Electromagnetic induction Electric currents generate magnetic fields
... Electric currents are pushed on by magnetic fields ...
... Electric currents are pushed on by magnetic fields ...
Magnetic Forces on a Current
... magnetic fields begin or end. Instead they form closed loops. The motion of charged particles in a Magnetic Field The motion of a charged particle in an electric field is much different than its motion in a magnetic field. ...
... magnetic fields begin or end. Instead they form closed loops. The motion of charged particles in a Magnetic Field The motion of a charged particle in an electric field is much different than its motion in a magnetic field. ...
Observations of electricity go back to the discovery of static cling
... The skiing analogy would say that if I were to keep the resistance constant, then I'm keeping the length of the skiing path the same, so if I increase the altitude, the only way I could do it would be to make the path steeper. This results in skiers going faster and coming out of the other end of th ...
... The skiing analogy would say that if I were to keep the resistance constant, then I'm keeping the length of the skiing path the same, so if I increase the altitude, the only way I could do it would be to make the path steeper. This results in skiers going faster and coming out of the other end of th ...
Teacher`s Notes
... 1. Students should discover that magnets stick to some things and not to others. These magnets are permanent magnets. They should discover that certain orientations of the two magnets will produce a repulsive force, while other orientations cause the two magnets to attract each other. They should re ...
... 1. Students should discover that magnets stick to some things and not to others. These magnets are permanent magnets. They should discover that certain orientations of the two magnets will produce a repulsive force, while other orientations cause the two magnets to attract each other. They should re ...
Teacher`s Notes - Electricity and Magnetism, Part 2 Electricity and
... 1. Students should discover that magnets stick to some things and not to others. These magnets are permanent magnets. They should discover that certain orientations of the two magnets will produce a repulsive force, while other orientations cause the two magnets to attract each other. They should re ...
... 1. Students should discover that magnets stick to some things and not to others. These magnets are permanent magnets. They should discover that certain orientations of the two magnets will produce a repulsive force, while other orientations cause the two magnets to attract each other. They should re ...
Archean - University of Hawaii at Hilo
... Gases condense to form stars. Stars form elements up to Fe, stars explode (supernova) and heavier elements form. Sun formed in the radial arm of the Milky Way Galaxy later from some of this material. Gravitational attraction of matter, condenses into a disk, meteorites collide into planetessimals. V ...
... Gases condense to form stars. Stars form elements up to Fe, stars explode (supernova) and heavier elements form. Sun formed in the radial arm of the Milky Way Galaxy later from some of this material. Gravitational attraction of matter, condenses into a disk, meteorites collide into planetessimals. V ...
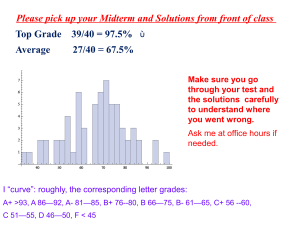
Top Grade 39/40 = 97.5% Average 27/40 = 67.5%
... Sun’s magnetic field also reverses regularly, every 22 years. (Related to droughts on earth?) Smaller and faster fluctuations in Earth’s field are from varying ion winds in atmosphere. Ions created from solar ultraviolet and x-rays interacting with atmospheric atoms. ...
... Sun’s magnetic field also reverses regularly, every 22 years. (Related to droughts on earth?) Smaller and faster fluctuations in Earth’s field are from varying ion winds in atmosphere. Ions created from solar ultraviolet and x-rays interacting with atmospheric atoms. ...
lesson 1
... Materials needed: current source, straight wire, electric key, connected wires, magnetic arrow, iron fillings, the straight wire on a clear plastic stand, the solenoid on a clear plastic stand Procedure I. Checking homework II. Warm up 1. “Yes”/”No” testing: 1. The magnet attracts iron bodies only. ...
... Materials needed: current source, straight wire, electric key, connected wires, magnetic arrow, iron fillings, the straight wire on a clear plastic stand, the solenoid on a clear plastic stand Procedure I. Checking homework II. Warm up 1. “Yes”/”No” testing: 1. The magnet attracts iron bodies only. ...
Ece 315 Lecture 11 – Maxwell`s Equations (Time
... 1) Time-varying magnetic field linking a stationary loop (opening or closing the switch in Faraday’s experiment). 2) Changing the surface area of the loop. This could be done by constricting the loop, but it is more often done by rotating a loop with a constant area. The rotation makes the area of t ...
... 1) Time-varying magnetic field linking a stationary loop (opening or closing the switch in Faraday’s experiment). 2) Changing the surface area of the loop. This could be done by constricting the loop, but it is more often done by rotating a loop with a constant area. The rotation makes the area of t ...
The Study of the Force Generated from a Changing Magnetic Field
... The Study of the Force Generated from a Changing Magnetic Field Abstract Objectives/Goals The objective of this experiment was to measure the induced magnetic force due to a changing magnetic field (Lenzs Law) by dropping a strong magnet down conductive metal tubes. Methods/Materials Two different s ...
... The Study of the Force Generated from a Changing Magnetic Field Abstract Objectives/Goals The objective of this experiment was to measure the induced magnetic force due to a changing magnetic field (Lenzs Law) by dropping a strong magnet down conductive metal tubes. Methods/Materials Two different s ...
IB Physics SL Y2 @ RIS – Unit 13, Magnetism: Faraday`s Lab
... Remember the paradigm for this unit: a current-carrying wire has a magnetic field around it. A permanent magnet also has a magnetic field around it, even though no current flows through it. Clearly, a net current is not necessary for a magnetic field. What is going on? It looks like we need moving c ...
... Remember the paradigm for this unit: a current-carrying wire has a magnetic field around it. A permanent magnet also has a magnetic field around it, even though no current flows through it. Clearly, a net current is not necessary for a magnetic field. What is going on? It looks like we need moving c ...
Elaborating on a Preexisting Concept
... 11. Glaciers retreat. Turn and go in the opposite direction, instead of melt. ...
... 11. Glaciers retreat. Turn and go in the opposite direction, instead of melt. ...
All about Magnets
... 7. Each magnet is actually consists of tiny micro-magnet (or domains) orderly line up from north to south poles within the magnet. 8. LAWS of Magnetism: (1) Like (Same) Poles repel, eg. A north and a north poles (2) Opposite Poles attract, eg. A north and a south pole 9. A compass consists of a need ...
... 7. Each magnet is actually consists of tiny micro-magnet (or domains) orderly line up from north to south poles within the magnet. 8. LAWS of Magnetism: (1) Like (Same) Poles repel, eg. A north and a north poles (2) Opposite Poles attract, eg. A north and a south pole 9. A compass consists of a need ...
Magnetism - MrSimonPorter
... a magnetic field The fact that this force is always at right angles to the velocity means that the charge will move in a circle (if the speed is constant) ...
... a magnetic field The fact that this force is always at right angles to the velocity means that the charge will move in a circle (if the speed is constant) ...
Hall Effect
... partly because it makes no difference whether you consider positive or negative charge to be moving. But the Hall voltage has a different polarity for positive and negative charge carriers, and it has been used to study the details of conduction in semiconductors and other materials which show a com ...
... partly because it makes no difference whether you consider positive or negative charge to be moving. But the Hall voltage has a different polarity for positive and negative charge carriers, and it has been used to study the details of conduction in semiconductors and other materials which show a com ...
1.3 Magnet Learning Center
... platinum, aluminum and more. They may however magnetize a small amount while placed in a magnetic field. Magnetism can attract magnetic objects or push them away. Magnets have a magnetic north pole and a magnetic south pole. If the same pole of two magnets is placed near each other they will push aw ...
... platinum, aluminum and more. They may however magnetize a small amount while placed in a magnetic field. Magnetism can attract magnetic objects or push them away. Magnets have a magnetic north pole and a magnetic south pole. If the same pole of two magnets is placed near each other they will push aw ...
History of geomagnetism

The history of geomagnetism is concerned with the history of the study of Earth's magnetic field. It encompasses the history of navigation using compasses, studies of the prehistoric magnetic field (archeomagnetism and paleomagnetism), and applications to plate tectonics.Magnetism has been known since prehistory, but knowledge of the Earth's field developed slowly. The horizontal direction of the Earth's field was first measured in the fourth century BC but the vertical direction was not measured until 1544 AD and the intensity was first measured in 1791. At first, compasses were thought to point towards locations in the heavens, then towards magnetic mountains. A modern experimental approach to understanding the Earth's field began with de Magnete, a book published by William Gilbert in 1600. His experiments with a magnetic model of the Earth convinced him that the Earth itself is a large magnet.