Riemannian manifolds with a semi-symmetric metric connection
... be a parallel unit vector field with respect to the Levi-Civita connection ∇. Then R · R̃ = 0 if and only if M is semisymmetric. Theorem 4.3. Let (M, g) be a semisymmetric n > 3 dimensional Riemannian manifold admitting a semisymmetric metric connection. If U is a parallel unit vector field with res ...
... be a parallel unit vector field with respect to the Levi-Civita connection ∇. Then R · R̃ = 0 if and only if M is semisymmetric. Theorem 4.3. Let (M, g) be a semisymmetric n > 3 dimensional Riemannian manifold admitting a semisymmetric metric connection. If U is a parallel unit vector field with res ...
Vectors and the Geometry of Space
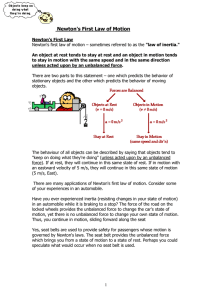
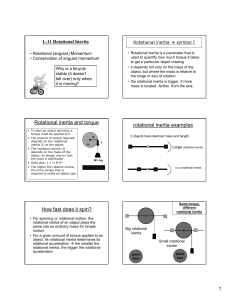
... descent down the plane is slowed by friction; if is not too large, friction will prevent the block from moving at all. The forces acting on the block are the weight W, where W 苷 mt ( t is the acceleration due to gravity); the normal force N (the normal component of the reactionary force of the pla ...
... descent down the plane is slowed by friction; if is not too large, friction will prevent the block from moving at all. The forces acting on the block are the weight W, where W 苷 mt ( t is the acceleration due to gravity); the normal force N (the normal component of the reactionary force of the pla ...
1 Sets and Set Notation.
... (2) W is closed under addition. That is, for each ~u, ~v ∈ W , we have ~u + ~v ∈ W . (3) W is closed under scalar multiplication. That is, for each c ∈ R and ~u ∈ W , we have c~u ∈ W . Proof. One direction of the proof is trivial: if W is a vector subspace of V , then W satisfies the three condition ...
... (2) W is closed under addition. That is, for each ~u, ~v ∈ W , we have ~u + ~v ∈ W . (3) W is closed under scalar multiplication. That is, for each c ∈ R and ~u ∈ W , we have c~u ∈ W . Proof. One direction of the proof is trivial: if W is a vector subspace of V , then W satisfies the three condition ...
Course of analytical geometry
... § 1. Three-dimensional Euclidean space. Acsiomatics and visual evidence. Like the elementary geometry explained in the book [6], the analytical geometry in this book is a geometry of threedimensional space E. We use the symbol E for to denote the space that we observe in our everyday life. Despite b ...
... § 1. Three-dimensional Euclidean space. Acsiomatics and visual evidence. Like the elementary geometry explained in the book [6], the analytical geometry in this book is a geometry of threedimensional space E. We use the symbol E for to denote the space that we observe in our everyday life. Despite b ...
MOMENTUM ANALYSIS OF FLOW SYSTEMS
... to the nozzle exit (in the direction opposite to that of the airplane); this is the velocity that should be used when evaluating the outflow of exhaust gases through the control surface (Fig. 6–4b). Note that the exhaust gases would appear motionless to an observer on the ground if the relative velo ...
... to the nozzle exit (in the direction opposite to that of the airplane); this is the velocity that should be used when evaluating the outflow of exhaust gases through the control surface (Fig. 6–4b). Note that the exhaust gases would appear motionless to an observer on the ground if the relative velo ...