PDF
... The above equation is called the secant method. This method now requires two initial guesses, but unlike the bisection method, the two initial guesses do not need to bracket the root of the equation. The secant method is an open method and may or may not converge. However, when secant method converg ...
... The above equation is called the secant method. This method now requires two initial guesses, but unlike the bisection method, the two initial guesses do not need to bracket the root of the equation. The secant method is an open method and may or may not converge. However, when secant method converg ...
LU Factorization
... Linear Algebra Review • Now that we have covered some examples of solving linear systems, there are several important questions: – How many numerical operations does Gaussian Elimination take? That is, how fast is it? – Why do we use LU factorization? In what cases does it speed up calculation? – H ...
... Linear Algebra Review • Now that we have covered some examples of solving linear systems, there are several important questions: – How many numerical operations does Gaussian Elimination take? That is, how fast is it? – Why do we use LU factorization? In what cases does it speed up calculation? – H ...
Plotting Points
... The other great thing about this form is that it allows us to use function notation and eliminate the need to write the dependent variable. Hence, y = mx + b becomes f(x) = mx + b since y is a function of x. We reviewed graphing a linear equation in 2 variables in §2.1, based upon 3 randomly chosen ...
... The other great thing about this form is that it allows us to use function notation and eliminate the need to write the dependent variable. Hence, y = mx + b becomes f(x) = mx + b since y is a function of x. We reviewed graphing a linear equation in 2 variables in §2.1, based upon 3 randomly chosen ...
Review answer key
... 3. A rectangular garden with an area of has a width of . what is the length of the garden? 4. Factor completely: x 4 – 16 5. Express in simplest form: ...
... 3. A rectangular garden with an area of has a width of . what is the length of the garden? 4. Factor completely: x 4 – 16 5. Express in simplest form: ...
... a) The words "at least" imply that the value of 48 inches is included in the solution set, so the inequality is written ash ≥ 48, where h is the height. In the context of this problem, it is not realisitic that someone is 100 inches tall. This would be considered a non-viable solution. Viable soluti ...
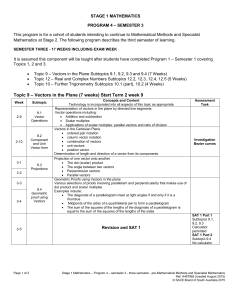
Practical Session 2
... seems to involve four real-number multiplications, it can in fact be done with just three: ac, bd, and (a + b)(c + d), since: bc + ad = (a + b)(c + d) − ac − bd. In our big-O way of thinking, reducing the number of multiplications from 4 to 3 seems wasted ingenuity. But this modest improvement becom ...
... seems to involve four real-number multiplications, it can in fact be done with just three: ac, bd, and (a + b)(c + d), since: bc + ad = (a + b)(c + d) − ac − bd. In our big-O way of thinking, reducing the number of multiplications from 4 to 3 seems wasted ingenuity. But this modest improvement becom ...
Section2.2
... • Decompose each number into its prime factors. The gcd is obtained by multiplying the prime factors the two numbers have in common. If the two numbers have no common prime factors, then the gcd = 1. ...
... • Decompose each number into its prime factors. The gcd is obtained by multiplying the prime factors the two numbers have in common. If the two numbers have no common prime factors, then the gcd = 1. ...