Year 9 Earthquakes and plate tectonics revision PowerPoint
... overpasses (Motor way bridges and fly overs) For example, a section of the Antelope Valley Freeway collapsed onto the Golden State Freeway south of Newhall. Also, a section of the Santa Monica Freeway in West Los Angeles collapsed. ...
... overpasses (Motor way bridges and fly overs) For example, a section of the Antelope Valley Freeway collapsed onto the Golden State Freeway south of Newhall. Also, a section of the Santa Monica Freeway in West Los Angeles collapsed. ...
Earth Science - Fayette County Schools
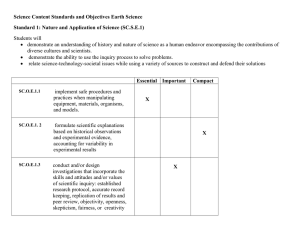
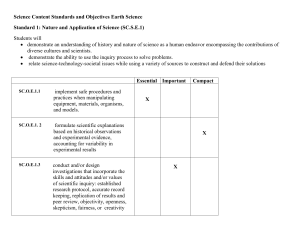
... SC.O.E.2.26 compare the relationship between earth processes and natural disasters with their impact on humans. SC.O.E.2.27 evaluate the potential conflicts, which arise between societal reliance on natural resources and the need to act as responsible stewards to reclaim the earth, including disposa ...
... SC.O.E.2.26 compare the relationship between earth processes and natural disasters with their impact on humans. SC.O.E.2.27 evaluate the potential conflicts, which arise between societal reliance on natural resources and the need to act as responsible stewards to reclaim the earth, including disposa ...
Chapter 3 Kūkulu-o-ka-honua Pillars of Earth Volcanism Among the
... a plate. The resulting magma (molten rock) can rise into the crust and generate active volcanism; such a point on Earth‟s surface is known as a hotspot. Hawai„i is the site of such a plume, a quasi-stationary hotspot that brings magma to the surface. It is this hotspot volcanism that produced Mauna ...
... a plate. The resulting magma (molten rock) can rise into the crust and generate active volcanism; such a point on Earth‟s surface is known as a hotspot. Hawai„i is the site of such a plume, a quasi-stationary hotspot that brings magma to the surface. It is this hotspot volcanism that produced Mauna ...
chapter 9 - Geoclassroom Home
... an ecologist at the University of California at Santa Barabara, calculated how much energy it costs to generate a new species. The answer is a staggering 1023 joules, more energy released by all the fossil fuels burned on the Earth in one year. Allen investigated foraminifera, one-celled plankton, a ...
... an ecologist at the University of California at Santa Barabara, calculated how much energy it costs to generate a new species. The answer is a staggering 1023 joules, more energy released by all the fossil fuels burned on the Earth in one year. Allen investigated foraminifera, one-celled plankton, a ...
Earth Science - Grant County Schools
... 1. How does information stored in rocks determine the order of Earth’s geologic events? 2. How do scientists determine relative and absolute age of rocks? 3. How do fossils form? ...
... 1. How does information stored in rocks determine the order of Earth’s geologic events? 2. How do scientists determine relative and absolute age of rocks? 3. How do fossils form? ...
LECTURE 19
... the Skiddaw Aureole, UK • The aureole around the Skiddaw granite was sub-divided into three zones, principally on the basis of textures: ...
... the Skiddaw Aureole, UK • The aureole around the Skiddaw granite was sub-divided into three zones, principally on the basis of textures: ...
lecture_2_earth_structure
... Primordial heat is the heat lost by the Earth as it continues to cool from its original formation, and this is in contrast to its still actively-produced radiogenic heat. The Earth core's heat flow—heat leaving the core and flowing into the overlying mantle—is thought to be due to primordial heat, a ...
... Primordial heat is the heat lost by the Earth as it continues to cool from its original formation, and this is in contrast to its still actively-produced radiogenic heat. The Earth core's heat flow—heat leaving the core and flowing into the overlying mantle—is thought to be due to primordial heat, a ...
Essentials of Geology, 10e (Lutgens/Tarbuck/Tasa)
... Critical thinking and discussion questions. Use complete sentences, correct spelling, and the information presented in Chapter 1 to answer the questions below. 66) Aside from near oceanic trenches, most earthquakes originate at depths of 100 kilometers or less. Considering the physical properties of ...
... Critical thinking and discussion questions. Use complete sentences, correct spelling, and the information presented in Chapter 1 to answer the questions below. 66) Aside from near oceanic trenches, most earthquakes originate at depths of 100 kilometers or less. Considering the physical properties of ...
here
... lavas that had been erupted along mid-ocean ridges. Symmetric patterns (“stripes”) on either side of spreading center (mid-ocean ridge) indicated that the seafloor was moving in opposing directions, away from the central ridge axis and acting as giant “tape recorder” for magnetic reversals. Chan ...
... lavas that had been erupted along mid-ocean ridges. Symmetric patterns (“stripes”) on either side of spreading center (mid-ocean ridge) indicated that the seafloor was moving in opposing directions, away from the central ridge axis and acting as giant “tape recorder” for magnetic reversals. Chan ...
a) normal fault - cloudfront.net
... In this activity, you will build a model of the earth’s crust. Using this model, you can demonstrate the action of the three types of faults we have discussed. A FAULT is a crack within the earth’s crust. A fault should not be confused with a BOUNDARY, which is the edge of an entire tectonic plate. ...
... In this activity, you will build a model of the earth’s crust. Using this model, you can demonstrate the action of the three types of faults we have discussed. A FAULT is a crack within the earth’s crust. A fault should not be confused with a BOUNDARY, which is the edge of an entire tectonic plate. ...
General geohydrology of the Pajarito Plateau
... The upper surface of the main aquifer rises westward from the Rio Grande through the Tesuque into the lower part of the Puye Formation beneath the central and western parts of the plateau (Fig. 2). The water in the aquifer moves from the major recharge area in the Valles Caldera eastward toward the ...
... The upper surface of the main aquifer rises westward from the Rio Grande through the Tesuque into the lower part of the Puye Formation beneath the central and western parts of the plateau (Fig. 2). The water in the aquifer moves from the major recharge area in the Valles Caldera eastward toward the ...
Essential Question: How did the theory of Plate Tectonics evolve
... like (puzzle, candy) pieces. He also knew that similar (geographic, facial) features and fossils could be found on different sides of the (ocean, face). His (observations, family) led him to conclude that millions of years ago, the continents had all been attached as one large continent called Panga ...
... like (puzzle, candy) pieces. He also knew that similar (geographic, facial) features and fossils could be found on different sides of the (ocean, face). His (observations, family) led him to conclude that millions of years ago, the continents had all been attached as one large continent called Panga ...
Chapter 11 Part 3
... 2) I can relate earthquake magnitude to the relative energy released and to the number of earthquakes that occur. 3) I can use seismographs to locate and earthquake and estimate its magnitude. ...
... 2) I can relate earthquake magnitude to the relative energy released and to the number of earthquakes that occur. 3) I can use seismographs to locate and earthquake and estimate its magnitude. ...
Ch 7 - 3 Plate Tectonic
... 1. Earth is an active planet with a hot interior. The heat inside Earth causes convention that powers the movement of Earth’s plates. 2. The interaction of plates produces forces that build mountains, create ocean basins, and cause volcanoes. ...
... 1. Earth is an active planet with a hot interior. The heat inside Earth causes convention that powers the movement of Earth’s plates. 2. The interaction of plates produces forces that build mountains, create ocean basins, and cause volcanoes. ...
7.3
... The circulation of material caused by differences in temperature and density is called convection. For example, the upstairs floors of homes are often warmer because hot air rises. Hot air is less dense than cold air. As the cold air sinks, the hot air rises. Convection in the mantle is related to p ...
... The circulation of material caused by differences in temperature and density is called convection. For example, the upstairs floors of homes are often warmer because hot air rises. Hot air is less dense than cold air. As the cold air sinks, the hot air rises. Convection in the mantle is related to p ...
supercontinent cycle
... plates. When continents move, the flow of air and moisture around the globe changes and causes climates to change. • Geologic evidence shows that ice once covered most of Earth’s continental surfaces. As continents began to drift around the globe, however, global temperatures changed and much of the ...
... plates. When continents move, the flow of air and moisture around the globe changes and causes climates to change. • Geologic evidence shows that ice once covered most of Earth’s continental surfaces. As continents began to drift around the globe, however, global temperatures changed and much of the ...
Cinder cones
... • Defined as the transfer of magma from one area of the earth to another, due to a change in the pressure of the earth. It is the drop in pressure that allows the semi-liquid molten rock to become liquid and rise to the top. ...
... • Defined as the transfer of magma from one area of the earth to another, due to a change in the pressure of the earth. It is the drop in pressure that allows the semi-liquid molten rock to become liquid and rise to the top. ...
Ch 7-3 Theory Plate Tectonics
... 1. Earth is an active planet with a hot interior. The heat inside Earth causes convention that powers the movement of Earth’s plates. 2. The interaction of plates produces forces that build mountains, create ocean basins, and cause volcanoes. ...
... 1. Earth is an active planet with a hot interior. The heat inside Earth causes convention that powers the movement of Earth’s plates. 2. The interaction of plates produces forces that build mountains, create ocean basins, and cause volcanoes. ...
chapter 12 – earthquakes
... 2. By studying the speed and direction of seismic waves, scientists have been able to locate the layers of the Earth. 3. Seismic waves also show shadow zones which are location on Earth’s surface where no body waves can be detected since the Earth’s interior are not uniform in rigidity. ...
... 2. By studying the speed and direction of seismic waves, scientists have been able to locate the layers of the Earth. 3. Seismic waves also show shadow zones which are location on Earth’s surface where no body waves can be detected since the Earth’s interior are not uniform in rigidity. ...
Photo Album - Imperial Valley College
... same time (unlike a pure substance such as ice). This is called partial melting. Minerals with the highest silica content melt at the lowest temperatures (so magma is always richer in silica than the rock that produced it). Granite contains more silica than basalt and melts at a lower temp. So, basa ...
... same time (unlike a pure substance such as ice). This is called partial melting. Minerals with the highest silica content melt at the lowest temperatures (so magma is always richer in silica than the rock that produced it). Granite contains more silica than basalt and melts at a lower temp. So, basa ...
FOSS Earth History, Second Edition Glossary abrasion
... theory of plate tectonics the idea that the Earth’s lithospheric plates have moved and changed over geological time based on the pattern that volcanoes and earthquakes make at Earth’s surface (IG) transform a fault where two plates slide past each other (SRB) transform boundary a boundary where pla ...
... theory of plate tectonics the idea that the Earth’s lithospheric plates have moved and changed over geological time based on the pattern that volcanoes and earthquakes make at Earth’s surface (IG) transform a fault where two plates slide past each other (SRB) transform boundary a boundary where pla ...
P-2, Advanced Proficiency, 6th Grade, Earth Science
... Compare and contrast conduction and convection. Identify the layers of the Earth on a diagram and explain the relationship among the layers. Explain how heat from Earth’s interior reaches the surface primarily through convection. Explain how lithospheric plates the size of continents and oceans, mov ...
... Compare and contrast conduction and convection. Identify the layers of the Earth on a diagram and explain the relationship among the layers. Explain how heat from Earth’s interior reaches the surface primarily through convection. Explain how lithospheric plates the size of continents and oceans, mov ...
Geology

Geology (from the Greek γῆ, gē, i.e. ""earth"" and -λoγία, -logia, i.e. ""study of, discourse"") is an earth science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change. Geology can also refer generally to the study of the solid features of any celestial body (such as the geology of the Moon or Mars).Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth by providing the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates. Geology is important for mineral and hydrocarbon exploration and exploitation, evaluating water resources, understanding of natural hazards, the remediation of environmental problems, and for providing insights into past climate change. Geology also plays a role in geotechnical engineering and is a major academic discipline.