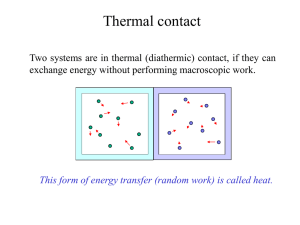
4.1 The Concepts of Force and Mass
... a material, with any bulk motion of the material playing no role in the transfer. ...
... a material, with any bulk motion of the material playing no role in the transfer. ...
Energy Savings Through Radiant Heat
... the closer to the ceiling you go, the warmer the air. Hot air systems do not distribute heat to the extremities where the body needs it most. In order to meet those needs, the air must be heated to a level that is much too hot and uncomfortable for the upper body. The choice is either cold feet or h ...
... the closer to the ceiling you go, the warmer the air. Hot air systems do not distribute heat to the extremities where the body needs it most. In order to meet those needs, the air must be heated to a level that is much too hot and uncomfortable for the upper body. The choice is either cold feet or h ...
States of matter - Tennessee State University
... The change in entropy between two equilibrium states is given by the heat transferred, dQr, in a quasi-static process leading from the initial to the final state divided by the absolute temperature, T, of the system ...
... The change in entropy between two equilibrium states is given by the heat transferred, dQr, in a quasi-static process leading from the initial to the final state divided by the absolute temperature, T, of the system ...
The fundamental principles of radiant heat barrier
... radiant heat barrier / reflective foil Reflective insulation materials work on a different concept than conventional bulk insulation like rigid foam boards or fibrous blankets. Unlike conventional bulk insulation, reflective insulation has very low emittance values “e-values” (typically 0.03, compar ...
... radiant heat barrier / reflective foil Reflective insulation materials work on a different concept than conventional bulk insulation like rigid foam boards or fibrous blankets. Unlike conventional bulk insulation, reflective insulation has very low emittance values “e-values” (typically 0.03, compar ...
Thermal Conduction Path Analysis in 3-D ICs
... insight into those issues that influence the heat propagation process, such as identification of the thermal paths. The dependence of thermal conductivity on temperatures is also shown to be significant. For certain thermal paths, a constant k produces lower temperatures by up to 19% as compared to a t ...
... insight into those issues that influence the heat propagation process, such as identification of the thermal paths. The dependence of thermal conductivity on temperatures is also shown to be significant. For certain thermal paths, a constant k produces lower temperatures by up to 19% as compared to a t ...
Lesson 1 - Introduction
... 0 oC P= constant • Under this condition, the junction temperature will be lower than the one predicted by static models, due to the fact that the total thermal impedance will be lower than the thermal resistance. ...
... 0 oC P= constant • Under this condition, the junction temperature will be lower than the one predicted by static models, due to the fact that the total thermal impedance will be lower than the thermal resistance. ...
Thermal Applications
... The input data requirements of the thermal applications are summarised below. The data is managed by utility programs invoked from the Application Views. Where possible, applications access common data so that it is never necessary to re-enter values in order to carry out different types of analysis ...
... The input data requirements of the thermal applications are summarised below. The data is managed by utility programs invoked from the Application Views. Where possible, applications access common data so that it is never necessary to re-enter values in order to carry out different types of analysis ...
preliminary tests of thermal conductivity of selected soil types
... Thermal conductivity is a property of engineering materials and its value is often determined in order to assess the insulation characteristics of building materials. However, in view of the current trend to efficiently use energy, soil thermal properties become interesting and scientific effort is ...
... Thermal conductivity is a property of engineering materials and its value is often determined in order to assess the insulation characteristics of building materials. However, in view of the current trend to efficiently use energy, soil thermal properties become interesting and scientific effort is ...
FSK Shield - Fi-Foil
... electricity. A radiant barri-er stops 97% of radiant heat transfer which improves the performance of the insulating material and lowers attic temperatures as much as 30oF. Another benefit is that a cooler attic will transfer less heat into air conditioner ducts. Radiant barriers also expand the use ...
... electricity. A radiant barri-er stops 97% of radiant heat transfer which improves the performance of the insulating material and lowers attic temperatures as much as 30oF. Another benefit is that a cooler attic will transfer less heat into air conditioner ducts. Radiant barriers also expand the use ...
Eco-technologies for energy efficient buildings in Italy
... moisture, typical of many areas of Italy, are less important. Italian regions have more differentiated climates: according to the seasons protection from summer heat or the energy containment during the winter have different levels of importance. In the alternation of seasons the buildings have to a ...
... moisture, typical of many areas of Italy, are less important. Italian regions have more differentiated climates: according to the seasons protection from summer heat or the energy containment during the winter have different levels of importance. In the alternation of seasons the buildings have to a ...
Thermodynamics - Centre for Theoretical Chemistry and Physics
... they are warmed up. But some substances do the opposite by shrinking in certain directions as they are heated and expanding when cooled. Now researchers in the UK have found an inorganic crystalline material composed of silver, cobalt, carbon and nitrogen that expands more than any other known mater ...
... they are warmed up. But some substances do the opposite by shrinking in certain directions as they are heated and expanding when cooled. Now researchers in the UK have found an inorganic crystalline material composed of silver, cobalt, carbon and nitrogen that expands more than any other known mater ...
notable example of a thermal mass
... Water has the highest amount of specific speci heat among common materials. however, its density is much lower than heavy materials such as stone and concrete. These properties can be compared between a range of materials as can be seen in (tab. [2]). Insulating materials have low thermal capacity s ...
... Water has the highest amount of specific speci heat among common materials. however, its density is much lower than heavy materials such as stone and concrete. These properties can be compared between a range of materials as can be seen in (tab. [2]). Insulating materials have low thermal capacity s ...
EQ: How can heat be transferred from one place to another?
... than a toe in the water. Why? It’s too cold! How can the sand be so hot and the water so cold since the sun heats them both? ...
... than a toe in the water. Why? It’s too cold! How can the sand be so hot and the water so cold since the sun heats them both? ...
Performance of Phase Change Materials for Cooling of
... The study is carried out for the city of Djelfa, Algeria a typical Mediterranean city with a subcontinental climate: a mild-warm climate and relatively hot and dry summer. When the indoor temperature exceeds 26°C, cooling is activated and split system room air conditioners with 100 ...
... The study is carried out for the city of Djelfa, Algeria a typical Mediterranean city with a subcontinental climate: a mild-warm climate and relatively hot and dry summer. When the indoor temperature exceeds 26°C, cooling is activated and split system room air conditioners with 100 ...
A Simplified Rapid Energy Model and Interface for Nontechnical Users
... are proportional to the indoor-outdoor temperature difference, and their magnitude can vary modestly within a single hour as the room’s air temperature floats between the upper and lower thermostat bounds. Thermal mass loads are more complicated: variation depends on the instantaneous indoor tempera ...
... are proportional to the indoor-outdoor temperature difference, and their magnitude can vary modestly within a single hour as the room’s air temperature floats between the upper and lower thermostat bounds. Thermal mass loads are more complicated: variation depends on the instantaneous indoor tempera ...
Analysis of Historic Buildings in Terms of their Microclimatic and
... of the Building Regulations the greatest emphasis must lie on the environmental aspect, and specifically the use of fossil energy. This is closely allied to the generation of carbon dioxide both from the creation of buildings and from their daily use. When they were first built and inhabited, all pr ...
... of the Building Regulations the greatest emphasis must lie on the environmental aspect, and specifically the use of fossil energy. This is closely allied to the generation of carbon dioxide both from the creation of buildings and from their daily use. When they were first built and inhabited, all pr ...
Convective heat transfer
... temperature difference(s) driving the conduction are constant, so that (after an equilibration time), the spatial distribution of temperatures (temperature field) in the conducting object does not change any further. Thus, all partial derivatives of temperature with respect to space may either be ze ...
... temperature difference(s) driving the conduction are constant, so that (after an equilibration time), the spatial distribution of temperatures (temperature field) in the conducting object does not change any further. Thus, all partial derivatives of temperature with respect to space may either be ze ...
Standard Method of Test for Thermal Conductivity of Rock
... uncertainty of the sample suite shall be compared with the measurement uncertainty to determine whether measurement error f sample variability is the dominant factor in the results. 11. Comments 11.1 Temperature effects on thermal conductivity 11.1.1 This standard is designed for measurements betwee ...
... uncertainty of the sample suite shall be compared with the measurement uncertainty to determine whether measurement error f sample variability is the dominant factor in the results. 11. Comments 11.1 Temperature effects on thermal conductivity 11.1.1 This standard is designed for measurements betwee ...
Submission 1
... The ‘landscape’ idea was generally interpreted as a horizontal array, but the emergence of the atrium as a feature of office design opened up the vertical dimension. With daylight from above and planting below, atria provide a protected version of nature for office workers to look onto or walk thro ...
... The ‘landscape’ idea was generally interpreted as a horizontal array, but the emergence of the atrium as a feature of office design opened up the vertical dimension. With daylight from above and planting below, atria provide a protected version of nature for office workers to look onto or walk thro ...
Round LED Module Thermal Management
... Ts meas is the measured LED temperature at the location in Figure 4 (⁰C) Ta avg spec is the expected average system ambient temperature (⁰C) Ta meas is the measured system ambient temperature (⁰C) The testing environment of the LED module and cooling system should simulate the application environmen ...
... Ts meas is the measured LED temperature at the location in Figure 4 (⁰C) Ta avg spec is the expected average system ambient temperature (⁰C) Ta meas is the measured system ambient temperature (⁰C) The testing environment of the LED module and cooling system should simulate the application environmen ...
THERMAL LOW
... In deserts, lack of ground and plant moisture that would normally provide evaporative cooling can lead to intense, rapid solar heating of the lower layers of air. The hot air is less dense than surrounding cooler air. This, combined with the rising of the hot air, results in a low pressure area call ...
... In deserts, lack of ground and plant moisture that would normally provide evaporative cooling can lead to intense, rapid solar heating of the lower layers of air. The hot air is less dense than surrounding cooler air. This, combined with the rising of the hot air, results in a low pressure area call ...
Spiral Store A PCM Thermal - Knowledge Transfer Ireland
... Spiral Store is a new type of thermal heat storage unit which involves using Phase Change Material (PCM) around a spiral triple chamber to store and release large amounts of energy at a time. The device can be used for both hot thermal storage and cold thermal storage at an industrial scale, in part ...
... Spiral Store is a new type of thermal heat storage unit which involves using Phase Change Material (PCM) around a spiral triple chamber to store and release large amounts of energy at a time. The device can be used for both hot thermal storage and cold thermal storage at an industrial scale, in part ...