Conserved quatities / Mirror / Tokamak
... associated with the pulsed character One can either: live with it / drive current another way / use a different concept ...
... associated with the pulsed character One can either: live with it / drive current another way / use a different concept ...
Plate Tectonics, Layers, and Continental Drift Mini
... a. rigid, hard layer of the Earth b. the process of hot material heating, rising, cooling, and sinking c. studies the process that shape planet Earth d. theory suggesting that the plates of the Earth are in constant motion e. plastic-like layer in Earth’s mantle f. theory that land has moved from a ...
... a. rigid, hard layer of the Earth b. the process of hot material heating, rising, cooling, and sinking c. studies the process that shape planet Earth d. theory suggesting that the plates of the Earth are in constant motion e. plastic-like layer in Earth’s mantle f. theory that land has moved from a ...
UNIT 5 – Earth`s Internal Structure
... It consists of partially molten rock. It is believed that this is the surface on which the tectonic plates move (the movement of continents). ...
... It consists of partially molten rock. It is believed that this is the surface on which the tectonic plates move (the movement of continents). ...
Read the following about the layers of the Earth and answer the
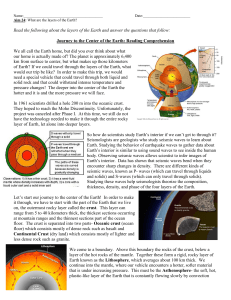
... Read the following about the layers of the Earth and answer the questions that follow: Journey to the Center of the Earth: Reading Comprehension We all call the Earth home, but did you ever think about what our home is actually made of? The planet is approximately 6,400 km from surface to center, bu ...
... Read the following about the layers of the Earth and answer the questions that follow: Journey to the Center of the Earth: Reading Comprehension We all call the Earth home, but did you ever think about what our home is actually made of? The planet is approximately 6,400 km from surface to center, bu ...
available
... Bullard, E., Everett, J.E., and Gilbert Smith, A., 1965, The fit of the continents around the Atlantic, in P.M.S. Blackett, E. Bullard and S.K. Runcorn (eds.), A symposium on continental drift, 1088: 41-51, Royal Society of London, Phil. Trans. Cox, A., 1973, Plate Tectonics and Geomagnetic Reversal ...
... Bullard, E., Everett, J.E., and Gilbert Smith, A., 1965, The fit of the continents around the Atlantic, in P.M.S. Blackett, E. Bullard and S.K. Runcorn (eds.), A symposium on continental drift, 1088: 41-51, Royal Society of London, Phil. Trans. Cox, A., 1973, Plate Tectonics and Geomagnetic Reversal ...
Nanostorage - Max-Planck
... is, their “spin” – are oriented to one another (spin component). Because the wave function of a system composed of electrons must be antisymmetric, a symmetric location component requires an antisymmetric spin component and vice versa. Physicists refer to this as exchange interaction. A symmetric sp ...
... is, their “spin” – are oriented to one another (spin component). Because the wave function of a system composed of electrons must be antisymmetric, a symmetric location component requires an antisymmetric spin component and vice versa. Physicists refer to this as exchange interaction. A symmetric sp ...
Quoting Glen Rein Ph
... toroid resistor which is folded back on itself, thereby allowing current to flow in opposite directions. Thus in addition to containing the magnetic fields, the mobius resistor will cancel them. This same principle is used in bifilar coils common in electrical engineering. Mobius resistors have simi ...
... toroid resistor which is folded back on itself, thereby allowing current to flow in opposite directions. Thus in addition to containing the magnetic fields, the mobius resistor will cancel them. This same principle is used in bifilar coils common in electrical engineering. Mobius resistors have simi ...
Basic electromagnetism and electromagnetic induction
... ”unthinking” answer is that with alternating current, there will be a force that alternates direction: repulsion one half-cycle, then attraction for the next half-cycle. You may find students divided on this assessment, some thinking there will an alternating force, while others think the force will ...
... ”unthinking” answer is that with alternating current, there will be a force that alternates direction: repulsion one half-cycle, then attraction for the next half-cycle. You may find students divided on this assessment, some thinking there will an alternating force, while others think the force will ...
IV. Plate Tectonics
... II. Earth’s Structure and Internal Energy C. Earth’s Crust Begins about 200 km beneath Earth’s surface Composed of the lithosphere (includes continental and oceanic crust) The asthenosphere lies directly beneath the lithosphere Continental crust is granite, very low density (2.7g/cm3). Oceanic crus ...
... II. Earth’s Structure and Internal Energy C. Earth’s Crust Begins about 200 km beneath Earth’s surface Composed of the lithosphere (includes continental and oceanic crust) The asthenosphere lies directly beneath the lithosphere Continental crust is granite, very low density (2.7g/cm3). Oceanic crus ...
Take Home 12 Complete the following on your own paper. Do not
... 11) (1) The study of seismic (earthquake) waves has provided most of what we know about the interior of the earth. (2) The seismic waves change direction and speed as they encounter different materials. (3) With this information, scientists have been able to subdivide the Earth into layers. (4) The ...
... 11) (1) The study of seismic (earthquake) waves has provided most of what we know about the interior of the earth. (2) The seismic waves change direction and speed as they encounter different materials. (3) With this information, scientists have been able to subdivide the Earth into layers. (4) The ...
Layers of the Earth, Continental Drift, and Plate Tectonic Overview
... 13. If the Earth's crust is growing at mid-ocean ridges, why doesn't the Earth itself grow larger? 14. What was Pangaea? 15. Where would you expect to see the following features? a. tall, wrinkled mountains in the middle of a continent b. a long parallel ridge on the ocean floor surrounded by parall ...
... 13. If the Earth's crust is growing at mid-ocean ridges, why doesn't the Earth itself grow larger? 14. What was Pangaea? 15. Where would you expect to see the following features? a. tall, wrinkled mountains in the middle of a continent b. a long parallel ridge on the ocean floor surrounded by parall ...
qualifying_exam_2
... In Magnetic Resonance Imaging this frequency is called the Larmor frequency. A nuclear magnetic moment can occupy one of two states in the context of NMR, corresponding to the moment parallel to the DC magnetic field and the other to anti-parallel orientation. The nuclear moment can either give up e ...
... In Magnetic Resonance Imaging this frequency is called the Larmor frequency. A nuclear magnetic moment can occupy one of two states in the context of NMR, corresponding to the moment parallel to the DC magnetic field and the other to anti-parallel orientation. The nuclear moment can either give up e ...
Magnetism Demonstrations: Magnetic Signatures of Some Common
... Although superconductors are so named for their zero electrical resistivity, the transition from the normal to the superconducting state below the critical temperature TC is accompanied by zero internal magnetic flux density due to the supercurrent, which is called the Meissner effect. The Meissner ...
... Although superconductors are so named for their zero electrical resistivity, the transition from the normal to the superconducting state below the critical temperature TC is accompanied by zero internal magnetic flux density due to the supercurrent, which is called the Meissner effect. The Meissner ...
HOW DO SEDIMENTS GET MAGNETIZED?
... detrital magnetic particles align passively with the geomagnetic field either during or after deposition. Single domain magnetic particles will align almost instantaneously with the geomagnetic field, yet observed magnetizations are generally about 1% of the saturation magnetization. Using a statist ...
... detrital magnetic particles align passively with the geomagnetic field either during or after deposition. Single domain magnetic particles will align almost instantaneously with the geomagnetic field, yet observed magnetizations are generally about 1% of the saturation magnetization. Using a statist ...
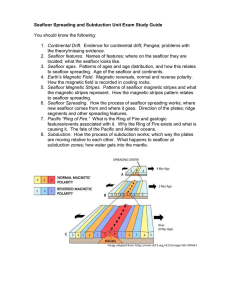
Seafloor Spreading and Subduction Unit Exam Study Guide You
... 6. Seafloor Spreading. How the process of seafloor spreading works; where new seafloor comes from and where it goes. Direction of the plates; ridge segments and other spreading features. 7. Pacific “Ring of Fire.” What is the Ring of Fire and geologic features/events associated with it. Why the Ring ...
... 6. Seafloor Spreading. How the process of seafloor spreading works; where new seafloor comes from and where it goes. Direction of the plates; ridge segments and other spreading features. 7. Pacific “Ring of Fire.” What is the Ring of Fire and geologic features/events associated with it. Why the Ring ...
General Geology
... • An understanding of geologic time and dating methods. • Development of skills to recognize major rock types, their constituent minerals, and their origin. • An appreciation of how the Scientific Method relates to the development of the Theory of Plate Tectonics. • An introduction to the origin and ...
... • An understanding of geologic time and dating methods. • Development of skills to recognize major rock types, their constituent minerals, and their origin. • An appreciation of how the Scientific Method relates to the development of the Theory of Plate Tectonics. • An introduction to the origin and ...
CLASS-10TH -CHAPTER -13 MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT
... 1. Why does a current carrying conductor kept in a magnetic field experience force? On what factors does the direction of this force depend? Name and state the rule used for determination of direction of this force. Answer: Force on a conductor carrying current in a magnetic field :A.M. Ampere sugge ...
... 1. Why does a current carrying conductor kept in a magnetic field experience force? On what factors does the direction of this force depend? Name and state the rule used for determination of direction of this force. Answer: Force on a conductor carrying current in a magnetic field :A.M. Ampere sugge ...
Notes - Sayre Geography Class
... Why are the days longer in some parts of the year? • The Earth’s axis is at an ___________________. • In about half of the Earth’s orbit, the tilt causes a region to face toward the sun for more hours than it faces away from the sun. • _______________________. • In other regions that face away from ...
... Why are the days longer in some parts of the year? • The Earth’s axis is at an ___________________. • In about half of the Earth’s orbit, the tilt causes a region to face toward the sun for more hours than it faces away from the sun. • _______________________. • In other regions that face away from ...
Name:
... and your knowledge of Earth science. The diagram represents Earth's interior zones. Scientists have classified Earth's interior into the zones shown based primarily on evidence gained by studying ...
... and your knowledge of Earth science. The diagram represents Earth's interior zones. Scientists have classified Earth's interior into the zones shown based primarily on evidence gained by studying ...
The Oldest Crust in Ocean Basins
... Scientists have been studying this area, in water depths of more than 6000m, through ocean drilling for more than three decades. The most recent penetration of the approximately 170 million-yearold crust by ODP occurred on Leg 185 as part of the "Subduction Factory Experiment". ...
... Scientists have been studying this area, in water depths of more than 6000m, through ocean drilling for more than three decades. The most recent penetration of the approximately 170 million-yearold crust by ODP occurred on Leg 185 as part of the "Subduction Factory Experiment". ...
History of geomagnetism

The history of geomagnetism is concerned with the history of the study of Earth's magnetic field. It encompasses the history of navigation using compasses, studies of the prehistoric magnetic field (archeomagnetism and paleomagnetism), and applications to plate tectonics.Magnetism has been known since prehistory, but knowledge of the Earth's field developed slowly. The horizontal direction of the Earth's field was first measured in the fourth century BC but the vertical direction was not measured until 1544 AD and the intensity was first measured in 1791. At first, compasses were thought to point towards locations in the heavens, then towards magnetic mountains. A modern experimental approach to understanding the Earth's field began with de Magnete, a book published by William Gilbert in 1600. His experiments with a magnetic model of the Earth convinced him that the Earth itself is a large magnet.