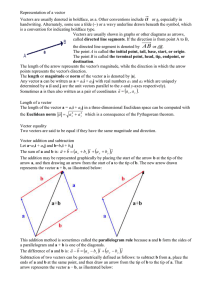
ECE 3300 Portfolio 1..
... For each point in 2-D or 3-D space vectors as they are defined, will have a magnitude and direction. For example, if we have an equation for E , it will be a vector that acts a s a function of x, y and z or whatever coordinate system applies. As we “plug-in” different values of x, y, and z, a vector ...
... For each point in 2-D or 3-D space vectors as they are defined, will have a magnitude and direction. For example, if we have an equation for E , it will be a vector that acts a s a function of x, y and z or whatever coordinate system applies. As we “plug-in” different values of x, y, and z, a vector ...
Kepler`s Laws
... Kepler’s Laws Johannes Kepler (1571–1630) discovered three laws of planetary motion in the early seventeenth century. These laws were discovered empirically, after studying for many years data collected primarily by the Danish astronomer Tycho Brahe (1546–1601). The first mathematical derivation of K ...
... Kepler’s Laws Johannes Kepler (1571–1630) discovered three laws of planetary motion in the early seventeenth century. These laws were discovered empirically, after studying for many years data collected primarily by the Danish astronomer Tycho Brahe (1546–1601). The first mathematical derivation of K ...
18 Lecture 18: Central forces and angular momentum
... namely, that for any central potential, angular momentum is a constant of motion. Note that the origin of this conservation law is the fact that the problem has spherical symmetry. Rotation around the origin leaves the potential invariant, implying the conservation of angular momentum. In particular ...
... namely, that for any central potential, angular momentum is a constant of motion. Note that the origin of this conservation law is the fact that the problem has spherical symmetry. Rotation around the origin leaves the potential invariant, implying the conservation of angular momentum. In particular ...













![Lecture 2A [pdf]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008845380_1-be6e705eb191ba98899bd42e027ab326-300x300.png)