worksheets extreme earth
... - Saucepan, saucepan, 1,2,3 opacity, opacity, disappear. - If the saucepan is not opaque, what does it look like now? - Now the saucepan is transparent. - We can see the water inside. - What is the water doing? - The water is ______ up and down, ___ and _____, ____ and ______. - The movement is call ...
... - Saucepan, saucepan, 1,2,3 opacity, opacity, disappear. - If the saucepan is not opaque, what does it look like now? - Now the saucepan is transparent. - We can see the water inside. - What is the water doing? - The water is ______ up and down, ___ and _____, ____ and ______. - The movement is call ...
seismic waves
... • 2 layers—a solid inner core; liquid outer core. – The inner core is solid due to great pressure. – The outer core is under less pressure and flows in a liquid phase. Earth’s magnetic field generating flowing molten core. ...
... • 2 layers—a solid inner core; liquid outer core. – The inner core is solid due to great pressure. – The outer core is under less pressure and flows in a liquid phase. Earth’s magnetic field generating flowing molten core. ...
Chapter 5. The Eclogite Engine
... Bermuda, Jan Mayen, Rio Grande rise and Walvis ridge may be examples; the isotopic signatures of these plateaus are expected to reflect lower crustal components. ...
... Bermuda, Jan Mayen, Rio Grande rise and Walvis ridge may be examples; the isotopic signatures of these plateaus are expected to reflect lower crustal components. ...
Ch 14 OIB mod 7
... • N-MORBs involve shallow melting of passively rising upper mantle → a significant volume of depleted upper mantle (DM which has lost lithophile elements to melts which ended in late fractionation rocks, and which has lost He). • OIBs seem to originate from deeper levels. Major- and trace-element da ...
... • N-MORBs involve shallow melting of passively rising upper mantle → a significant volume of depleted upper mantle (DM which has lost lithophile elements to melts which ended in late fractionation rocks, and which has lost He). • OIBs seem to originate from deeper levels. Major- and trace-element da ...
The strength of faults in the crust in the western
... where the temperature is high enough to achieve substantial sliprates. The depth of the transition between the two for each fault element (brittle–ductile transition depth) is calculated by assuming that the rheology resulting in the lowest shear stress will prevail. The only boundary conditions tha ...
... where the temperature is high enough to achieve substantial sliprates. The depth of the transition between the two for each fault element (brittle–ductile transition depth) is calculated by assuming that the rheology resulting in the lowest shear stress will prevail. The only boundary conditions tha ...
Pulsed channel flow in Bhutan
... 35–45 km. The location of initial melting was down-dip and over 200 km to the north of Bhutan. Melt was produced and injected into ductilely deforming metamorphic rocks as they were extruded towards the south between the Main Central Thrust (MCT) and the South Tibetan Detachment zones. The lateral f ...
... 35–45 km. The location of initial melting was down-dip and over 200 km to the north of Bhutan. Melt was produced and injected into ductilely deforming metamorphic rocks as they were extruded towards the south between the Main Central Thrust (MCT) and the South Tibetan Detachment zones. The lateral f ...
Morganfest brochure
... spreading ocean floor. This insight was fundamental to Meteor Seamount. Today, Jason Morgan, with other the revolutionary theory then developing, and sharing hotspot theorists, is not only prepared to suggest its that office with Fred Vine drew Morgan into the subject general origin but to indicate ...
... spreading ocean floor. This insight was fundamental to Meteor Seamount. Today, Jason Morgan, with other the revolutionary theory then developing, and sharing hotspot theorists, is not only prepared to suggest its that office with Fred Vine drew Morgan into the subject general origin but to indicate ...
ESS 8 - Earthquakes - UW Courses Web Server
... Tectonic plates move about 40 mm/year This is 40 km per million years The mantle is moving at similar velocities It takes about 100 million years for the mantle to overturn Outer core is liquid, and is also convecting, but much faster creating the Earth’s magnetic field ...
... Tectonic plates move about 40 mm/year This is 40 km per million years The mantle is moving at similar velocities It takes about 100 million years for the mantle to overturn Outer core is liquid, and is also convecting, but much faster creating the Earth’s magnetic field ...
Living Things - Mountain View Middle School
... 6.1.a Students know evidence of plate tectonics is derived from the fit of the continents; the location of earthquakes, volcanoes, and mid-ocean ridges; and the distribution of fossils, rock types and ancient climatic zones. ...
... 6.1.a Students know evidence of plate tectonics is derived from the fit of the continents; the location of earthquakes, volcanoes, and mid-ocean ridges; and the distribution of fossils, rock types and ancient climatic zones. ...
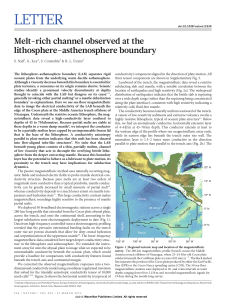
Melt-rich channel observed at the lithosphere
... the colder temperatures above. We infer that this freezing front forms a permeability barrier that traps buoyant melt beneath, rather than allowing it to percolate to shallower depths. This barrier is further reinforced by the higher viscosity of the uppermost mantle above; this higher viscosity occ ...
... the colder temperatures above. We infer that this freezing front forms a permeability barrier that traps buoyant melt beneath, rather than allowing it to percolate to shallower depths. This barrier is further reinforced by the higher viscosity of the uppermost mantle above; this higher viscosity occ ...
The cold and relatively dry nature of mantle forearcs in subduction
... The cold and relatively dry nature of mantle forearcs in subduction zones G. A. Abers1*, P. E. van Keken2 and B. R. Hacker3 Some of Earth’s coldest mantle is found in subduction zones at the tip of the mantle wedge that lies between the subducting and overriding plates. This forearc mantle is isolat ...
... The cold and relatively dry nature of mantle forearcs in subduction zones G. A. Abers1*, P. E. van Keken2 and B. R. Hacker3 Some of Earth’s coldest mantle is found in subduction zones at the tip of the mantle wedge that lies between the subducting and overriding plates. This forearc mantle is isolat ...
Author`s personal copy - Laboratoire de Planétologie et
... magmatic reservoir. Alkaline bimodal magmatism is typically found in extensional tectonic settings such as continental rift zones. In the present case, the intrusions are aligned along the Zeballos Fault Zone, which is interpreted as a recent extensional zone (Lagabrielle et al., 2004, 2007; Scalabr ...
... magmatic reservoir. Alkaline bimodal magmatism is typically found in extensional tectonic settings such as continental rift zones. In the present case, the intrusions are aligned along the Zeballos Fault Zone, which is interpreted as a recent extensional zone (Lagabrielle et al., 2004, 2007; Scalabr ...
PLATE TECTONICS
... tremendous heat found in the Earth’s interior. This heat causes the rocks in the mantle to melt and become molten rock called magma. When magma is heated, it expands, rises and generates convection currents which push the plates away from each other. When it cools, the magma sinks and brings the ...
... tremendous heat found in the Earth’s interior. This heat causes the rocks in the mantle to melt and become molten rock called magma. When magma is heated, it expands, rises and generates convection currents which push the plates away from each other. When it cools, the magma sinks and brings the ...
Earthquake Depth-Energy Release: Thermomechanical Implications
... glacial-isostatic rebound as evidence in favor of their view. This stance is necessary, only because the ...
... glacial-isostatic rebound as evidence in favor of their view. This stance is necessary, only because the ...
Abstract_Midcontinen..
... look at the role of faults in the release of stress accumulated by the relative motion of tectonic plates. The stage will then be set for contrasting these conventional interplate earthquakes with those that occur within the stable continent, where tectonic loading is instead accommodated by a compl ...
... look at the role of faults in the release of stress accumulated by the relative motion of tectonic plates. The stage will then be set for contrasting these conventional interplate earthquakes with those that occur within the stable continent, where tectonic loading is instead accommodated by a compl ...
Volcanic and sedimentary stratigraphy of the Rio Grande gorge and
... Manley (1979) and Baldridge and others (1980) have published single K—Ar dates of 2.8 m.y. and 4.6 m.y., respectively, on stratigraphically young Servilleta flow units. Baldridge and others (1980) have criticized the Ozima and others (1967) chronology on two counts. The lack of a mass discrimination ...
... Manley (1979) and Baldridge and others (1980) have published single K—Ar dates of 2.8 m.y. and 4.6 m.y., respectively, on stratigraphically young Servilleta flow units. Baldridge and others (1980) have criticized the Ozima and others (1967) chronology on two counts. The lack of a mass discrimination ...
Dismantling the Deep Earth: Geochemical
... ratios (e.g., Nb/U) are little changed between solid and melt. -Lavas erupted at hotspots reveal significant isotopic and trace element heterogeneity. Therefore: the solid mantle sources of these lavas are heterogeneous. http://cache.eb.com ...
... ratios (e.g., Nb/U) are little changed between solid and melt. -Lavas erupted at hotspots reveal significant isotopic and trace element heterogeneity. Therefore: the solid mantle sources of these lavas are heterogeneous. http://cache.eb.com ...
3-D crustal structure of the extensional Granada Basin in the
... within the upper part of the crust, large-scale fracturing may have an analogous effect. In deeper portions of the crust and in the upper mantle, however, it is likely that fractures and microcracks are no longer present because of the high confining pressures and metamorphic recrystallization. In s ...
... within the upper part of the crust, large-scale fracturing may have an analogous effect. In deeper portions of the crust and in the upper mantle, however, it is likely that fractures and microcracks are no longer present because of the high confining pressures and metamorphic recrystallization. In s ...
Decoupling along plate boundaries: Key variable controlling the
... increases, or the effect of shear heating at plate contacts diminishes as shortening velocities decrease (Faccenda et al., 2008). In such cases, an increase of coupling among the orogen and the foreland plates is expected to occur, leading to the change of the dominant deformation mechanism through ...
... increases, or the effect of shear heating at plate contacts diminishes as shortening velocities decrease (Faccenda et al., 2008). In such cases, an increase of coupling among the orogen and the foreland plates is expected to occur, leading to the change of the dominant deformation mechanism through ...
Chapter 9
... Geologist study the bending or refraction and reflection of P‐ and S‐waves to help understand Earth's interior. ...
... Geologist study the bending or refraction and reflection of P‐ and S‐waves to help understand Earth's interior. ...
Geology

Geology (from the Greek γῆ, gē, i.e. ""earth"" and -λoγία, -logia, i.e. ""study of, discourse"") is an earth science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change. Geology can also refer generally to the study of the solid features of any celestial body (such as the geology of the Moon or Mars).Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth by providing the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates. Geology is important for mineral and hydrocarbon exploration and exploitation, evaluating water resources, understanding of natural hazards, the remediation of environmental problems, and for providing insights into past climate change. Geology also plays a role in geotechnical engineering and is a major academic discipline.