Wind Opacity Issues
... edge is that of (a single ion state of) nitrogen. This seems pretty crude. And it makes me wonder what elements are included in the calculation of the overall opacity and how reliable the smooth portions of the curves are. As you look at the figures in this document, keep in mind that some plot cros ...
... edge is that of (a single ion state of) nitrogen. This seems pretty crude. And it makes me wonder what elements are included in the calculation of the overall opacity and how reliable the smooth portions of the curves are. As you look at the figures in this document, keep in mind that some plot cros ...
Excited states of 136−138Sb from β decay
... this nucleus5) . A consequence of this is that levels with πs1/2 and πd3/2 components predicted at energies above 2 MeV in 135 Sb may be found at energies below 500 keV in 137 Sb. In order to investigate the structure of the nuclei ...
... this nucleus5) . A consequence of this is that levels with πs1/2 and πd3/2 components predicted at energies above 2 MeV in 135 Sb may be found at energies below 500 keV in 137 Sb. In order to investigate the structure of the nuclei ...
Low-Res Version - Chandra X
... need detectors that are especially designed to see those other wavelengths, such as the instruments on Chandra. Sometimes images taken by telescopes that look at the "invisible" wavelengths are called "false color images". That is because the colors we use in them are not "real" but are chosen to br ...
... need detectors that are especially designed to see those other wavelengths, such as the instruments on Chandra. Sometimes images taken by telescopes that look at the "invisible" wavelengths are called "false color images". That is because the colors we use in them are not "real" but are chosen to br ...
X-ray polarimetry in astrophysics
... Accretion physics: magnetic NS In X-ray pulsators the plasma from a companion accretes on the magnetic poles of a neutron star following the magnetic (B ~1012 gauss) field lines. Cyclotron lines of different orders are produced by the transition between the Landau levels. Scattering in such an accr ...
... Accretion physics: magnetic NS In X-ray pulsators the plasma from a companion accretes on the magnetic poles of a neutron star following the magnetic (B ~1012 gauss) field lines. Cyclotron lines of different orders are produced by the transition between the Landau levels. Scattering in such an accr ...
Back ground information
... radiation is next on the spectrum and has more energy than visible light. Often called UV radiation, this type of energy emitted from the Sun is what produces sunburns. X-rays and then gamma rays are the last two regions on the electromagnetic spectrum. Xray radiation is so powerful that it can be u ...
... radiation is next on the spectrum and has more energy than visible light. Often called UV radiation, this type of energy emitted from the Sun is what produces sunburns. X-rays and then gamma rays are the last two regions on the electromagnetic spectrum. Xray radiation is so powerful that it can be u ...
TDE in the XMM-Newton slew survey
... Arcavi et al. 2014; French et al. 2016 - E+A galaxies disproportionately represented in optical TDE samples ...
... Arcavi et al. 2014; French et al. 2016 - E+A galaxies disproportionately represented in optical TDE samples ...
The Satellites of Uranus and Neptune: A New Astrometrie Programme
... It appears that Klemola 44 is such a case. Maccacaro et al. (1977) already noted that the velocity dispersion ~ V was too low to fit the Solinger and Tucker relationship. But their value of ~ V was based on measurements of only 8 galaxies in the cluster. More measurements were needed to be certain o ...
... It appears that Klemola 44 is such a case. Maccacaro et al. (1977) already noted that the velocity dispersion ~ V was too low to fit the Solinger and Tucker relationship. But their value of ~ V was based on measurements of only 8 galaxies in the cluster. More measurements were needed to be certain o ...
Name
... could measure infrared light and not with a satellite that could measure visible light? A) no satellites that could measure visible light are currently in space B) the particles in the rings are so cold that they are brighter in the infrared than in the visible C) visible light can’t penetrate the E ...
... could measure infrared light and not with a satellite that could measure visible light? A) no satellites that could measure visible light are currently in space B) the particles in the rings are so cold that they are brighter in the infrared than in the visible C) visible light can’t penetrate the E ...
Lecture 18, Gravitational Waves, Future Missions and
... - IRIS: near-infrared IFU spectrometer with imaging capability - IRMS: near-infrared spectrometer with imaging capability The near-IR instruments will use the AO system, and the plan is to get diffraction limited resolution (~10 milliarcsecs). Science (some): first galaxies, epoch of reionization, s ...
... - IRIS: near-infrared IFU spectrometer with imaging capability - IRMS: near-infrared spectrometer with imaging capability The near-IR instruments will use the AO system, and the plan is to get diffraction limited resolution (~10 milliarcsecs). Science (some): first galaxies, epoch of reionization, s ...
Name
... could measure infrared light and not with a satellite that could measure visible light? A) no satellites that could measure visible light are currently in space B) the particles in the rings are so cold that they are brighter in the infrared than in the visible C) visible light can’t penetrate the E ...
... could measure infrared light and not with a satellite that could measure visible light? A) no satellites that could measure visible light are currently in space B) the particles in the rings are so cold that they are brighter in the infrared than in the visible C) visible light can’t penetrate the E ...
LIGHT QUESTIONS and ANSWERS
... Photographs can be made such that they show individual photons striking the film/detector. Interference patterns can be observed being built up photon by photon. 20. Why won’t a very bright beam of red light impart more energy to an ejected electron than a feeble beam of violet light? A single photo ...
... Photographs can be made such that they show individual photons striking the film/detector. Interference patterns can be observed being built up photon by photon. 20. Why won’t a very bright beam of red light impart more energy to an ejected electron than a feeble beam of violet light? A single photo ...
Name
... could measure infrared light and not with a satellite that could measure visible light? A) no satellites that could measure visible light are currently in space B) the particles in the rings are so cold that they are brighter in the infrared than in the visible C) visible light can’t penetrate the E ...
... could measure infrared light and not with a satellite that could measure visible light? A) no satellites that could measure visible light are currently in space B) the particles in the rings are so cold that they are brighter in the infrared than in the visible C) visible light can’t penetrate the E ...
Observation of anticorrelation between scintillation and ionization for
... tuations by combining ionization and scintillation signals. Since recombination also produces scintillation photons, fluctuations of the combined signal should be reduced. This was originally suggested by Ypsilantis et al. many years ago.15 The simultaneous detection of scintillation and ionization ...
... tuations by combining ionization and scintillation signals. Since recombination also produces scintillation photons, fluctuations of the combined signal should be reduced. This was originally suggested by Ypsilantis et al. many years ago.15 The simultaneous detection of scintillation and ionization ...
AMUSE-Virgo on the survival of super-massive black holes
... Duty cycle of super-massive black hole (highly sub-Eddington) activity ...
... Duty cycle of super-massive black hole (highly sub-Eddington) activity ...
The Milky Way at Different Wavelengths
... lower energies especially, the interstellar medium strongly absorbs X-rays, and cold clouds of interstellar gas are seen as shadows against background X-ray emission. Color variations indicate variations of absorption or of the temperatures of emitting regions. The black regions indicate gaps in the ...
... lower energies especially, the interstellar medium strongly absorbs X-rays, and cold clouds of interstellar gas are seen as shadows against background X-ray emission. Color variations indicate variations of absorption or of the temperatures of emitting regions. The black regions indicate gaps in the ...
Non-thermal hard X-ray emission from stellar coronae
... Independent analyses of a few flares observed with RHESSI and Coronal-F yield consistent results within uncertainties ...
... Independent analyses of a few flares observed with RHESSI and Coronal-F yield consistent results within uncertainties ...
Chandra Automated Point Source Processing
... Figure 2 shows the 90% encircled energy radius (EE) at 1.49 keV vs. off-axis angle (θ) from the the nominal aimpoint for sources combined from throughout the Chandra mission. The ACIS-I CCD is a 4-chip array, arranged 2 X 2, for a total field-of-view of 16.9’ X 16.9’. Highly piled-up (bright) source ...
... Figure 2 shows the 90% encircled energy radius (EE) at 1.49 keV vs. off-axis angle (θ) from the the nominal aimpoint for sources combined from throughout the Chandra mission. The ACIS-I CCD is a 4-chip array, arranged 2 X 2, for a total field-of-view of 16.9’ X 16.9’. Highly piled-up (bright) source ...
Astronomical observations
... • correction of interpixel nonuniformities (division by a uniform field exposure: flat field) • detection of cosmic ray impacts + `cosmetic ´correction (scientifically, the information is lost in these pixels → σ = ∞) • subtraction of sky background • computation of an image containing the intensity ...
... • correction of interpixel nonuniformities (division by a uniform field exposure: flat field) • detection of cosmic ray impacts + `cosmetic ´correction (scientifically, the information is lost in these pixels → σ = ∞) • subtraction of sky background • computation of an image containing the intensity ...
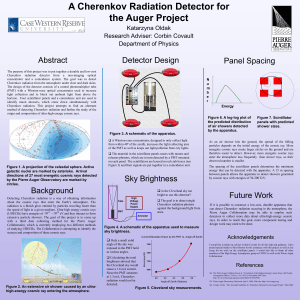
Miriam Israelowitz1 and Dr. David L. Wilson2 1Department
... Cherenkov radiation detector from a non-imaging optical concentrator and a coincidence system. The goal was to detect Cherenkov radiation from the atmosphere under clear and dark skies. The design of the detector consists of a central photomultiplier tube (PMT) with a Winston-cone optical concentrat ...
... Cherenkov radiation detector from a non-imaging optical concentrator and a coincidence system. The goal was to detect Cherenkov radiation from the atmosphere under clear and dark skies. The design of the detector consists of a central photomultiplier tube (PMT) with a Winston-cone optical concentrat ...
Global Telescope Network - XMM-Newton
... By compressing clouds of gas and dust to initiate the process of forming new stars ...
... By compressing clouds of gas and dust to initiate the process of forming new stars ...
Homework Assignment 7 — Solutions
... nλ dλ = dλ. exp(hc/λkT ) − 1 (b). The total number density of photons can be obtained by integrating nλ dλ over all wavelengths, Z ∞ Z ∞ 8π/λ4 n= nλ dλ = dλ. exp(hc/λkT ) − 1 ...
... nλ dλ = dλ. exp(hc/λkT ) − 1 (b). The total number density of photons can be obtained by integrating nλ dλ over all wavelengths, Z ∞ Z ∞ 8π/λ4 n= nλ dλ = dλ. exp(hc/λkT ) − 1 ...
kiosk em - Solon City Schools
... Because microwaves reflect off the inside walls of a microwave oven, they may form standing waves. Food lying at the antinodes where the vibrations are at maximum, get cooked more than food lying at the nodes, where there are no vibrations. For that reason, most microwave ovens rotate food items to ...
... Because microwaves reflect off the inside walls of a microwave oven, they may form standing waves. Food lying at the antinodes where the vibrations are at maximum, get cooked more than food lying at the nodes, where there are no vibrations. For that reason, most microwave ovens rotate food items to ...
Coronal magnetic topology and the production of solar impulsive
... Figure 4 shows the three successive solar flares recorded by the GOES soft X-ray (SXR) in 1−8 Å and the accompanied three groups of type III radio bursts observed by the Wind/WAVES radio spectrograms in the frequency range from 20 kHz to 14 MHz. Two vertical dashed lines mark the SPR times (plus 8.3 ...
... Figure 4 shows the three successive solar flares recorded by the GOES soft X-ray (SXR) in 1−8 Å and the accompanied three groups of type III radio bursts observed by the Wind/WAVES radio spectrograms in the frequency range from 20 kHz to 14 MHz. Two vertical dashed lines mark the SPR times (plus 8.3 ...
Using a distant X-ray source to detect small Transneptunian Objects
... used measurements from the satellite ROSSI X-ray Timing Explorer of the brightest X-ray object in the sky, Scorpius X-1, which is a pulsar (a neutron star). The team used 90 hours of data obtained between 1996 and 2002. Computer searches of the satellite’s data revealed 58 breaks in the X-rays which ...
... used measurements from the satellite ROSSI X-ray Timing Explorer of the brightest X-ray object in the sky, Scorpius X-1, which is a pulsar (a neutron star). The team used 90 hours of data obtained between 1996 and 2002. Computer searches of the satellite’s data revealed 58 breaks in the X-rays which ...
X-ray astronomy detector

X-ray astronomy detectors are instruments that detect X-rays for use in the study of X-ray astronomy.X-ray astronomy is an observational branch of astronomy which deals with the study of X-ray emission from celestial objects. X-radiation is absorbed by the Earth's atmosphere, so instruments to detect X-rays must be taken to high altitude by balloons, sounding rockets, and satellites. X-ray astronomy is part of space science.X-ray astronomy detectors have been designed and configured primarily for energy and occasionally for wavelength detection using a variety of techniques usually limited to the technology of the time.