Long-tailed Weasel - Extension Store
... keeping its face clean. However, the reason for lapping up the blood has more to do with its nutritive value rather than a weasel’s neatness. When able to hunt down a large prey item, a weasel will first consume organ meat, including heart, liver, and kidney. The weasel may be sated after eating onl ...
... keeping its face clean. However, the reason for lapping up the blood has more to do with its nutritive value rather than a weasel’s neatness. When able to hunt down a large prey item, a weasel will first consume organ meat, including heart, liver, and kidney. The weasel may be sated after eating onl ...
Pike are just plain designed to eat fish: elongated snout, strong jaws
... In the case of pike and other species, it’s a good idea to have throw-backs-a second lure ready on a nearby rod – available to quickly toss back to tempt fish that might be following a hooked fish. “I see this a lot when fishing smallmouths in early season, but pike commonly display this behavior,” ...
... In the case of pike and other species, it’s a good idea to have throw-backs-a second lure ready on a nearby rod – available to quickly toss back to tempt fish that might be following a hooked fish. “I see this a lot when fishing smallmouths in early season, but pike commonly display this behavior,” ...
as a PDF - Instituto Nacional da Mata Atlântica
... Trophic ontogeny was observed in O. striatus in this study. As there is no evidence of spatial partitioning between juvenile and adults, both may be dividing the available food resource. Only for the smallest juveniles was the size of prey ingested significantly different from the other size classes ...
... Trophic ontogeny was observed in O. striatus in this study. As there is no evidence of spatial partitioning between juvenile and adults, both may be dividing the available food resource. Only for the smallest juveniles was the size of prey ingested significantly different from the other size classes ...
Combining molecular gut content analysis and functional
... how body size affects prey choice in soil predators Bernhard Eitzinger1,2*, Björn C. Rall3,4, Michael Traugott5, Stefan Scheu1 ...
... how body size affects prey choice in soil predators Bernhard Eitzinger1,2*, Björn C. Rall3,4, Michael Traugott5, Stefan Scheu1 ...
In the Wild - The Maryland Zoo in Baltimore
... Have tan and light brown coloration with a partial arrow-shaped marking on the top of the head – each scale is a single color Habitat and Range: Are native to India, Sri Lanka, Pakistan, and Nepal Are generally found in rainforests, but can also be found in river valleys, woodlands, scrublands, gras ...
... Have tan and light brown coloration with a partial arrow-shaped marking on the top of the head – each scale is a single color Habitat and Range: Are native to India, Sri Lanka, Pakistan, and Nepal Are generally found in rainforests, but can also be found in river valleys, woodlands, scrublands, gras ...
Evolved Flocking
... groups respond and act for the collective interest of the group • Flocking in animals is usually observed in prey species – studies have demonstrated a link between predation and ...
... groups respond and act for the collective interest of the group • Flocking in animals is usually observed in prey species – studies have demonstrated a link between predation and ...
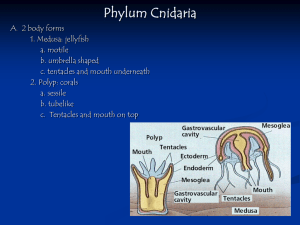
Phylum Cnidaria
... Reproduce: asexually: budding. Sexually be releasing eggs and sperm into the ocean where fertilization will occur. Most species live in warm water and they are brightly colored. Feeding: They feed on fishes, which are caught by means of the numerous nematocysts in their tentacles. These animals are ...
... Reproduce: asexually: budding. Sexually be releasing eggs and sperm into the ocean where fertilization will occur. Most species live in warm water and they are brightly colored. Feeding: They feed on fishes, which are caught by means of the numerous nematocysts in their tentacles. These animals are ...
Comb Jellies
... - The body of the ctenophora consists of a thick mesoglea which is pressed between two layers of epithelia. - The outer layer of the skin consists of: sensory cells, cells that secrete mucus which protects the comb jellies body, and interstitial cells which are able to transform into other types of ...
... - The body of the ctenophora consists of a thick mesoglea which is pressed between two layers of epithelia. - The outer layer of the skin consists of: sensory cells, cells that secrete mucus which protects the comb jellies body, and interstitial cells which are able to transform into other types of ...
4. symbiosis - Hicksville Public Schools
... Oxpeckers and zebras or rhinos the oxpecker (a bird) lives on the zebra or rhino, and eats all of the bugs and parasites on the animal. – The bird benefits by having a readily available source of food. – The zebra or rhino benefits from having the bugs removed. – when there is a danger to the zebra ...
... Oxpeckers and zebras or rhinos the oxpecker (a bird) lives on the zebra or rhino, and eats all of the bugs and parasites on the animal. – The bird benefits by having a readily available source of food. – The zebra or rhino benefits from having the bugs removed. – when there is a danger to the zebra ...
Relationships in the Ecosystem
... for food. Prey = animal that is eaten by another. Predator / Prey populations will change in response to each other’s population. ...
... for food. Prey = animal that is eaten by another. Predator / Prey populations will change in response to each other’s population. ...
Dietary biology of the Eurasian eagle-owl
.jpg?width=300)
The Eurasian eagle-owl (Bubo bubo) may well be the most powerful extant species of owl, able to attack and kill large prey far beyond the capacities of most other living owls. However, the species is even more marked for its ability to live on more diverse prey than possibly any other comparably sized raptorial bird, which, given its considerable size, is almost fully restricted to eagles. This species can adapt to surprisingly small prey where it is the only kind available and to large prey where it is abundant. Eurasian eagle-owls feed most commonly on small mammals in the 100 to 2,000 g (0.22 to 4.41 lb) weight range, although nearly 45% of the prey species recorded have an average adult body mass of less than 100 g (3.5 oz). Usually 55-80% of the food of eagle-owls is mammalian.