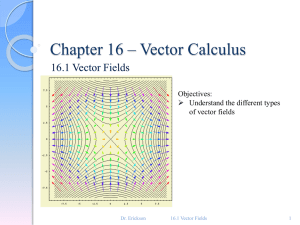
Problem Set 5 Solutions MATH 110: Linear Algebra
... Proof: We can write x = s + sp where s ∈ S and sp is in the space Sp of vectors orthogonal to S. For any t ∈ S, we have x − t = (x − s) + (s − t) Since s−t ∈ S and x−s = sp ∈ Sp , this is an orthogonal decomposition of x − t, so its norm is given by the Pythagorean formula (i.e. its norm squared is ...
... Proof: We can write x = s + sp where s ∈ S and sp is in the space Sp of vectors orthogonal to S. For any t ∈ S, we have x − t = (x − s) + (s − t) Since s−t ∈ S and x−s = sp ∈ Sp , this is an orthogonal decomposition of x − t, so its norm is given by the Pythagorean formula (i.e. its norm squared is ...
Review1 - UCF Physics
... Choose a convenient xy coordinate system Find the x and y components of each force in the FBD Add the x and y components separately ...
... Choose a convenient xy coordinate system Find the x and y components of each force in the FBD Add the x and y components separately ...