Plate Tectonics - Warren County Public Schools
... rate of 4 cm per year (1.6 in./yr) *The Pacific Ocean plate moves northward at the same rate. ...
... rate of 4 cm per year (1.6 in./yr) *The Pacific Ocean plate moves northward at the same rate. ...
Plate Tectonics
... Continental Drift – Ex: Mesosaurus and Lystrosaurus (ancient freshwater reptiles) now separated by an ocean ...
... Continental Drift – Ex: Mesosaurus and Lystrosaurus (ancient freshwater reptiles) now separated by an ocean ...
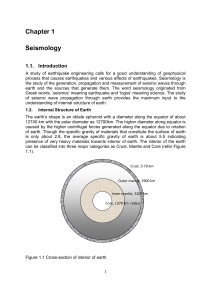
Chapter 1
... more homogeneous mass of magnesium and iron oxide and quartz. No earthquakes are recorded in the lower mantle. The specific gravity of mantle is about 5. The mantle has an average temperature of about 2200degree Celsius and the material is in a viscous semi molten state. The mantle act like fluid in ...
... more homogeneous mass of magnesium and iron oxide and quartz. No earthquakes are recorded in the lower mantle. The specific gravity of mantle is about 5. The mantle has an average temperature of about 2200degree Celsius and the material is in a viscous semi molten state. The mantle act like fluid in ...
PC_Earth_Science_Macomb_April08
... Students describe the interactions within and between Earth systems. Students will explain how both fluids (water cycle) and solids (rock cycle) move within Earth systems and how these movements form and change their environment. They will describe the relationship between physical process and human ...
... Students describe the interactions within and between Earth systems. Students will explain how both fluids (water cycle) and solids (rock cycle) move within Earth systems and how these movements form and change their environment. They will describe the relationship between physical process and human ...
Quaking, Shaking, Earth
... • Reverse faults result from compression forces that squeeze rock. • If rock breaks from forces pushing from opposite directions, rock above a reverse fault surface is forced up and over the rock below the fault surface. ...
... • Reverse faults result from compression forces that squeeze rock. • If rock breaks from forces pushing from opposite directions, rock above a reverse fault surface is forced up and over the rock below the fault surface. ...
ASSIGNMENT 1 - INTRODUCTION TO GEOLOGY
... special attention to: 1) the origin and evolution of magmas, keeping in mind the plate tectonic setting; 2) the difference between plutonic and volcanic rocks, in terms of their texture, mineral make-up and names; and 3) the various ways in which a single parent magma can produce a variety of igneou ...
... special attention to: 1) the origin and evolution of magmas, keeping in mind the plate tectonic setting; 2) the difference between plutonic and volcanic rocks, in terms of their texture, mineral make-up and names; and 3) the various ways in which a single parent magma can produce a variety of igneou ...
Plate Tectonics - Open Earth Systems
... • Wegener could not provide an explanation of exactly what made the continents move. News technology lead to findings which then lead to a new theory called plate tectonics. ...
... • Wegener could not provide an explanation of exactly what made the continents move. News technology lead to findings which then lead to a new theory called plate tectonics. ...
What is an earthquake?
... Reverse Fault • Reverse faults result from compression forces that squeeze rock. • If rock breaks from forces pushing from opposite directions, rock above a reverse fault surface is forced up and over the rock below the fault surface. • Cascadia ...
... Reverse Fault • Reverse faults result from compression forces that squeeze rock. • If rock breaks from forces pushing from opposite directions, rock above a reverse fault surface is forced up and over the rock below the fault surface. • Cascadia ...
Mechanism of Earthquake and Damages of Structures
... Structures are in general designed to resist their own weight and other loads applied on them vertically downward which are called gravity loads. They can usually carry a small quantity of snow and a few other floor loads and suspended loads as well, vertically; so even badly constructed structures ...
... Structures are in general designed to resist their own weight and other loads applied on them vertically downward which are called gravity loads. They can usually carry a small quantity of snow and a few other floor loads and suspended loads as well, vertically; so even badly constructed structures ...
Bathymetric stripping corrections to gravity gradient components Robert Tenzer and Pavel Nov´ak
... In gravimetric inverse methods for studying the lithosphere structure, the topographic, bathymetric, and additional corrections of all known anomalous mass density structures within the Earth’s crust are applied to observed gravity data in order to model the unknown (and sought) density structure or ...
... In gravimetric inverse methods for studying the lithosphere structure, the topographic, bathymetric, and additional corrections of all known anomalous mass density structures within the Earth’s crust are applied to observed gravity data in order to model the unknown (and sought) density structure or ...
Plate Tectonics
... solid rocky upper layer of the mantle. It’s about 100 km (60 miles) thick on average. Asthenosphere (Asthenes means “Weak” in Greek) below the lithosphere this layer is softer and flows very slowly. ...
... solid rocky upper layer of the mantle. It’s about 100 km (60 miles) thick on average. Asthenosphere (Asthenes means “Weak” in Greek) below the lithosphere this layer is softer and flows very slowly. ...
Structure of the Earth
... volcanoes -- as well as most earthquakes and mountains -- occur only in certain places. The Earth’s crust is split into seven pieces called plates. Most volcanoes are formed where two plates collide. Volcanoes can also be formed when two plates spread apart. This usually takes place on the ocean flo ...
... volcanoes -- as well as most earthquakes and mountains -- occur only in certain places. The Earth’s crust is split into seven pieces called plates. Most volcanoes are formed where two plates collide. Volcanoes can also be formed when two plates spread apart. This usually takes place on the ocean flo ...
Volcanism - MsMonroesScience
... ___________________________________________ erupts far from plate boundaries. Tectonic plates collide at convergent boundaries, which can form subduction zones – _________ _______________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ ...
... ___________________________________________ erupts far from plate boundaries. Tectonic plates collide at convergent boundaries, which can form subduction zones – _________ _______________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ ...
GEOL_10_final_source..
... D) It is the discordant boundary between older strata and an intrusive body of granite. (29) 2 pts. Sandstone strata and a mass of granite are observed to be in contact. Which of the following statements is correct geologically? A) The sandstone is younger if it shows evidence of contact metamorphis ...
... D) It is the discordant boundary between older strata and an intrusive body of granite. (29) 2 pts. Sandstone strata and a mass of granite are observed to be in contact. Which of the following statements is correct geologically? A) The sandstone is younger if it shows evidence of contact metamorphis ...
Supplemental Readings on Plate Tectonics and
... As the textbook states on p. 219, “Convective flow in the rocky 2900-kilometer-thick mantle—in which warm, less dense rock rises and cooler, more dense material sinks—is the basic driving force for plate movement.” Specifically, the earth is MUCH hotter in the center than it is on the outside. How m ...
... As the textbook states on p. 219, “Convective flow in the rocky 2900-kilometer-thick mantle—in which warm, less dense rock rises and cooler, more dense material sinks—is the basic driving force for plate movement.” Specifically, the earth is MUCH hotter in the center than it is on the outside. How m ...
Tsunamis
... • Sometimes weather events such as hurricanes or cyclones (with high winds) can cause storm surges which look similar to a tsunami but are not true tsunamis. ...
... • Sometimes weather events such as hurricanes or cyclones (with high winds) can cause storm surges which look similar to a tsunami but are not true tsunamis. ...
Geology G
... recurring events on the Earth that ultimately influence all of our lives. This course introduces the physical features and processes of the Earth that control these events. The course has a laboratory component. Fall, Spring GE-3, GE-10 GEOL 108 (3) Oceans of the World An introduction to the world’s ...
... recurring events on the Earth that ultimately influence all of our lives. This course introduces the physical features and processes of the Earth that control these events. The course has a laboratory component. Fall, Spring GE-3, GE-10 GEOL 108 (3) Oceans of the World An introduction to the world’s ...
Plate Tectonics
... Continents that were once connected also have identical landform shapes and features and identical rock formations ...
... Continents that were once connected also have identical landform shapes and features and identical rock formations ...
PDF
... pieces of a puzzle. The continents form part of the tectonic plates and, in fact, some of the plates fit perfectly. It is know that some plates move with respect to others. Sometimes they separate, and sometimes they move closer and sometimes collide or slip and rub against each other. The result is ...
... pieces of a puzzle. The continents form part of the tectonic plates and, in fact, some of the plates fit perfectly. It is know that some plates move with respect to others. Sometimes they separate, and sometimes they move closer and sometimes collide or slip and rub against each other. The result is ...
Nature

Nature, in the broadest sense, is the natural, physical, or material world or universe. ""Nature"" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large part of science. Although humans are part of nature, human activity is often understood as a separate category from other natural phenomena.The word nature is derived from the Latin word natura, or ""essential qualities, innate disposition"", and in ancient times, literally meant ""birth"". Natura is a Latin translation of the Greek word physis (φύσις), which originally related to the intrinsic characteristics that plants, animals, and other features of the world develop of their own accord. The concept of nature as a whole, the physical universe, is one of several expansions of the original notion; it began with certain core applications of the word φύσις by pre-Socratic philosophers, and has steadily gained currency ever since. This usage continued during the advent of modern scientific method in the last several centuries.Within the various uses of the word today, ""nature"" often refers to geology and wildlife. Nature can refer to the general realm of living plants and animals, and in some cases to the processes associated with inanimate objects – the way that particular types of things exist and change of their own accord, such as the weather and geology of the Earth. It is often taken to mean the ""natural environment"" or wilderness–wild animals, rocks, forest, and in general those things that have not been substantially altered by human intervention, or which persist despite human intervention. For example, manufactured objects and human interaction generally are not considered part of nature, unless qualified as, for example, ""human nature"" or ""the whole of nature"". This more traditional concept of natural things which can still be found today implies a distinction between the natural and the artificial, with the artificial being understood as that which has been brought into being by a human consciousness or a human mind. Depending on the particular context, the term ""natural"" might also be distinguished from the unnatural or the supernatural.