chapter 2 - Geophile.net
... 5. Distinguish between Earth’s crust, lithosphere, asthenosphere, and mantle. Earth’s crust overlies mantle – distinguished by composition: oceanic crust is basaltic composition and continental crust is “granitic” composition. Earth’s lithosphere overlies asthenosphere – distinguished by rock pr ...
... 5. Distinguish between Earth’s crust, lithosphere, asthenosphere, and mantle. Earth’s crust overlies mantle – distinguished by composition: oceanic crust is basaltic composition and continental crust is “granitic” composition. Earth’s lithosphere overlies asthenosphere – distinguished by rock pr ...
Powerpoint Presentation Physical Geology, 10/e
... • Oceanic mountain ranges and deep trenches – Ocean bottom is mostly about 3.7 km deep, with two areas of exception: – Continuous mountain ranges extend more than 65,000 km along the ocean floors • Volcanic mountains that form at spreading centers, where plates pull apart and magma rises to fill the ...
... • Oceanic mountain ranges and deep trenches – Ocean bottom is mostly about 3.7 km deep, with two areas of exception: – Continuous mountain ranges extend more than 65,000 km along the ocean floors • Volcanic mountains that form at spreading centers, where plates pull apart and magma rises to fill the ...
The crust is the outermost of several onion
... structure of the Earth. It is much thinner than the deeper layers being only about 30 to 60 km thick beneath continents and about 5 to 8 km thick beneath the oceans. The crust and a portion of the next layer, the 'mantle', forms a relatively rigid shell which has been called the 'lithosphere'. This ...
... structure of the Earth. It is much thinner than the deeper layers being only about 30 to 60 km thick beneath continents and about 5 to 8 km thick beneath the oceans. The crust and a portion of the next layer, the 'mantle', forms a relatively rigid shell which has been called the 'lithosphere'. This ...
Chapter 17 Mountain Building
... The Pacific coast consists of accreted terranes or igneous intrusions • composed of volcanic island arcs, oceanic ridges, seamounts, and fragments of continents scraped off by the continent’s margin ...
... The Pacific coast consists of accreted terranes or igneous intrusions • composed of volcanic island arcs, oceanic ridges, seamounts, and fragments of continents scraped off by the continent’s margin ...
Earth Systems,Structures and Processes-Science Exam
... The earth's plates sit on a dense, hot, somewhat melted layer of the earth. The plates move very slowly, pressing against one another in some places and pulling apart in other places, sometimes scraping alongside each other as they do. Mountains form as two continental plates, or an ocean plat ...
... The earth's plates sit on a dense, hot, somewhat melted layer of the earth. The plates move very slowly, pressing against one another in some places and pulling apart in other places, sometimes scraping alongside each other as they do. Mountains form as two continental plates, or an ocean plat ...
DATE DUE: Name: Instructor: Ms. Terry J. Boroughs Geology 305
... preserved in the magnetic properties of rocks. It allows the reconstruction of changes in the position of the magnetic poles and reversals of the magnetic poles in the geologic past. 3. The theory that the Earth's crust is near to a state of equilibrium, and that large blocks of crust behave like bl ...
... preserved in the magnetic properties of rocks. It allows the reconstruction of changes in the position of the magnetic poles and reversals of the magnetic poles in the geologic past. 3. The theory that the Earth's crust is near to a state of equilibrium, and that large blocks of crust behave like bl ...
Directed Reading
... ______ 37. One mountain range that formed when Pangaea was created was a. the Rocky Mountains. b. the Alps. c. the Himalayas. d. the Appalachians. ______ 38. How were Laurasia and Gondwanaland created? a. Pangaea collided with another supercontinent. b. North America collided with Eurasia. c. Pangae ...
... ______ 37. One mountain range that formed when Pangaea was created was a. the Rocky Mountains. b. the Alps. c. the Himalayas. d. the Appalachians. ______ 38. How were Laurasia and Gondwanaland created? a. Pangaea collided with another supercontinent. b. North America collided with Eurasia. c. Pangae ...
What Can Changes Inside Earth Communicate? Pre/Post Test 1
... The geological time scale placed Earth’s rocks in order by_____. ...
... The geological time scale placed Earth’s rocks in order by_____. ...
December Final 2013
... found, and there are no unconformities, the layer of sandstone must be ____. a. older than 300 million years c. about 300 million years old b. younger than 300 million years d. older than 600 million years ...
... found, and there are no unconformities, the layer of sandstone must be ____. a. older than 300 million years c. about 300 million years old b. younger than 300 million years d. older than 600 million years ...
Key concepts
... Key terms density crust granite basalt mantle core lithosphere asthenosphere mesosphere (lower mantle) outer core inner core convection conduction Alfred Wegener continental drift Pangea seafloor Spreading subduction zones Plate Tectonics divergent plate boundary convergent plate boundary transform ...
... Key terms density crust granite basalt mantle core lithosphere asthenosphere mesosphere (lower mantle) outer core inner core convection conduction Alfred Wegener continental drift Pangea seafloor Spreading subduction zones Plate Tectonics divergent plate boundary convergent plate boundary transform ...
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 7 Earth Science, 12e Tarbuck
... seafloor • Ocean ridges and seafloor spreading • Oceanic ridges develop along welldeveloped boundaries • Along ridges, seafloor spreading creates new seafloor ...
... seafloor • Ocean ridges and seafloor spreading • Oceanic ridges develop along welldeveloped boundaries • Along ridges, seafloor spreading creates new seafloor ...
Physical Geology 1330
... What is Geology – The scientific study of the processes, events, and consequences of the Earth's past, present, and future. ...
... What is Geology – The scientific study of the processes, events, and consequences of the Earth's past, present, and future. ...
HISTORICAL GEOLOGY LECTURE TEST # 2
... through" the ancient ocean basins. 8. Plate tectonic theory states that the Earth is divided into a series of large lithospheric plates. 9. The concept of "Stochastic Processes" says that origin and extinction events are predictable, and are due to environmental circumstances. 10. The early stages o ...
... through" the ancient ocean basins. 8. Plate tectonic theory states that the Earth is divided into a series of large lithospheric plates. 9. The concept of "Stochastic Processes" says that origin and extinction events are predictable, and are due to environmental circumstances. 10. The early stages o ...
What are the three types of convergent boundaries? oceanic
... Stretching along the western coasts of North and South America and down the eastern coast of Asia, the CircumPacific Belt marks the location of most convergent boundary volcanoes. Both temperature and pressure increase(s) with depth below Earth surface (geothermal gradient). Rhyolitic magma has the ...
... Stretching along the western coasts of North and South America and down the eastern coast of Asia, the CircumPacific Belt marks the location of most convergent boundary volcanoes. Both temperature and pressure increase(s) with depth below Earth surface (geothermal gradient). Rhyolitic magma has the ...
Section 1
... The Four Layers The Earth is composed of four different layers. The crust is the layer that you live on. The mantle is much hotter and has the ability to flow. The outer core and inner core are even hotter with pressures so great you would be squeezed into a ball smaller than a marble if you were a ...
... The Four Layers The Earth is composed of four different layers. The crust is the layer that you live on. The mantle is much hotter and has the ability to flow. The outer core and inner core are even hotter with pressures so great you would be squeezed into a ball smaller than a marble if you were a ...
On Which Crust Do Volcanoes Form? - EHS
... Q3 – Oceanic Crust 3) Try to duplicate the oceanic crust as accurately as possible. On the diagram at right, show where you set each variable. ...
... Q3 – Oceanic Crust 3) Try to duplicate the oceanic crust as accurately as possible. On the diagram at right, show where you set each variable. ...
Earth`s Layers Sunshine State STANDARDS SC.B.1.3.1: The
... away. As scientists continued to study the sea-floor rock, they made a surprising discovery about Earth’s magnetic field. To understand Earth’s magnetic field, you can compare the planet to a bar magnet, which has a north and a south pole. Earth’s magnetic field affects the entire planet, as shown i ...
... away. As scientists continued to study the sea-floor rock, they made a surprising discovery about Earth’s magnetic field. To understand Earth’s magnetic field, you can compare the planet to a bar magnet, which has a north and a south pole. Earth’s magnetic field affects the entire planet, as shown i ...
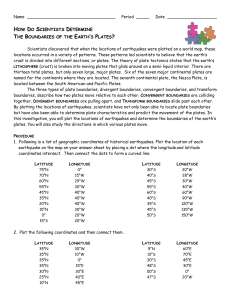
How do Scientists determine the boundaries of the plates?
... Scientists discovered that when the locations of earthquakes were plotted on a world map, these locations occurred in a variety of patterns. These patterns led scientists to believe that the earth’s crust is divided into different sections, or plates. The theory of plate tectonics states that the ea ...
... Scientists discovered that when the locations of earthquakes were plotted on a world map, these locations occurred in a variety of patterns. These patterns led scientists to believe that the earth’s crust is divided into different sections, or plates. The theory of plate tectonics states that the ea ...
Tectonic Plates The theory of plate tectonics has done for geology
... Places where plates are coming apart are called divergent boundaries. As shown in the drawing above, when Earth's brittle surface layer (the lithosphere) is pulled apart, it typically breaks along parallel faults that tilt slightly outward from each other. As the plates separate along the boundary, ...
... Places where plates are coming apart are called divergent boundaries. As shown in the drawing above, when Earth's brittle surface layer (the lithosphere) is pulled apart, it typically breaks along parallel faults that tilt slightly outward from each other. As the plates separate along the boundary, ...
Grade 9 Social Studies Canadian Identity
... 2) Relief - is the difference in elevation between points on the earths surface 3) Gradient - refers to the steepness of slopes 4) Geology - refers to the types of rocks and the history of those rocks 5) General Appearance - the general look of the area How are Landforms Built 1) The heat of the ear ...
... 2) Relief - is the difference in elevation between points on the earths surface 3) Gradient - refers to the steepness of slopes 4) Geology - refers to the types of rocks and the history of those rocks 5) General Appearance - the general look of the area How are Landforms Built 1) The heat of the ear ...
The Earth`s Layers Foldable
... 4. The crust and the upper layer of the mantle together make up a zone of rigid, brittle rock called ___________________________________. ...
... 4. The crust and the upper layer of the mantle together make up a zone of rigid, brittle rock called ___________________________________. ...
Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics (from the Late Latin tectonicus, from the Greek: τεκτονικός ""pertaining to building"") is a scientific theory that describes the large-scale motion of Earth's lithosphere. This theoretical model builds on the concept of continental drift which was developed during the first few decades of the 20th century. The geoscientific community accepted the theory after the concepts of seafloor spreading were later developed in the late 1950s and early 1960s.The lithosphere, which is the rigid outermost shell of a planet (on Earth, the crust and upper mantle), is broken up into tectonic plates. On Earth, there are seven or eight major plates (depending on how they are defined) and many minor plates. Where plates meet, their relative motion determines the type of boundary; convergent, divergent, or transform. Earthquakes, volcanic activity, mountain-building, and oceanic trench formation occur along these plate boundaries. The lateral relative movement of the plates typically varies from zero to 100 mm annually.Tectonic plates are composed of oceanic lithosphere and thicker continental lithosphere, each topped by its own kind of crust. Along convergent boundaries, subduction carries plates into the mantle; the material lost is roughly balanced by the formation of new (oceanic) crust along divergent margins by seafloor spreading. In this way, the total surface of the globe remains the same. This prediction of plate tectonics is also referred to as the conveyor belt principle. Earlier theories (that still have some supporters) propose gradual shrinking (contraction) or gradual expansion of the globe.Tectonic plates are able to move because the Earth's lithosphere has greater strength than the underlying asthenosphere. Lateral density variations in the mantle result in convection. Plate movement is thought to be driven by a combination of the motion of the seafloor away from the spreading ridge (due to variations in topography and density of the crust, which result in differences in gravitational forces) and drag, with downward suction, at the subduction zones. Another explanation lies in the different forces generated by the rotation of the globe and the tidal forces of the Sun and Moon. The relative importance of each of these factors and their relationship to each other is unclear, and still the subject of much debate.