Instructor`s Guide
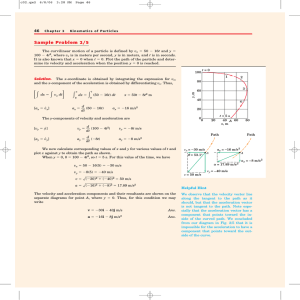
... Dividing the mass by the volume, the result is r = [3.952 x 10-25 kg] / [2.739 x 10-42 m3] = 1.443 x 1017 kg/m3. ...
... Dividing the mass by the volume, the result is r = [3.952 x 10-25 kg] / [2.739 x 10-42 m3] = 1.443 x 1017 kg/m3. ...
here.
... for systems with conservative forces. It leads to Lagrange’s equations of motion, which are equivalent to Newton’s 2nd law. One advantage of Lagrange’s equations is that they retain the same form in all systems of coordinates on configuration space. • The idea of the action principle is as follows. ...
... for systems with conservative forces. It leads to Lagrange’s equations of motion, which are equivalent to Newton’s 2nd law. One advantage of Lagrange’s equations is that they retain the same form in all systems of coordinates on configuration space. • The idea of the action principle is as follows. ...
Rotational Kinematics
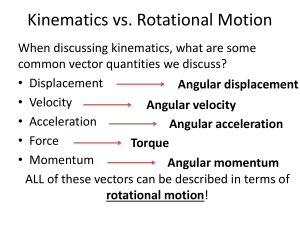
... When discussing kinematics, what are some common vector quantities we discuss? • Displacement Angular displacement • Velocity Angular velocity • Acceleration Angular acceleration • Force Torque • Momentum Angular momentum ALL of these vectors can be described in terms of rotational motion! ...
... When discussing kinematics, what are some common vector quantities we discuss? • Displacement Angular displacement • Velocity Angular velocity • Acceleration Angular acceleration • Force Torque • Momentum Angular momentum ALL of these vectors can be described in terms of rotational motion! ...