On the electron temperature downstream of the solar wind
... that Voyager-2 measurements at the termination shock (TS) crossing (Richardson et al., 2008) deliver data which are unpredicted by presently existing TS models in the literature, like those by Fahr and Chalov (2008) or Wu et al. (2009). Based on identical upstream plasma conditions, none of the pres ...
... that Voyager-2 measurements at the termination shock (TS) crossing (Richardson et al., 2008) deliver data which are unpredicted by presently existing TS models in the literature, like those by Fahr and Chalov (2008) or Wu et al. (2009). Based on identical upstream plasma conditions, none of the pres ...
Cosmic Rays and Plasma Astrophysics
... The late 1800’s was an extremely active period in physics, leading to the observation of fundamental new particles, the theoretical foundations of electromagnetic theory and the seeds of quantum mechanics and relativity. Various types of “rays” were found, many using “Crooke’s tubes,” an evacuated t ...
... The late 1800’s was an extremely active period in physics, leading to the observation of fundamental new particles, the theoretical foundations of electromagnetic theory and the seeds of quantum mechanics and relativity. Various types of “rays” were found, many using “Crooke’s tubes,” an evacuated t ...
Modelling magnetic fields in spiral galaxies
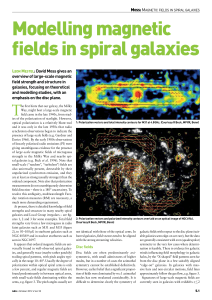
... fields with even parity with respect to the galactic plane are the first to be excited as dynamo numbers are increased. By the late 1980s, increasing computer resources meant that axisymmetric models, with dynamo active discs embedded in largely passive diffusive spherical halos, could be investigat ...
... fields with even parity with respect to the galactic plane are the first to be excited as dynamo numbers are increased. By the late 1980s, increasing computer resources meant that axisymmetric models, with dynamo active discs embedded in largely passive diffusive spherical halos, could be investigat ...
MSc Project: A combined fit of neutrino models using astrophysics
... • Most models that explain small neutrino masses (see-saw) predict ‘sterile’ neutrinos. • Sterile means they only interact gravitationally through their mass, but not through weak interaction. • Sterile neutrino masses can be anywhere between 1 eV and GUT scale. ...
... • Most models that explain small neutrino masses (see-saw) predict ‘sterile’ neutrinos. • Sterile means they only interact gravitationally through their mass, but not through weak interaction. • Sterile neutrino masses can be anywhere between 1 eV and GUT scale. ...