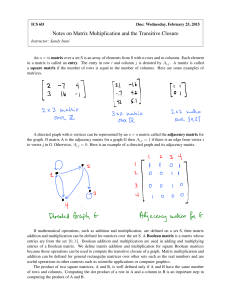
Separating Doubly Nonnegative and Completely
... • Can be shown that DNN relaxation is equivalent to “SDP+RLT” relaxation, and for n = 2 problem is equivalent to QPB [AB10]. • Constraints from Boolean Quadric Polytope (BQP) are valid for off-diagonal components of X [BL09]. For n = 3, BQP is completely determined by triangle inequalities and RLT c ...
... • Can be shown that DNN relaxation is equivalent to “SDP+RLT” relaxation, and for n = 2 problem is equivalent to QPB [AB10]. • Constraints from Boolean Quadric Polytope (BQP) are valid for off-diagonal components of X [BL09]. For n = 3, BQP is completely determined by triangle inequalities and RLT c ...
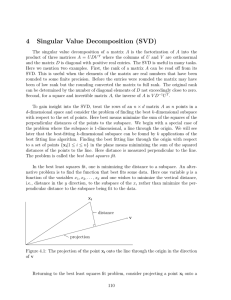
4 Singular Value Decomposition (SVD)
... provided that for each i > 1, σi (A) < σ1 (A). This suggests a way of finding σ1 and u1 , by successively powering B. But there are two issues. First, if there is a significant gap between the first and second singular values of a matrix, then the above argument applies and the power method will qui ...
... provided that for each i > 1, σi (A) < σ1 (A). This suggests a way of finding σ1 and u1 , by successively powering B. But there are two issues. First, if there is a significant gap between the first and second singular values of a matrix, then the above argument applies and the power method will qui ...
Neighborly Polytopes and Sparse Solution of Underdetermined
... Students of `1 /`0 equivalence have also used weaker notions of correspondence between solutions of the two problems – correspondence between the solutions for most x with ≤ k nonzeros, rather than for all x with ≤ k nonzeros. Below we describe the two main such notions which have been proposed, and ...
... Students of `1 /`0 equivalence have also used weaker notions of correspondence between solutions of the two problems – correspondence between the solutions for most x with ≤ k nonzeros, rather than for all x with ≤ k nonzeros. Below we describe the two main such notions which have been proposed, and ...
Beginning Algebra - Tillamook Bay Community College
... referred to as the double-negative property19. For any real number a, 18. Real numbers whose graphs are on opposite sides of the origin with the same distance to the origin. 19. The opposite of a negative number is positive: −(−a) = a. ...
... referred to as the double-negative property19. For any real number a, 18. Real numbers whose graphs are on opposite sides of the origin with the same distance to the origin. 19. The opposite of a negative number is positive: −(−a) = a. ...
Pre-Algebra
... 1. To solve one-step inequalities using subtraction 2. To solve one-step inequalities using addition ...
... 1. To solve one-step inequalities using subtraction 2. To solve one-step inequalities using addition ...
file
... most appropriate method of calculation in a question; for example, finding 62% of £80. calculate a percentage of a quantity work out what percentage one is of another understand the meaning of ratio notation interpret a ratio as a fraction simplify a ratio to its simplest form, a : b, wher ...
... most appropriate method of calculation in a question; for example, finding 62% of £80. calculate a percentage of a quantity work out what percentage one is of another understand the meaning of ratio notation interpret a ratio as a fraction simplify a ratio to its simplest form, a : b, wher ...
The Monte Carlo Framework, Examples from Finance and
... Step 1 is straightforward and only involves a few lines of algebra. (See Law and Kelton for more details.) In particular, we now also know how to generate multivariate log-normal random vectors. ...
... Step 1 is straightforward and only involves a few lines of algebra. (See Law and Kelton for more details.) In particular, we now also know how to generate multivariate log-normal random vectors. ...