Deep Origin of Hotspots— the Mantle Plume Model
... cooling of the mantle by the subduction of tectonic plates allows large variations of viscosity to exist at the base of the mantle, and hence between the plume and its surroundings (11). Deep mantle plumes may not be the cause of all hotspots. Courtillot et al. (12) argue that the main features pred ...
... cooling of the mantle by the subduction of tectonic plates allows large variations of viscosity to exist at the base of the mantle, and hence between the plume and its surroundings (11). Deep mantle plumes may not be the cause of all hotspots. Courtillot et al. (12) argue that the main features pred ...
Document
... Region, What is the Azimut of The SAF ? What can you tell about the components of GPS velocity vectors perpendicular to the Pa/NA direction ? ...
... Region, What is the Azimut of The SAF ? What can you tell about the components of GPS velocity vectors perpendicular to the Pa/NA direction ? ...
Our Haven, Planet Earth
... observe that when we are on Earth, we are walking around on a solid crust which is mainly made up of elements such as O, Fe, Mg, Si and Al forming crystalline compounds, which we call minerals and rocks. Another direct source of knowledge about the composition of our planet comes from the meteorites ...
... observe that when we are on Earth, we are walking around on a solid crust which is mainly made up of elements such as O, Fe, Mg, Si and Al forming crystalline compounds, which we call minerals and rocks. Another direct source of knowledge about the composition of our planet comes from the meteorites ...
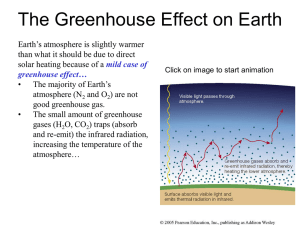
The Greenhouse Effect on Earth
... 100 years…It has risen about 1°C since 1900… • Are human activities causing global warming? • What other (non-human) factors can cause global warming? • How does global warming affect our life? Just watch the movies… ...
... 100 years…It has risen about 1°C since 1900… • Are human activities causing global warming? • What other (non-human) factors can cause global warming? • How does global warming affect our life? Just watch the movies… ...
Part I. Geo and Bio: Key relationships
... Humankind is under the permanent influence of the geological environment. Roles of some geological biotropic factors, such as volcanic explosions, strong earthquakes, and geochemical anomalies, have been well studied. Little is known about biotropic effects of the Earth’s fluid degassing, geomagneti ...
... Humankind is under the permanent influence of the geological environment. Roles of some geological biotropic factors, such as volcanic explosions, strong earthquakes, and geochemical anomalies, have been well studied. Little is known about biotropic effects of the Earth’s fluid degassing, geomagneti ...
Final Exam 345
... 4. How do surface waves compare to P waves? a. Surface waves are the slowest waves; P waves are the fastest b. P waves produce vertical and horizontal motion; surface waves produce horizontal motion only c. P waves are the most dangerous waves; surface waves are the least dangerous d. P waves cause ...
... 4. How do surface waves compare to P waves? a. Surface waves are the slowest waves; P waves are the fastest b. P waves produce vertical and horizontal motion; surface waves produce horizontal motion only c. P waves are the most dangerous waves; surface waves are the least dangerous d. P waves cause ...
AICE Env Day 5 Evidence of Plate Tectonics Stations
... formed before, pushing it aside. This process, called sea-floor spreading, continually adds new material to the ocean floor. Scientists have found strange rocks shaped like pillows in the central valley of mid-ocean ridges. Such rocks can form only if molten material hardens quickly after erupting u ...
... formed before, pushing it aside. This process, called sea-floor spreading, continually adds new material to the ocean floor. Scientists have found strange rocks shaped like pillows in the central valley of mid-ocean ridges. Such rocks can form only if molten material hardens quickly after erupting u ...
No Slide Title
... • What features in the rock record can geologists use to recognize ancient rifting? ...
... • What features in the rock record can geologists use to recognize ancient rifting? ...
“Volcanoes”
... 2. Magma is forced upward because it is less dense than the rock layers around it.and other gases reach the surface it 3. When magma 3. When magma and other turns to lava or volcanic ash. gases reach the surface it turns to lava or volcanic ash. ...
... 2. Magma is forced upward because it is less dense than the rock layers around it.and other gases reach the surface it 3. When magma 3. When magma and other turns to lava or volcanic ash. gases reach the surface it turns to lava or volcanic ash. ...
File - Geological Engineering
... Alternating normal faults lead to a characteristic pattern called a Horst and Graben system. An area under tension will often have Multiple mountain ranges as a result. ...
... Alternating normal faults lead to a characteristic pattern called a Horst and Graben system. An area under tension will often have Multiple mountain ranges as a result. ...
Test Bank Questions 6th Edition
... become more dense. As its density increases, it sinks, and returns to the original level where it will eventually become heated again. ...
... become more dense. As its density increases, it sinks, and returns to the original level where it will eventually become heated again. ...
Volcanism - MsMonroesScience
... At divergent plate boundaries tectonic plates move apart and ____________________________ ___________________________________________________________ At ocean ridges, _______________________________________________________ and is called pillow lava. Unlike the explosive volcanoes that occur at ...
... At divergent plate boundaries tectonic plates move apart and ____________________________ ___________________________________________________________ At ocean ridges, _______________________________________________________ and is called pillow lava. Unlike the explosive volcanoes that occur at ...
Earth Geodynamic Hypotheses Updated
... key, and the tectonic revolution was underway. At the 1966 Geological Society of America meeting in San Francisco, Lynn Sykes proved Wilson’s hypothesis by studying earthquake motion (Sykes, 1966). Even though the shallow and deep earthquakes were known to be decoupled in every case, Benioff’s great ...
... key, and the tectonic revolution was underway. At the 1966 Geological Society of America meeting in San Francisco, Lynn Sykes proved Wilson’s hypothesis by studying earthquake motion (Sykes, 1966). Even though the shallow and deep earthquakes were known to be decoupled in every case, Benioff’s great ...
HANDOUTAWITHANSWERS
... When pressed hard enough, pressure and tension build up and eventually release a burst of energy and motion causing some of the shell to break apart. Transform boundary or transform fault margin. Earthquake. San Andreas Fault in California. 6. Why is using a hard-boiled egg to model the motion of th ...
... When pressed hard enough, pressure and tension build up and eventually release a burst of energy and motion causing some of the shell to break apart. Transform boundary or transform fault margin. Earthquake. San Andreas Fault in California. 6. Why is using a hard-boiled egg to model the motion of th ...
9.5 Geology of Venus
... The only surface data we have comes from Sovietera (1970/80s) Venera missions, which each survived ~ 1 hr on the surface. ...
... The only surface data we have comes from Sovietera (1970/80s) Venera missions, which each survived ~ 1 hr on the surface. ...
Earthquakes - Rosierulescience
... of the United States, why do these earthquakes take place? • Geologists are beginning to understand the answer. The New Madrid Fault Zone is part of an ancient plate boundary. • In this area, the North American Plate tried to form a divergent plate boundary about 500 million years ago. The splitting ...
... of the United States, why do these earthquakes take place? • Geologists are beginning to understand the answer. The New Madrid Fault Zone is part of an ancient plate boundary. • In this area, the North American Plate tried to form a divergent plate boundary about 500 million years ago. The splitting ...
Malakhova_081211 - Geological Society of America
... be elaborated and unified, synonyms eliminated, and fundamental tectonic concepts, such as “epeirogeny”, “orogeny”, “stiff masses”, “platforms”, “barriers”, “deep folding”, and “alpine tectonics”, defined. (b) Compilation of a history and description of all tectonic theories, with detailed biblioghr ...
... be elaborated and unified, synonyms eliminated, and fundamental tectonic concepts, such as “epeirogeny”, “orogeny”, “stiff masses”, “platforms”, “barriers”, “deep folding”, and “alpine tectonics”, defined. (b) Compilation of a history and description of all tectonic theories, with detailed biblioghr ...
Is the Empirical Evidence for Plate Tectonics Enough? Quote: Plate
... Although solid, the asthenosphere has relatively low viscosity and shear strength and can flow like a liquid on geological time scales. The deeper mantle below the asthenosphere is more rigid again. This is, however, not due to cooler temperatures but due to high pressure. The lithosphere is broken ...
... Although solid, the asthenosphere has relatively low viscosity and shear strength and can flow like a liquid on geological time scales. The deeper mantle below the asthenosphere is more rigid again. This is, however, not due to cooler temperatures but due to high pressure. The lithosphere is broken ...
Subduction-zone metamorphism, calc-alkaline - U
... exposed at the Earth's surface. HP–UHP belts worldwide consist dominantly of such low-aggregate-density lithologies. Thus, attending Pacific-type subduction of a largely sedimentary mélange, devolatilization and increased ductility cause decoupling of subducted HP materials from the sinking oceanic p ...
... exposed at the Earth's surface. HP–UHP belts worldwide consist dominantly of such low-aggregate-density lithologies. Thus, attending Pacific-type subduction of a largely sedimentary mélange, devolatilization and increased ductility cause decoupling of subducted HP materials from the sinking oceanic p ...
(volcanic) Landforms - Scoil Mhuire Geography
... • Subduction occurs where the heavier plate is pulled down under the lighter plate due to gravity and is melted deep in the mantle • This produces an explosive viscous (thick) lava; eruptions are violent due to intense build up of pressure • Dome volcanoes are steeply sloping cones with convex sides ...
... • Subduction occurs where the heavier plate is pulled down under the lighter plate due to gravity and is melted deep in the mantle • This produces an explosive viscous (thick) lava; eruptions are violent due to intense build up of pressure • Dome volcanoes are steeply sloping cones with convex sides ...
Geology

Geology (from the Greek γῆ, gē, i.e. ""earth"" and -λoγία, -logia, i.e. ""study of, discourse"") is an earth science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change. Geology can also refer generally to the study of the solid features of any celestial body (such as the geology of the Moon or Mars).Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth by providing the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates. Geology is important for mineral and hydrocarbon exploration and exploitation, evaluating water resources, understanding of natural hazards, the remediation of environmental problems, and for providing insights into past climate change. Geology also plays a role in geotechnical engineering and is a major academic discipline.