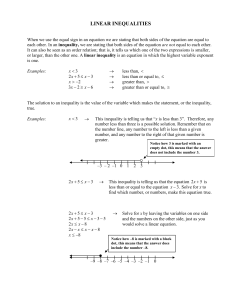
Example 1.
... - Denominator: determinant of the matrix with coefficients in the left side (M) - Numerator: for x, replace x part in M with right side part, and take the determinant. for y, replace y part in M with right side part, and take the determinant. - We can use this method when you get the solution for th ...
... - Denominator: determinant of the matrix with coefficients in the left side (M) - Numerator: for x, replace x part in M with right side part, and take the determinant. for y, replace y part in M with right side part, and take the determinant. - We can use this method when you get the solution for th ...
5_6 Parallel-Perpendicular Lines
... SOLUTION: Looking at the given info we have the following: A line passes through (-3, -1) and is parallel to the graph of y = 2x +3. What equation represents the line in slope-intercept form? ...
... SOLUTION: Looking at the given info we have the following: A line passes through (-3, -1) and is parallel to the graph of y = 2x +3. What equation represents the line in slope-intercept form? ...
notes
... where r is the rank of A. This decomposition of A is called the singular value decomposition, or SVD. The values σi , for i = 1, 2, . . . , n, are the singular values of A. The columns of U are the left singular vectors, and the columns of V are the right singular vectors. An alternative decompositi ...
... where r is the rank of A. This decomposition of A is called the singular value decomposition, or SVD. The values σi , for i = 1, 2, . . . , n, are the singular values of A. The columns of U are the left singular vectors, and the columns of V are the right singular vectors. An alternative decompositi ...
SectionGroups
... Note that U m is closer under multiplication since if a, b U m , a b U m since (a b) b a U m . U m is associative since it is a subset of Z m and all elements of Z m are associative under multiplication. The identity element is 1 U m and all elements in U m have multiplicative invers ...
... Note that U m is closer under multiplication since if a, b U m , a b U m since (a b) b a U m . U m is associative since it is a subset of Z m and all elements of Z m are associative under multiplication. The identity element is 1 U m and all elements in U m have multiplicative invers ...
SectionGroups
... Note that U m is closer under multiplication since if a, b U m , a b U m since (a b) b a U m . U m is associative since it is a subset of Z m and all elements of Z m are associative under multiplication. The identity element is 1 U m and all elements in U m have multiplicative invers ...
... Note that U m is closer under multiplication since if a, b U m , a b U m since (a b) b a U m . U m is associative since it is a subset of Z m and all elements of Z m are associative under multiplication. The identity element is 1 U m and all elements in U m have multiplicative invers ...
linear mappings
... Let V and U be vector spaces over a filed K. Then the collection of all linear mapping from V into U with the operations of addition and scalar multiplication form a vector space over K. The space in the above theorem is usually denoted by Hom (V,U) Here Hom comes from the word homomorphism. In the ...
... Let V and U be vector spaces over a filed K. Then the collection of all linear mapping from V into U with the operations of addition and scalar multiplication form a vector space over K. The space in the above theorem is usually denoted by Hom (V,U) Here Hom comes from the word homomorphism. In the ...
Document
... 9.4 The Inverse Sine Function Solving a Trigonometric Equation Analytically 1. Decide whether the equation is linear or quadratic, so you can determine the solution method. 2. If only one trigonometric function is present, solve the equation for that function. 3. If more than one trigonometric func ...
... 9.4 The Inverse Sine Function Solving a Trigonometric Equation Analytically 1. Decide whether the equation is linear or quadratic, so you can determine the solution method. 2. If only one trigonometric function is present, solve the equation for that function. 3. If more than one trigonometric func ...