at an angle, and are faint because they are so distant [6]. At first it was not universally a ...
... regular elliptical shapes and seem to be a great distance beyond the Galaxy. Kant seems to have been the first to suggest that these latter might be circular discs, but appear elliptical because we see them at an angle, and are faint because they are so distant [6]. At first it was not universally a ...
Planet Earth
... Step 6 – Repeat Steps 1-5 for each of the other Topics in this Unit. Step 7 – Look over the Unit Outline to review the Key Concepts once you have completed all of the Topics. Step 8 – Complete the Unit Review, using your Learning Pack and Textbook. Step 9 – Highlight those sections of the Review tha ...
... Step 6 – Repeat Steps 1-5 for each of the other Topics in this Unit. Step 7 – Look over the Unit Outline to review the Key Concepts once you have completed all of the Topics. Step 8 – Complete the Unit Review, using your Learning Pack and Textbook. Step 9 – Highlight those sections of the Review tha ...
The Dynamic Crust
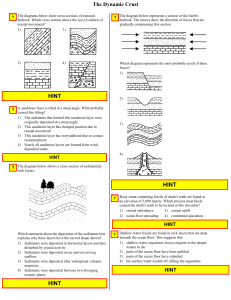
... The present North magnetic pole was once the South magnetic pole, and the present South magnetic pole was once the North magnetic pole. A record of these changes is preserved in the igneous rocks that formed at mid-ocean ridges and moved away from the ridges. The diagram below represents the pattern ...
... The present North magnetic pole was once the South magnetic pole, and the present South magnetic pole was once the North magnetic pole. A record of these changes is preserved in the igneous rocks that formed at mid-ocean ridges and moved away from the ridges. The diagram below represents the pattern ...
Chapter 1 Introduction
... that globular clusters may have originated as gravitationally bound gas clouds before the galaxies form. Their idea follows from what was then called the primitive-fireball picture (and is now referred to as the Big Bang theory) and they showed that the first bound systems to have formed in the expa ...
... that globular clusters may have originated as gravitationally bound gas clouds before the galaxies form. Their idea follows from what was then called the primitive-fireball picture (and is now referred to as the Big Bang theory) and they showed that the first bound systems to have formed in the expa ...
Study Guide
... Related or supporting concepts: - Densities in the interior of Earth must be very high since the average density of Earth is almost twice as great as the average density of the crust. - The interior must consist of roughly spherical homogeneous layers since Earth doesn’t wobble much as it rotates an ...
... Related or supporting concepts: - Densities in the interior of Earth must be very high since the average density of Earth is almost twice as great as the average density of the crust. - The interior must consist of roughly spherical homogeneous layers since Earth doesn’t wobble much as it rotates an ...
here
... valuable information about the Earth’s interior,” explains Hikaru Iwamori, Director of Department of Solid Earth Geochemistry who carries out geochemical probe research. Geochemical probes can also be used to date material. For example, by studying radioactive isotopes of strontium, neodymium, lead, ...
... valuable information about the Earth’s interior,” explains Hikaru Iwamori, Director of Department of Solid Earth Geochemistry who carries out geochemical probe research. Geochemical probes can also be used to date material. For example, by studying radioactive isotopes of strontium, neodymium, lead, ...
lithosphere oceanic crust, and the origin of the first continental The
... ridges would have been emergent if oceanic crust covered 95% of Earth's surface (Fig. lb). For this value of total heat flow, however, the ridges would never have been emergent with basal temperatures of only 1450~ (Fig. lb). Twice the present total heat flow through the oceans is still an improbabl ...
... ridges would have been emergent if oceanic crust covered 95% of Earth's surface (Fig. lb). For this value of total heat flow, however, the ridges would never have been emergent with basal temperatures of only 1450~ (Fig. lb). Twice the present total heat flow through the oceans is still an improbabl ...
PDF (Chapter 2. Earth and Moon)
... differentiated into an iron-rich core and a crust. In these theories it proved difficult to transport molten iron to the center of the planet because of the effect of pressure on the melting point: Molten iron in the upper mantle would freeze before it reached the lower mantle. A central iron-rich n ...
... differentiated into an iron-rich core and a crust. In these theories it proved difficult to transport molten iron to the center of the planet because of the effect of pressure on the melting point: Molten iron in the upper mantle would freeze before it reached the lower mantle. A central iron-rich n ...
Unit Objectives
... • Be able to locate features on topographic maps using latitude and longitude in degrees, minutes, seconds, and identify features, using map symbols and colors • Be able to interpret four kinds of map scales and convert one scale to another • Interpret landform features using contour lines and stere ...
... • Be able to locate features on topographic maps using latitude and longitude in degrees, minutes, seconds, and identify features, using map symbols and colors • Be able to interpret four kinds of map scales and convert one scale to another • Interpret landform features using contour lines and stere ...
Schiehallion experiment

The Schiehallion experiment was an 18th-century experiment to determine the mean density of the Earth. Funded by a grant from the Royal Society, it was conducted in the summer of 1774 around the Scottish mountain of Schiehallion, Perthshire. The experiment involved measuring the tiny deflection of a pendulum due to the gravitational attraction of a nearby mountain. Schiehallion was considered the ideal location after a search for candidate mountains, thanks to its isolation and almost symmetrical shape. One of the triggers for the experiment were anomalies noted during the survey of the Mason–Dixon Line.The experiment had previously been considered, but rejected, by Isaac Newton as a practical demonstration of his theory of gravitation. However, a team of scientists, notably Nevil Maskelyne, the Astronomer Royal, were convinced that the effect would be detectable and undertook to conduct the experiment. The deflection angle depended on the relative densities and volumes of the Earth and the mountain: if the density and volume of Schiehallion could be ascertained, then so could the density of the Earth. Once this was known, then this would in turn yield approximate values for those of the other planets, their moons, and the Sun, previously known only in terms of their relative ratios. As an additional benefit, the concept of contour lines, devised to simplify the process of surveying the mountain, later became a standard technique in cartography.