Mineral resource
... 2. Igneous • Forms below or at earth’s surface from magma • Granite • Lava rocks ...
... 2. Igneous • Forms below or at earth’s surface from magma • Granite • Lava rocks ...
rocks.
... Igneous rocks solidify from volcanic magma They vary in composition from basalt to granite and in texture from rapidly cooled glasses, such as obsidian, to slowly cooled coarse grains, such as ...
... Igneous rocks solidify from volcanic magma They vary in composition from basalt to granite and in texture from rapidly cooled glasses, such as obsidian, to slowly cooled coarse grains, such as ...
DYNAMIC PLANET I
... • All the Earth’s oceans have a continuous mountain range, called a mid-ocean ridge • Located above rising currents in the mantle convection cells • Stand high because they are heated by hot rising material which expands the rocks ...
... • All the Earth’s oceans have a continuous mountain range, called a mid-ocean ridge • Located above rising currents in the mantle convection cells • Stand high because they are heated by hot rising material which expands the rocks ...
Chapter 8 Study Guide
... Andes Mountains where an ocean plate is being pushed under a continental plate is an example of a converging (subduction) boundary, meaning the Andes mountains must be volcanic While the Himalayas are non-volcanic 43. Oceanic crust is always subducted under continental crust because it is more dense ...
... Andes Mountains where an ocean plate is being pushed under a continental plate is an example of a converging (subduction) boundary, meaning the Andes mountains must be volcanic While the Himalayas are non-volcanic 43. Oceanic crust is always subducted under continental crust because it is more dense ...
Unit Rationale - (Secondary) Teacher
... safety in earthquake or volcanic areas. Although student interests and relevancy may not seem to directly promote educational equity, to create a classroom where the students feel that their point of view, interests and life context is relevant promotes equity in the ...
... safety in earthquake or volcanic areas. Although student interests and relevancy may not seem to directly promote educational equity, to create a classroom where the students feel that their point of view, interests and life context is relevant promotes equity in the ...
SAMPLE PAGES - Oxford University Press
... In some parts of the world they are moving away from one another; in other parts they are colliding. Landforms such as fold mountain ranges, deep valleys and ocean ridges and trenches form the boundaries between two plates. (We will learn what these terms mean later.) Let us look more closely at wha ...
... In some parts of the world they are moving away from one another; in other parts they are colliding. Landforms such as fold mountain ranges, deep valleys and ocean ridges and trenches form the boundaries between two plates. (We will learn what these terms mean later.) Let us look more closely at wha ...
Component 4: Oils, Earth and Atmosphere
... The oil from these fruits and seeds can be used for f____________ or for fuel. To extract the oil the fruits or seeds need to be c____________ and then p____________. D____________ refines oil and removes water and any i____________. ...
... The oil from these fruits and seeds can be used for f____________ or for fuel. To extract the oil the fruits or seeds need to be c____________ and then p____________. D____________ refines oil and removes water and any i____________. ...
1. What is rock? 2. The layer of solid rock that surrounds Earth`s
... a. Magma that cools quickly forms igneous rocks with large crystals. b. Igneous rock that formed beneath Earth’s surface is intrusive rock. c. Granite is an extrusive rock. d. Basalt is extrusive rock that makes up the ocean floor. ...
... a. Magma that cools quickly forms igneous rocks with large crystals. b. Igneous rock that formed beneath Earth’s surface is intrusive rock. c. Granite is an extrusive rock. d. Basalt is extrusive rock that makes up the ocean floor. ...
Ch 5 S 4 Sea-Floor Spreading
... c. Subduction and Earth’s Oceans i. Subduction and sea-floor spreading can change the size and shape of the oceans ii. The ocean floor is renewed about every 200 million years iii.The Pacific Ocean covers almost 1/3 of Earth 1. It is shrinking 2. Sometimes a deep ocean trench swallows more oceanic ...
... c. Subduction and Earth’s Oceans i. Subduction and sea-floor spreading can change the size and shape of the oceans ii. The ocean floor is renewed about every 200 million years iii.The Pacific Ocean covers almost 1/3 of Earth 1. It is shrinking 2. Sometimes a deep ocean trench swallows more oceanic ...
Density of Minerals and Rocks
... The importance of density lies in the fact that when there are two objects with different densities and phases, the more density will sink. The fact that you are here at the bottom of the ocean of air is one trivial example. Also, when two fluids (liquids or gases) have different densities, the less ...
... The importance of density lies in the fact that when there are two objects with different densities and phases, the more density will sink. The fact that you are here at the bottom of the ocean of air is one trivial example. Also, when two fluids (liquids or gases) have different densities, the less ...
Section 1: Continental Drift
... Earth’s continental surfaces. As continents began to drift around the globe, however, global temperatures changed and much of the ice sheet melted. • As continents rift or as mountains form, populations of ...
... Earth’s continental surfaces. As continents began to drift around the globe, however, global temperatures changed and much of the ice sheet melted. • As continents rift or as mountains form, populations of ...
8Ha – Explaining the Earth/Sedimentary rocks
... Rocks that have been formed from igneous or sedimentary rocks by heat and pressure. A sedimentary rock made of tiny particles. ...
... Rocks that have been formed from igneous or sedimentary rocks by heat and pressure. A sedimentary rock made of tiny particles. ...
Guided Notes for Plate Tectonics
... Plates are found in the __________________________. Plates _________________ on top of the _______________________________. ____________________________ cause plates to move, producing changes in Earth’s surface such as _______________________, _____________________, ________________________, ...
... Plates are found in the __________________________. Plates _________________ on top of the _______________________________. ____________________________ cause plates to move, producing changes in Earth’s surface such as _______________________, _____________________, ________________________, ...
Falcon Focus
... layer that you live on, and it is the most widely studied and understood. The mantle is much hotter and has the ability to flow. The core (outer core and inner core) are even hotter with pressures so great you would be squeezed into a ball smaller than a marble if you were able to go to the center o ...
... layer that you live on, and it is the most widely studied and understood. The mantle is much hotter and has the ability to flow. The core (outer core and inner core) are even hotter with pressures so great you would be squeezed into a ball smaller than a marble if you were able to go to the center o ...
Stress and Strain - El Molino High School
... critical point. At these breaks, rocks can move, releasing the energy built up as a result of stress. Earthquakes are the result of this movement and release of energy. ...
... critical point. At these breaks, rocks can move, releasing the energy built up as a result of stress. Earthquakes are the result of this movement and release of energy. ...
GEO Colonnade courses
... Explorations Courses, or junior status to enroll in Connections courses. Courses must be from 3 separate disciplines. Social and Cultural: (Students need 3 credits) GEOG 200: Latin American Society: Past and Present – This course is a broad, interdisciplinary introduction to the study of Latin Ameri ...
... Explorations Courses, or junior status to enroll in Connections courses. Courses must be from 3 separate disciplines. Social and Cultural: (Students need 3 credits) GEOG 200: Latin American Society: Past and Present – This course is a broad, interdisciplinary introduction to the study of Latin Ameri ...
Energy Resources
... friction in a localized area to cause the rock to melt. This molten rock will burn up to the surface and create a volcano over time. Most volcanoes are located in the Pacific Ring of Fire because of subduction zone around the Pacific Ocean. • Not all volcanoes are created this way. Some are created ...
... friction in a localized area to cause the rock to melt. This molten rock will burn up to the surface and create a volcano over time. Most volcanoes are located in the Pacific Ring of Fire because of subduction zone around the Pacific Ocean. • Not all volcanoes are created this way. Some are created ...
3rd Nine Weeks Study Guide Earth + Space 6.6B Calculate density
... The MANTLE is the thick middle layer in the solid part of Earth. o More dense than either type of crust o Made of rock that contains elements iron and magnesium o Grouped into 4 layers uppermost mantle, asthenosphere, upper mantle and lower mantle ...
... The MANTLE is the thick middle layer in the solid part of Earth. o More dense than either type of crust o Made of rock that contains elements iron and magnesium o Grouped into 4 layers uppermost mantle, asthenosphere, upper mantle and lower mantle ...
convection-and-the-mantel-1st-one-of-week-5
... In the 1960’s scientist were able to dive to the ocean floor in Alvin a small submarine designed to take the enormous amount of pressures at the bottom of the ocean. – When they got down there they saw pillow shaped or they look like they just got squeezed from a tube of tooth past shaped ...
... In the 1960’s scientist were able to dive to the ocean floor in Alvin a small submarine designed to take the enormous amount of pressures at the bottom of the ocean. – When they got down there they saw pillow shaped or they look like they just got squeezed from a tube of tooth past shaped ...
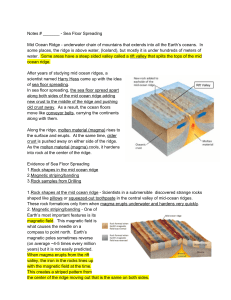
Notes # ______ Sea Floor Spreading Mid Ocean Ridge underwater
... One of Earth’s most important features is its magnetic field . This magnetic field is what causes the needle on a compass to point north. Earth’s magnetic poles sometimes reverse (on average ~45 times every million years) but it is not easily predicted. When magma erupts from the rift ...
... One of Earth’s most important features is its magnetic field . This magnetic field is what causes the needle on a compass to point north. Earth’s magnetic poles sometimes reverse (on average ~45 times every million years) but it is not easily predicted. When magma erupts from the rift ...
Minerals, Rocks and Resources
... • Can be found by either dividing the mass of a sample by its volume or flotation • Water’s density is 1 g/mL • A substance will sink in water if it is more dense than 1g/mL and float if it is less dense ...
... • Can be found by either dividing the mass of a sample by its volume or flotation • Water’s density is 1 g/mL • A substance will sink in water if it is more dense than 1g/mL and float if it is less dense ...
continental drift theory Now called PLATE TECTONICS
... • Transform faults – occur when plates slide past one another along a fracture (fault) in the lithosphere ...
... • Transform faults – occur when plates slide past one another along a fracture (fault) in the lithosphere ...
PostTest
... so new plants can’t grow there, it is easier for soil to dry out and erode. D. When people farm the land, it is impossible to avoid over-farming the soil such that new plants can’t grow there, making it easier for soil to dry out and erode. ____ 19. The figure below shows a tectonically active area ...
... so new plants can’t grow there, it is easier for soil to dry out and erode. D. When people farm the land, it is impossible to avoid over-farming the soil such that new plants can’t grow there, making it easier for soil to dry out and erode. ____ 19. The figure below shows a tectonically active area ...
The Composition of Earth
... – Over long periods, large amounts of sediment build to large thicknesses – Exert enormous pressure that causes particles in sediment to interlock – Chemical cementation takes place – Strata – horizontal layers of sedimentary rock; sometimes tilted into vertical by Earth processes ...
... – Over long periods, large amounts of sediment build to large thicknesses – Exert enormous pressure that causes particles in sediment to interlock – Chemical cementation takes place – Strata – horizontal layers of sedimentary rock; sometimes tilted into vertical by Earth processes ...
Nature

Nature, in the broadest sense, is the natural, physical, or material world or universe. ""Nature"" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large part of science. Although humans are part of nature, human activity is often understood as a separate category from other natural phenomena.The word nature is derived from the Latin word natura, or ""essential qualities, innate disposition"", and in ancient times, literally meant ""birth"". Natura is a Latin translation of the Greek word physis (φύσις), which originally related to the intrinsic characteristics that plants, animals, and other features of the world develop of their own accord. The concept of nature as a whole, the physical universe, is one of several expansions of the original notion; it began with certain core applications of the word φύσις by pre-Socratic philosophers, and has steadily gained currency ever since. This usage continued during the advent of modern scientific method in the last several centuries.Within the various uses of the word today, ""nature"" often refers to geology and wildlife. Nature can refer to the general realm of living plants and animals, and in some cases to the processes associated with inanimate objects – the way that particular types of things exist and change of their own accord, such as the weather and geology of the Earth. It is often taken to mean the ""natural environment"" or wilderness–wild animals, rocks, forest, and in general those things that have not been substantially altered by human intervention, or which persist despite human intervention. For example, manufactured objects and human interaction generally are not considered part of nature, unless qualified as, for example, ""human nature"" or ""the whole of nature"". This more traditional concept of natural things which can still be found today implies a distinction between the natural and the artificial, with the artificial being understood as that which has been brought into being by a human consciousness or a human mind. Depending on the particular context, the term ""natural"" might also be distinguished from the unnatural or the supernatural.