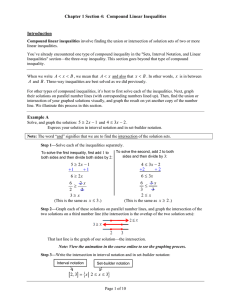
Chap. 6 Quadratics
... In math most everything has an opposite. Multiplication’s opposite is division. Addition’s opposite is subtraction. Distribution and FOIL are two kinds of multiplication. The opposite is factorization. Review distribution and factoring from previous lessons. 4x2 – 20x factors to 4x(x –5) 7y (3y + 8) ...
... In math most everything has an opposite. Multiplication’s opposite is division. Addition’s opposite is subtraction. Distribution and FOIL are two kinds of multiplication. The opposite is factorization. Review distribution and factoring from previous lessons. 4x2 – 20x factors to 4x(x –5) 7y (3y + 8) ...
Transcendence Degree and Noether Normalization
... The strategy will be to replace the y j , j < s, by elements z j so that k[z , . . . , zs− , ys ] = k[y , . . . , ys ] and so that when written in terms of the new variables the polynomial P(y j ) becomes a monic polynomial in ys , or at least a polynomial with leading term a constant in k, which ...
... The strategy will be to replace the y j , j < s, by elements z j so that k[z , . . . , zs− , ys ] = k[y , . . . , ys ] and so that when written in terms of the new variables the polynomial P(y j ) becomes a monic polynomial in ys , or at least a polynomial with leading term a constant in k, which ...
Self Study : Matrices
... Please click on the following links to access the materials on matrices. 1. Click on this link to introduction of matrices. http://www.intmath.com/Matrices-determinants/Matrix-determinant-intro.php 2. Click on this link to find out more on determinant (2 x 2) http://www.intmath.com/Matrices-determin ...
... Please click on the following links to access the materials on matrices. 1. Click on this link to introduction of matrices. http://www.intmath.com/Matrices-determinants/Matrix-determinant-intro.php 2. Click on this link to find out more on determinant (2 x 2) http://www.intmath.com/Matrices-determin ...
Slopes and Lines
... of slope m that passes through the point (x1, y1) is two points find the slope using the points, y – y1 = m(x – x1) Ifandgiven use one of the coordinates in the equation Write the point-slope form of the equation of the line passing through (-1,3) with a slope of 4. Then solve the equation for y. So ...
... of slope m that passes through the point (x1, y1) is two points find the slope using the points, y – y1 = m(x – x1) Ifandgiven use one of the coordinates in the equation Write the point-slope form of the equation of the line passing through (-1,3) with a slope of 4. Then solve the equation for y. So ...
Definitions:
... c. Vector-vector multiplication is somewhat special. There are two kinds. First, if they are considered as matrices then you can multiply a row vector (1 x n) times a column vector (1 x n) in the same way that you multiply matrices when their dimensions are appropriate. Notice that, by the rule abov ...
... c. Vector-vector multiplication is somewhat special. There are two kinds. First, if they are considered as matrices then you can multiply a row vector (1 x n) times a column vector (1 x n) in the same way that you multiply matrices when their dimensions are appropriate. Notice that, by the rule abov ...
CHAPTER 2: Linear codes
... IV054 Equivalence of linear codes Definition Two linear codes GF(q) are called equivalent if one can be obtained from another by the following operations: (a) permutation of the positions of the code; (b) multiplication of symbols appearing in a fixed position by a non-zero scalar. Theorem Two k ...
... IV054 Equivalence of linear codes Definition Two linear codes GF(q) are called equivalent if one can be obtained from another by the following operations: (a) permutation of the positions of the code; (b) multiplication of symbols appearing in a fixed position by a non-zero scalar. Theorem Two k ...
CHAPTER 2: Linear codes
... IV054 Equivalence of linear codes Definition Two linear codes GF(q) are called equivalent if one can be obtained from another by the following operations: (a) permutation of the positions of the code; (b) multiplication of symbols appearing in a fixed position by a non-zero scalar. Theorem Two k ...
... IV054 Equivalence of linear codes Definition Two linear codes GF(q) are called equivalent if one can be obtained from another by the following operations: (a) permutation of the positions of the code; (b) multiplication of symbols appearing in a fixed position by a non-zero scalar. Theorem Two k ...
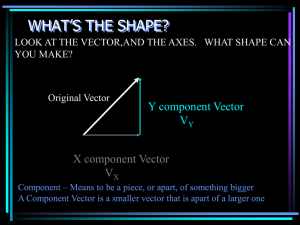
VECTORS - Katy Independent School District
... the work into a few simple steps that anyone can do Lets look at the same problem again using the box method, on the side will be the longer method In the end chose the method that works best for you. ...
... the work into a few simple steps that anyone can do Lets look at the same problem again using the box method, on the side will be the longer method In the end chose the method that works best for you. ...
VECTORS comp box method addition 2015-16
... the work into a few simple steps that anyone can do Lets look at the same problem again using the box method, on the side will be the longer method In the end chose the method that works best for you. ...
... the work into a few simple steps that anyone can do Lets look at the same problem again using the box method, on the side will be the longer method In the end chose the method that works best for you. ...