Inside the Earth
... Made up of more iron and magnesium so is very dense • Convection currents occur in the mantle ...
... Made up of more iron and magnesium so is very dense • Convection currents occur in the mantle ...
Earth_Yesterday_Today_and_Tomorrow
... the rubbing and friction create great pressure. An earthquakes results! ( pg.44) ...
... the rubbing and friction create great pressure. An earthquakes results! ( pg.44) ...
Snickers Plate Tectonics
... First step: Set your snickers bar on a flat surface. Take your toothpick and make a few breaks in the snickers outer covering. This covering plays as the earths crust. Second step: Pull on the edges of the snickers bar. This illustrates the tension associated with normal faults(when the plates start ...
... First step: Set your snickers bar on a flat surface. Take your toothpick and make a few breaks in the snickers outer covering. This covering plays as the earths crust. Second step: Pull on the edges of the snickers bar. This illustrates the tension associated with normal faults(when the plates start ...
Earth, Yesterday, Today and Tomorrow
... the rubbing and friction create great pressure. An earthquakes results! ( pg.44) ...
... the rubbing and friction create great pressure. An earthquakes results! ( pg.44) ...
Unit 3 Geology - Manatee School For the Arts / Homepage
... sea floor. The age of the rocks increases as one moves away from the rift zone. The midoceanic ridge is the primary site for sea-floor spreading. Earthquakes and volcanoes are where seafloor spreading is occurring. ...
... sea floor. The age of the rocks increases as one moves away from the rift zone. The midoceanic ridge is the primary site for sea-floor spreading. Earthquakes and volcanoes are where seafloor spreading is occurring. ...
7.3 Landforms are the result of the interaction of constructive and
... 1. Earth’s surface features, such as mountains, volcanoes and continents, are the constantly changing result of dynamic processes and forces at work inside the Earth. 2. Earth is formed of three basic layers, with the densest being the iron and nickel core. The middle layer, the mantle, of the Earth ...
... 1. Earth’s surface features, such as mountains, volcanoes and continents, are the constantly changing result of dynamic processes and forces at work inside the Earth. 2. Earth is formed of three basic layers, with the densest being the iron and nickel core. The middle layer, the mantle, of the Earth ...
Tectonic Plates - Rural Institute
... • Two plates moving towards each other collide; causing one plate to be forced under the other. This process is called subduction. • Subduction zones typically see a change of 2 to 8 centimeters per year. • Known for high rates of volcanic activity, earthquakes, and mountain building. ...
... • Two plates moving towards each other collide; causing one plate to be forced under the other. This process is called subduction. • Subduction zones typically see a change of 2 to 8 centimeters per year. • Known for high rates of volcanic activity, earthquakes, and mountain building. ...
Lesson 7.1: Volcanoes and Plate Boundaries
... • Magma is less dense than the rocks above it, so it pushes up. • Different plate boundaries results in volcanoes forming. ...
... • Magma is less dense than the rocks above it, so it pushes up. • Different plate boundaries results in volcanoes forming. ...
Earth`s Interior
... – The forces that make and shape planet Earth. – The chemical and physical characteristics of rock. – The processes that create Earth’s features and search for clues about Earth’s history. ...
... – The forces that make and shape planet Earth. – The chemical and physical characteristics of rock. – The processes that create Earth’s features and search for clues about Earth’s history. ...
Plate boundaries - Secondary One Geography for AHS 2012
... divergence • These plate boundaries are also major zones of sea-floor spreading and volcanic activity because of such upwelling magma • Mid-oceanic ridges are characterized by recent and frequent volcanic activity and formation of volcanic islands • Magma is injected into faults or rifts • Example: ...
... divergence • These plate boundaries are also major zones of sea-floor spreading and volcanic activity because of such upwelling magma • Mid-oceanic ridges are characterized by recent and frequent volcanic activity and formation of volcanic islands • Magma is injected into faults or rifts • Example: ...
Document
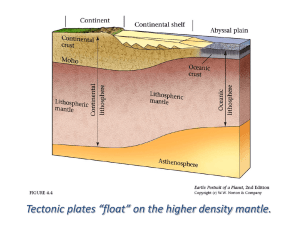
... • Please IGNORE these….. • They are based on outdated information and will be marked wrong in geology exams • They often also show continental crust floating on oceanic crust, this is also incorrect. ...
... • Please IGNORE these….. • They are based on outdated information and will be marked wrong in geology exams • They often also show continental crust floating on oceanic crust, this is also incorrect. ...
AoW: Plate Tectonics - watertown.k12.wi.us
... tectonic plate. When two huge earthquakes ripped through the floor of the Indian Ocean, they triggered large aftershocks on faults the world over, and provided the best evidence yet that the vast Indo-Australian plate is being torn in two. Geologists have spent five months puzzling over the twin qua ...
... tectonic plate. When two huge earthquakes ripped through the floor of the Indian Ocean, they triggered large aftershocks on faults the world over, and provided the best evidence yet that the vast Indo-Australian plate is being torn in two. Geologists have spent five months puzzling over the twin qua ...
Crust, Mantle, Core Review!
... The crust that is found on the continents and at the beginning of the oceans (the continental shelf) is ________________. ...
... The crust that is found on the continents and at the beginning of the oceans (the continental shelf) is ________________. ...
continental shelf
... that between two ______________ plates. • There are three types of lithospheric plate boundaries: divergent (where lithosphere and oceanic crust is created at mid-ocean ridges), convergent (where one lithospheric plate sinks beneath another and returns to the mantle), and transform (where two lithos ...
... that between two ______________ plates. • There are three types of lithospheric plate boundaries: divergent (where lithosphere and oceanic crust is created at mid-ocean ridges), convergent (where one lithospheric plate sinks beneath another and returns to the mantle), and transform (where two lithos ...
Chapter 9 - reynolds study center
... 8. Yellowstone National Park and the Hawaiian Islands; there are about 40 known hotspots around the world. 9. B: Over-Riding Plate 10. lagoon; atoll. 11. Atlantic, Pacific, Indian, and Arctic. 12. A deep-ocean trench is a site where the lithosphere descends and melts to create a new asthenosphere as ...
... 8. Yellowstone National Park and the Hawaiian Islands; there are about 40 known hotspots around the world. 9. B: Over-Riding Plate 10. lagoon; atoll. 11. Atlantic, Pacific, Indian, and Arctic. 12. A deep-ocean trench is a site where the lithosphere descends and melts to create a new asthenosphere as ...
File - Mrs. Leachman Science
... higher in the underlying mantle. As the rocks move away from the spreading center, they cool and become denser and less buoyant. Typically, these types of plate boundaries only produce around 5% of all seismic energy released in a given year and recently determined that they have a moderate amount o ...
... higher in the underlying mantle. As the rocks move away from the spreading center, they cool and become denser and less buoyant. Typically, these types of plate boundaries only produce around 5% of all seismic energy released in a given year and recently determined that they have a moderate amount o ...
• earthquake locations define plate boundaries. • subduction of
... earthquakes taking place below, on the already subducted oceanic plate, are showing up as a thicker band of point distribution in these subduction zones. diverging boundaries => not so many earthquake subduction of Indian plate below Eurasian one (continent-continet convergent boundary) is giving ri ...
... earthquakes taking place below, on the already subducted oceanic plate, are showing up as a thicker band of point distribution in these subduction zones. diverging boundaries => not so many earthquake subduction of Indian plate below Eurasian one (continent-continet convergent boundary) is giving ri ...
welcome to gg 101 physical geology
... • UNIFYING THEORY of plate motion • PLATES (same as lithosphere) - 7 major plates & many minor plates • MOVE with respect to each other as fast as finger nails grow • **remember that crust rides in lithosphere over the asthenosphere** • Three (3) kinds of PLATE MARGINS • [CD: INTERNAL, PLATE TECTONI ...
... • UNIFYING THEORY of plate motion • PLATES (same as lithosphere) - 7 major plates & many minor plates • MOVE with respect to each other as fast as finger nails grow • **remember that crust rides in lithosphere over the asthenosphere** • Three (3) kinds of PLATE MARGINS • [CD: INTERNAL, PLATE TECTONI ...
Inside the Earth
... Layer of the Earth that extends from below the mantle to the center of the Earth. Outer core – liquid, inner core - solid 33% of Earth’s mass Radius of 3,420 km Temp. ranges from 3,700°C to 7,000°C (sun’s surface temp – 5500°C Composed mainly of iron and contains smaller amounts of nickel ...
... Layer of the Earth that extends from below the mantle to the center of the Earth. Outer core – liquid, inner core - solid 33% of Earth’s mass Radius of 3,420 km Temp. ranges from 3,700°C to 7,000°C (sun’s surface temp – 5500°C Composed mainly of iron and contains smaller amounts of nickel ...
restless continents text
... Mid-Ocean Ridges and Sea-Floor Spreading A chain of submerged mountains runs through the center of the Atlantic Ocean. The chain is part of a worldwide system of mid-ocean ridges. Mid-ocean ridges are underwater mountain chains that run through Earth’s ocean basins. Mid-ocean ridges are places where ...
... Mid-Ocean Ridges and Sea-Floor Spreading A chain of submerged mountains runs through the center of the Atlantic Ocean. The chain is part of a worldwide system of mid-ocean ridges. Mid-ocean ridges are underwater mountain chains that run through Earth’s ocean basins. Mid-ocean ridges are places where ...
File
... a trench. Cone-shaped volcanoes can form from magma seeping to the surface. This is how the volcanic belt of the North America’s west coast has formed. Mountain ranges like the Coast Mountain range also form from the collision. Earthquakes can occur when subduction, ridge push, and slab pull ...
... a trench. Cone-shaped volcanoes can form from magma seeping to the surface. This is how the volcanic belt of the North America’s west coast has formed. Mountain ranges like the Coast Mountain range also form from the collision. Earthquakes can occur when subduction, ridge push, and slab pull ...
Plate Tectonics
... continental plates. When an oceanic plate collides with a continental plate, the continental plate rides over the edge of the oceanic plate and pushes the ocean plate underneath. This is known as subduction. The subduction of the oceanic plate causes the plate to start to melt back into magma. Some ...
... continental plates. When an oceanic plate collides with a continental plate, the continental plate rides over the edge of the oceanic plate and pushes the ocean plate underneath. This is known as subduction. The subduction of the oceanic plate causes the plate to start to melt back into magma. Some ...
tectonics for lab-short version
... material rises at ridges and cooler mantle material sinks at subduction zones. ...
... material rises at ridges and cooler mantle material sinks at subduction zones. ...
Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics (from the Late Latin tectonicus, from the Greek: τεκτονικός ""pertaining to building"") is a scientific theory that describes the large-scale motion of Earth's lithosphere. This theoretical model builds on the concept of continental drift which was developed during the first few decades of the 20th century. The geoscientific community accepted the theory after the concepts of seafloor spreading were later developed in the late 1950s and early 1960s.The lithosphere, which is the rigid outermost shell of a planet (on Earth, the crust and upper mantle), is broken up into tectonic plates. On Earth, there are seven or eight major plates (depending on how they are defined) and many minor plates. Where plates meet, their relative motion determines the type of boundary; convergent, divergent, or transform. Earthquakes, volcanic activity, mountain-building, and oceanic trench formation occur along these plate boundaries. The lateral relative movement of the plates typically varies from zero to 100 mm annually.Tectonic plates are composed of oceanic lithosphere and thicker continental lithosphere, each topped by its own kind of crust. Along convergent boundaries, subduction carries plates into the mantle; the material lost is roughly balanced by the formation of new (oceanic) crust along divergent margins by seafloor spreading. In this way, the total surface of the globe remains the same. This prediction of plate tectonics is also referred to as the conveyor belt principle. Earlier theories (that still have some supporters) propose gradual shrinking (contraction) or gradual expansion of the globe.Tectonic plates are able to move because the Earth's lithosphere has greater strength than the underlying asthenosphere. Lateral density variations in the mantle result in convection. Plate movement is thought to be driven by a combination of the motion of the seafloor away from the spreading ridge (due to variations in topography and density of the crust, which result in differences in gravitational forces) and drag, with downward suction, at the subduction zones. Another explanation lies in the different forces generated by the rotation of the globe and the tidal forces of the Sun and Moon. The relative importance of each of these factors and their relationship to each other is unclear, and still the subject of much debate.