Chapter 10
... Point P will rotate about the origin in a circle of radius r Every particle on the disc undergoes circular motion about the origin, O Polar coordinates are convenient to use to represent the position of P (or any other point) P is located at (r, q) where r is the distance from the origin to P and q ...
... Point P will rotate about the origin in a circle of radius r Every particle on the disc undergoes circular motion about the origin, O Polar coordinates are convenient to use to represent the position of P (or any other point) P is located at (r, q) where r is the distance from the origin to P and q ...
Intro to Physics - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... Explain the relationship between impulse and change in momentum using the impulse-momentum theorem. Solve problems using the impulse-momentum theorem. Explain how impulse is influenced by changes in the acting force and the length of time the force acts. Explain why impulse is so important to safety ...
... Explain the relationship between impulse and change in momentum using the impulse-momentum theorem. Solve problems using the impulse-momentum theorem. Explain how impulse is influenced by changes in the acting force and the length of time the force acts. Explain why impulse is so important to safety ...
Circular
... the end by a hinge (allowing vertical motion) to a rigid rod. If this rod, and also the tube, is rapidly rotated in a horizontal plane with an angular velocity w, compare the excess forces on a small elemental volume A r of each liquid at distance r from the centre of motion (A being the area of cr ...
... the end by a hinge (allowing vertical motion) to a rigid rod. If this rod, and also the tube, is rapidly rotated in a horizontal plane with an angular velocity w, compare the excess forces on a small elemental volume A r of each liquid at distance r from the centre of motion (A being the area of cr ...
ƒ A S ƒ ƒ B
... rules of arithmetic. Vector quantities have direction as well as magnitude and combine according to the rules of vector addition. The negative of a vector has the same magnitude but points in the opposite direction. (See Example 1.5.) Vector components and vector addition: Vector addition can be car ...
... rules of arithmetic. Vector quantities have direction as well as magnitude and combine according to the rules of vector addition. The negative of a vector has the same magnitude but points in the opposite direction. (See Example 1.5.) Vector components and vector addition: Vector addition can be car ...
Rigid Body Rotation
... Inertia of Rotation Consider Newton’s second law for the inertia of rotation to be patterned after the law for translation. ...
... Inertia of Rotation Consider Newton’s second law for the inertia of rotation to be patterned after the law for translation. ...
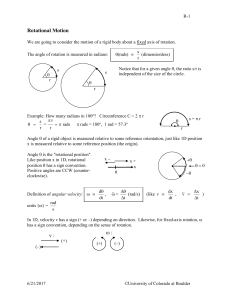
RotationalMotion - University of Colorado Boulder
... Definition of vector torque : r F = cross product of r and F: "r cross F" Vector Math interlude: The cross-product of two vectors is a third vector A B C defined like this: The magnitude of A B is A B sin . The direction of A B is the direction perpendicular to the plane defined by th ...
... Definition of vector torque : r F = cross product of r and F: "r cross F" Vector Math interlude: The cross-product of two vectors is a third vector A B C defined like this: The magnitude of A B is A B sin . The direction of A B is the direction perpendicular to the plane defined by th ...
Momentum and Impulse (updated)
... LAW OF CONSERVATION OF MOMENTUM The total momentum of an isolated system of bodies remains constant. ...
... LAW OF CONSERVATION OF MOMENTUM The total momentum of an isolated system of bodies remains constant. ...