Numbers of subsequences without isolated odd members
... As may be expected from sequences defined from recurrence relations, there are congruence and divisibility properties. The terms of odd rank are alternately congruent to 1 and 5 modulo 8, and those of even rank after the second are congruent to 3 and 7 modulo 8 alternately. Every fourth term, starti ...
... As may be expected from sequences defined from recurrence relations, there are congruence and divisibility properties. The terms of odd rank are alternately congruent to 1 and 5 modulo 8, and those of even rank after the second are congruent to 3 and 7 modulo 8 alternately. Every fourth term, starti ...
Full text in pdf
... Figure 2: Example of the algorithm in work lowest possible column numbers. Now, we process the 3rd row. We see a 0-match (3, 0), but it does not improve any 0-match, since we already have a 0-match for column 0 (the 0-match is marked as a small dot which indicates it is not processed in lines 08–19) ...
... Figure 2: Example of the algorithm in work lowest possible column numbers. Now, we process the 3rd row. We see a 0-match (3, 0), but it does not improve any 0-match, since we already have a 0-match for column 0 (the 0-match is marked as a small dot which indicates it is not processed in lines 08–19) ...
Algorithms and Data Structures
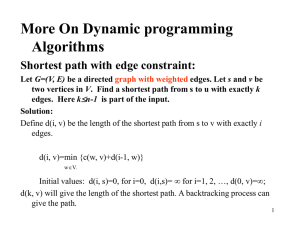
... requirements, by “forgetting” solutions to subproblems that will not be used any more 4. Construct an optimal solution from computed information (which records a sequence of choices made that lead to an optimal solution) ...
... requirements, by “forgetting” solutions to subproblems that will not be used any more 4. Construct an optimal solution from computed information (which records a sequence of choices made that lead to an optimal solution) ...
tut0911
... subsequence of a sequence of n numbers. Can you give a linear space algorithm? (Assume that each integer appears once in the input sequence of n numbers) Example: Consider sequence 1,8, 2,9, 3,10, 4, 5. Both subsequences 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 1, 8, 9, 10 are monotonically increasing subsequences. Howeve ...
... subsequence of a sequence of n numbers. Can you give a linear space algorithm? (Assume that each integer appears once in the input sequence of n numbers) Example: Consider sequence 1,8, 2,9, 3,10, 4, 5. Both subsequences 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 1, 8, 9, 10 are monotonically increasing subsequences. Howeve ...