tectonic plates
... Paleomagnetism = Earth’s magnetic memory Iron in new crust pushes the older crust aside; they record their polar-charge for thousands of years ...
... Paleomagnetism = Earth’s magnetic memory Iron in new crust pushes the older crust aside; they record their polar-charge for thousands of years ...
earthquake
... An earthquake is the vibration of Earth produced by the rapid release of energy Focus and Epicenter • Focus is the point within Earth where the earthquake starts. • Epicenter is the location on the surface directly above the focus. ...
... An earthquake is the vibration of Earth produced by the rapid release of energy Focus and Epicenter • Focus is the point within Earth where the earthquake starts. • Epicenter is the location on the surface directly above the focus. ...
key1 - Scioly.org
... a. plow their way through the sea floor. b. passively ride along as the sea floor spreads. c. may subduct if they are old and dense enough. d. consist of rock that is younger than sea-floor rock. e. have retained the same size and shape throughout earth’s history. 2. Which statement is FALSE? a. As ...
... a. plow their way through the sea floor. b. passively ride along as the sea floor spreads. c. may subduct if they are old and dense enough. d. consist of rock that is younger than sea-floor rock. e. have retained the same size and shape throughout earth’s history. 2. Which statement is FALSE? a. As ...
gEOLOGy AND earth structure
... Sir Charles Lyell (mid-1800s) is given the most credit for advancing the basic principles of modern geology with the publication of the eleven editions of his great work, Principles of Geology. Using the principles of relative dating, the placing of events in their proper sequence or order without k ...
... Sir Charles Lyell (mid-1800s) is given the most credit for advancing the basic principles of modern geology with the publication of the eleven editions of his great work, Principles of Geology. Using the principles of relative dating, the placing of events in their proper sequence or order without k ...
test - Scioly.org
... 41. Which is NOT one of the ideas Wegener offered to support his theory: a. the good fit of the outline of the continents. b. the matching of the distribution of similar fossils across oceans. c. the existence of the mid-ocean ridge, where sea-floor spreading starts. d. paleoclimatic evidence of ex ...
... 41. Which is NOT one of the ideas Wegener offered to support his theory: a. the good fit of the outline of the continents. b. the matching of the distribution of similar fossils across oceans. c. the existence of the mid-ocean ridge, where sea-floor spreading starts. d. paleoclimatic evidence of ex ...
Earth Science Curriculum Map 11-12
... theories of the fate of the Universe. Analyze different types of galaxies and solar systems and how scientists study them in order to better understand the universe. Understand how Cosmic ...
... theories of the fate of the Universe. Analyze different types of galaxies and solar systems and how scientists study them in order to better understand the universe. Understand how Cosmic ...
File
... Two plates moving AWAY from each other and forming a gap or RIFT. • Mostly associated with OCEANIC crust [seafloor spreading = Mid-Atlantic Ridge] – as molten rock [MAGMA] from the asthenosphere rises the plates move apart, and fills the space between the plates. – as it cools, it hardens onto the e ...
... Two plates moving AWAY from each other and forming a gap or RIFT. • Mostly associated with OCEANIC crust [seafloor spreading = Mid-Atlantic Ridge] – as molten rock [MAGMA] from the asthenosphere rises the plates move apart, and fills the space between the plates. – as it cools, it hardens onto the e ...
Lesson 4 – A Deeper Look at Plate Movement - Project 3D-VIEW
... Melted rock, called magma, moves toward the surface of the Earth because of the high temperatures and pressure in the mantle. At the crust, gases that have been trapped with plate movement cause volcanoes to erupt! When magma reaches the surface of the Earth, it is then called lava. Outer core and I ...
... Melted rock, called magma, moves toward the surface of the Earth because of the high temperatures and pressure in the mantle. At the crust, gases that have been trapped with plate movement cause volcanoes to erupt! When magma reaches the surface of the Earth, it is then called lava. Outer core and I ...
Theme Short Term Plan: Mighty Mountains Y3/4 Spring 2 Lesson 1
... On IWB show a map of Europe & ask what continent it is. Ask chn to name some of the countries in Europe & to come & point them out on the map, e.g. France, Spain, Poland, Norway, etc. Name some of the major countries. Look at Eastern Europe & discuss how it has changed over the last 30 years. Show a ...
... On IWB show a map of Europe & ask what continent it is. Ask chn to name some of the countries in Europe & to come & point them out on the map, e.g. France, Spain, Poland, Norway, etc. Name some of the major countries. Look at Eastern Europe & discuss how it has changed over the last 30 years. Show a ...
earthquake - SPS186.org
... Cause of Tsunamis • A tsunami triggered by an earthquake occurs where a slab of the ocean floor is displaced vertically along a fault. • A tsunami also can occur when the vibration of a quake sets an underwater landslide into motion. • Tsunami is the Japanese word for “seismic sea ...
... Cause of Tsunamis • A tsunami triggered by an earthquake occurs where a slab of the ocean floor is displaced vertically along a fault. • A tsunami also can occur when the vibration of a quake sets an underwater landslide into motion. • Tsunami is the Japanese word for “seismic sea ...
3D modelling of controlled-source electromagnetic fields in applied
... • Maya Neytcheva, Sci. Computing, Department of Information Technology, Uppsala University, [email protected]. ...
... • Maya Neytcheva, Sci. Computing, Department of Information Technology, Uppsala University, [email protected]. ...
study guide questions 3rd nine weeks 2017
... Describe the form of energy that is created from the heat of the Earth. Draw label and define the rock cycle Contrast latitude and longitude. Give an example of each. Define soil and describe what it is made of Define physical weathering and give 3 examples Describe how climate affects weathering. E ...
... Describe the form of energy that is created from the heat of the Earth. Draw label and define the rock cycle Contrast latitude and longitude. Give an example of each. Define soil and describe what it is made of Define physical weathering and give 3 examples Describe how climate affects weathering. E ...
Earth as a Planet
... Certainly no one today doubts that Earth orbits a star, the Sun. Photos taken from space, observations made by astronauts, and the fact that there has been so much successful space exploration that depends on understanding the structure of the solar system all confirm it. But in the early 17th centu ...
... Certainly no one today doubts that Earth orbits a star, the Sun. Photos taken from space, observations made by astronauts, and the fact that there has been so much successful space exploration that depends on understanding the structure of the solar system all confirm it. But in the early 17th centu ...
Week 7 - Geophile.net
... Types of maps: planimetric, topographic, bathymetric, geologic, and weather Map legends: North arrow, magnetic north, scale, location, and symbols Scale: statement/verbal, representative fraction, and scale bar Latitude and longitude Topography Contour lines, contour interval, index contour, bench m ...
... Types of maps: planimetric, topographic, bathymetric, geologic, and weather Map legends: North arrow, magnetic north, scale, location, and symbols Scale: statement/verbal, representative fraction, and scale bar Latitude and longitude Topography Contour lines, contour interval, index contour, bench m ...
Volcanoes and Igneous Activity Earth - Chapter 4
... The Science of Geology Some historical notes about geology • The nature of Earth has been a focus of study for centuries • Catastrophism: shaping of the Earth’s landscape by rare catastrophes • Uniformitarianism: a principle first proposed by James Hutton that represented the Birth of Modern Geolog ...
... The Science of Geology Some historical notes about geology • The nature of Earth has been a focus of study for centuries • Catastrophism: shaping of the Earth’s landscape by rare catastrophes • Uniformitarianism: a principle first proposed by James Hutton that represented the Birth of Modern Geolog ...
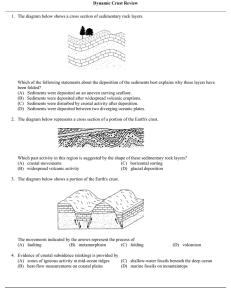
Dynamic Crust Review
... 7. Fossils of organisms that lived in shallow water can be found in horizontal sedimentary rock layers at great ocean depths. This fact is generally interpreted by most Earth scientists as evidence that (A) the cold water deep in the ocean kills shallow-water organisms (B) sunlight once penetrated t ...
... 7. Fossils of organisms that lived in shallow water can be found in horizontal sedimentary rock layers at great ocean depths. This fact is generally interpreted by most Earth scientists as evidence that (A) the cold water deep in the ocean kills shallow-water organisms (B) sunlight once penetrated t ...
Earthquakes - Leon County Schools
... http://elearning.niu.edu/simulations/images/S_portfolio/Mercalli/Mercalli_Scale.swf ...
... http://elearning.niu.edu/simulations/images/S_portfolio/Mercalli/Mercalli_Scale.swf ...
Lecture PowerPoint Slides
... directly proportional to the density of the material through which it is traveling ...
... directly proportional to the density of the material through which it is traveling ...
When the seafloor diverges, what is formed?
... are the two types of evidence that were initially used to support the Theory of Continental Drift. ► What are similar shapes of coastlines and fossil evidence? ► Double ...
... are the two types of evidence that were initially used to support the Theory of Continental Drift. ► What are similar shapes of coastlines and fossil evidence? ► Double ...
Seafloor Spreading: 100
... This is why Wegner’s theory of Continental Drift was not accepted. What is the “how the continents” were able to move? Bonus: This is the mechanism for movement of the continents. What is seafloor spreading and ...
... This is why Wegner’s theory of Continental Drift was not accepted. What is the “how the continents” were able to move? Bonus: This is the mechanism for movement of the continents. What is seafloor spreading and ...
2 Precambrian Time and the Paleozoic Era
... Most scientists agree that Earth formed about 4.6 billion years ago. Earth formed as part of a cloud of dust, or nebula. Over time, particles from the cloud formed Earth and other planets. The formation of Earth was the beginning of Precambrian time. Precambrian time lasted about 4 billion years and ...
... Most scientists agree that Earth formed about 4.6 billion years ago. Earth formed as part of a cloud of dust, or nebula. Over time, particles from the cloud formed Earth and other planets. The formation of Earth was the beginning of Precambrian time. Precambrian time lasted about 4 billion years and ...
Chapter 32
... • A fracture along which visible movement can be detected on one side relative to the other. ...
... • A fracture along which visible movement can be detected on one side relative to the other. ...
History of geomagnetism

The history of geomagnetism is concerned with the history of the study of Earth's magnetic field. It encompasses the history of navigation using compasses, studies of the prehistoric magnetic field (archeomagnetism and paleomagnetism), and applications to plate tectonics.Magnetism has been known since prehistory, but knowledge of the Earth's field developed slowly. The horizontal direction of the Earth's field was first measured in the fourth century BC but the vertical direction was not measured until 1544 AD and the intensity was first measured in 1791. At first, compasses were thought to point towards locations in the heavens, then towards magnetic mountains. A modern experimental approach to understanding the Earth's field began with de Magnete, a book published by William Gilbert in 1600. His experiments with a magnetic model of the Earth convinced him that the Earth itself is a large magnet.