Chapter 6 Review
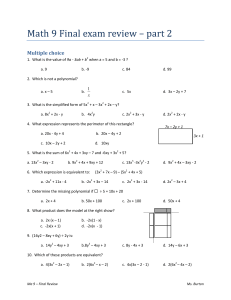
... and explain what they mean. c) Graph the relation. d) What would a 4-h house call cost? 7. Determine the x- and y-intercepts of each line. Then, graph the line. a) 4x + 5y = 20 b) 2x − 3y = 6 8. Christopher is at a movie with his younger sister, Cindy. He has $24 to spend on popcorn and pop. Popcorn ...
... and explain what they mean. c) Graph the relation. d) What would a 4-h house call cost? 7. Determine the x- and y-intercepts of each line. Then, graph the line. a) 4x + 5y = 20 b) 2x − 3y = 6 8. Christopher is at a movie with his younger sister, Cindy. He has $24 to spend on popcorn and pop. Popcorn ...
Section 4.4
... contains only one fraction, you may be able to solve it easily by applying the Addition and/or Multiplication Properties. If the equation has several fractions, it is easier to use the method of clearing fractions to solve the equation. In this method, you find the LCD for all of the fractions in th ...
... contains only one fraction, you may be able to solve it easily by applying the Addition and/or Multiplication Properties. If the equation has several fractions, it is easier to use the method of clearing fractions to solve the equation. In this method, you find the LCD for all of the fractions in th ...
Math 240 Fall 2012 Sample Exam 2 with Solutions Contents
... both have determinants equal to zero and are thus singular. On the other hand they add up to the identity matrix which has determinant 1 and is non-singular. The collection (d) is a subspace. Indeed this collection consists of all 2 × 2 matrices A that satisfy AB = BA. If A1 and A2 are two such matr ...
... both have determinants equal to zero and are thus singular. On the other hand they add up to the identity matrix which has determinant 1 and is non-singular. The collection (d) is a subspace. Indeed this collection consists of all 2 × 2 matrices A that satisfy AB = BA. If A1 and A2 are two such matr ...
Matrix Multiplication
... order. Thus, to calculate, say, ABC, you can first form AB and then multiply this result from the right by matrix C, or, you can first form BC and then multiply this result by A from the left. The final result will be the same (see exercise 4 below). iii) The square matrix with diagonal elements ...
... order. Thus, to calculate, say, ABC, you can first form AB and then multiply this result from the right by matrix C, or, you can first form BC and then multiply this result by A from the left. The final result will be the same (see exercise 4 below). iii) The square matrix with diagonal elements ...
The von Neumann inequality for linear matrix functions of several
... maximum modulus principle for analytic functions in the disk). Note that it is unessential here that the set T is commutative. However, for matrix-valued polynomials (i.e., polynomials with matrix coefficients) in several independent variables, the notion of polynomial in several commuting contracti ...
... maximum modulus principle for analytic functions in the disk). Note that it is unessential here that the set T is commutative. However, for matrix-valued polynomials (i.e., polynomials with matrix coefficients) in several independent variables, the notion of polynomial in several commuting contracti ...