The IMF of intermediate-mass stars in young star clusters
... pleteness should be properly accounted for. Field star contamination increases with decreasing stellar brightness while data incompleteness increases with both increasing stellar crowding and decreasing stellar brightness. The procedures used for their corrections are described in detail by Mateo (1 ...
... pleteness should be properly accounted for. Field star contamination increases with decreasing stellar brightness while data incompleteness increases with both increasing stellar crowding and decreasing stellar brightness. The procedures used for their corrections are described in detail by Mateo (1 ...
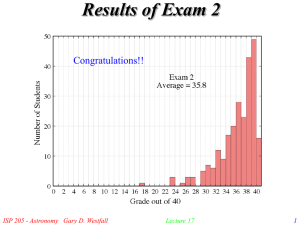
Lecture17
... Energy is generated through fusion in the core of the star which extends 1/4 of the way to the surface The core contains 1/3 of the mass of the star Temperatures reach 15 million K and the density is 150 times the density of water The energy is transported toward the surface by radiation until it re ...
... Energy is generated through fusion in the core of the star which extends 1/4 of the way to the surface The core contains 1/3 of the mass of the star Temperatures reach 15 million K and the density is 150 times the density of water The energy is transported toward the surface by radiation until it re ...
Possibility of explosion of a giant planet.
... value of 1: 6000), the ocean could propagate an equilibrium thermonuclear detonation wave at a temperature £2 keV (although a fantastic 1030 ergs—2 x 107 MT, or the total amount of solar energy incident on the Earth for a two-week period— would be required to initiate such a detonation at a deuteriu ...
... value of 1: 6000), the ocean could propagate an equilibrium thermonuclear detonation wave at a temperature £2 keV (although a fantastic 1030 ergs—2 x 107 MT, or the total amount of solar energy incident on the Earth for a two-week period— would be required to initiate such a detonation at a deuteriu ...
Folie 1
... Superconducting type I protons (instead of type II) or neutrons are normal in the outer core ...
... Superconducting type I protons (instead of type II) or neutrons are normal in the outer core ...
Boron is the chemical element with atomic number 5 and
... Boron is similar to carbon in its capability to form stable covalently bonded molecular networks. Even nominally disordered (amorphous) boron contains regular boron icosahedra which are, however, bonded randomly to each other without long‐range order. Crystalline boron is a very hard, black mater ...
... Boron is similar to carbon in its capability to form stable covalently bonded molecular networks. Even nominally disordered (amorphous) boron contains regular boron icosahedra which are, however, bonded randomly to each other without long‐range order. Crystalline boron is a very hard, black mater ...
The Physics of Massive Star Formation
... Stars can accrete by capturing unbound gas (Bondi-Hoyle) or capturing other cores Analytically compute fm from captures: (Krumholz, McKee, & Klein, 2005, Nature, 438, 332) ...
... Stars can accrete by capturing unbound gas (Bondi-Hoyle) or capturing other cores Analytically compute fm from captures: (Krumholz, McKee, & Klein, 2005, Nature, 438, 332) ...
X-ray Binaries
... metal-rich (all except GRO J1655-40) and possess large peculiar abundances of αelements. Comparison with supernova models is, however, not straightforward given current uncertainties in model parameters such as mixing. ...
... metal-rich (all except GRO J1655-40) and possess large peculiar abundances of αelements. Comparison with supernova models is, however, not straightforward given current uncertainties in model parameters such as mixing. ...
Hvězdný make up Proč jsou hvězdy skvrnité?
... Assuming magnetic field of tepid MS stars is fossil one → all photospheres should be in some extent controlled by magnetic field → transient spot structures on even ‘normal’ (non-CP) tepid MS stars are allowed. ...
... Assuming magnetic field of tepid MS stars is fossil one → all photospheres should be in some extent controlled by magnetic field → transient spot structures on even ‘normal’ (non-CP) tepid MS stars are allowed. ...
Fusion: Our Friend the Nucleus
... Temperature needed for thermonuclear fusion Beam fusion: acclerating a beam of nuclei into a target (stationary or another beam) is generally not an effective way to produce energy. However, this is still useful for studying the basic physics of fusion, or making sources of, e.g., neutrons. Thermon ...
... Temperature needed for thermonuclear fusion Beam fusion: acclerating a beam of nuclei into a target (stationary or another beam) is generally not an effective way to produce energy. However, this is still useful for studying the basic physics of fusion, or making sources of, e.g., neutrons. Thermon ...
Spectral modeling of nebular-phase supernovae Anders Jerkstrand Department of Astronomy
... sun is only ∼ 107 K at its center), and fusion was therefore rejected as their power source. However, two effects make fusion effective even at ∼ 103 times lower temperature; some nuclei have much higher kinetic energies than kT , and secondly quantum mechanical tunneling allows reactions to occur a ...
... sun is only ∼ 107 K at its center), and fusion was therefore rejected as their power source. However, two effects make fusion effective even at ∼ 103 times lower temperature; some nuclei have much higher kinetic energies than kT , and secondly quantum mechanical tunneling allows reactions to occur a ...
A minimum column density of 1gcm(
... galaxies and the dominant energy sources in the Universe today. They form rarely because efficient radiative cooling keeps most star-forming gas clouds close to isothermal as they collapse, and this favours fragmentation into stars of one solar mass or lower1–3. Heating of a cloud by accreting low-m ...
... galaxies and the dominant energy sources in the Universe today. They form rarely because efficient radiative cooling keeps most star-forming gas clouds close to isothermal as they collapse, and this favours fragmentation into stars of one solar mass or lower1–3. Heating of a cloud by accreting low-m ...
TNO Time Allocation Committee
... photosphere. Prominences are arcs of gas, held above the surface of the Sun by a strong magnetic field. This gas, which contains cool and dense material, will appear as dark filamentz against the Solar disk. Typical prominences erupt quickly and last several minutes to hours, but the quiescent ones ...
... photosphere. Prominences are arcs of gas, held above the surface of the Sun by a strong magnetic field. This gas, which contains cool and dense material, will appear as dark filamentz against the Solar disk. Typical prominences erupt quickly and last several minutes to hours, but the quiescent ones ...
File - Mr. Catt`s Class
... 1. The solar wind is the continuous flow of nuclear particles (mostly protons and electrons) from the Sun. 2. Coronal holes, dark areas in an X-ray image of the Sun, correspond to regions of low density where the magnetic field lines are open; they provide a corridor for charged particles to escape ...
... 1. The solar wind is the continuous flow of nuclear particles (mostly protons and electrons) from the Sun. 2. Coronal holes, dark areas in an X-ray image of the Sun, correspond to regions of low density where the magnetic field lines are open; they provide a corridor for charged particles to escape ...
Binary Stars/Star Clusters
... Star Clusters Assumption: all stars of a given cluster formed from same Nebula ∴ All stars of a single cluster are (1) the same distance from Earth & (2) the same age ...
... Star Clusters Assumption: all stars of a given cluster formed from same Nebula ∴ All stars of a single cluster are (1) the same distance from Earth & (2) the same age ...
Document
... • This apparent contradiction to our model of stellar evolution is known as the Algol Paradox. ...
... • This apparent contradiction to our model of stellar evolution is known as the Algol Paradox. ...
Investigation of alpha-induced reactions on the p nucleus 168Yb
... and r- process seeds [6]. It was found that these γ-induced reactions may occur within O/Ne burning layers of core-collapse supernovae at temperatures of about 2 GK to 3 GK [4, 6, 10]. The supernova shock wave allows photodisintegration reactions and subsequent β decays to produce p nuclei. Recent ...
... and r- process seeds [6]. It was found that these γ-induced reactions may occur within O/Ne burning layers of core-collapse supernovae at temperatures of about 2 GK to 3 GK [4, 6, 10]. The supernova shock wave allows photodisintegration reactions and subsequent β decays to produce p nuclei. Recent ...
Discovery of extremely lead-rich subdwarfs: does heavy metal signal
... 1 I N T RO D U C T I O N The formation of hot subdwarf B (sdB) stars remains a puzzle; they are observed as single stars, and as both close and wide binaries. They are widely regarded to be core-helium burners; the majority have hydrogen-rich atmospheres, but this is only a thin veneer, since they b ...
... 1 I N T RO D U C T I O N The formation of hot subdwarf B (sdB) stars remains a puzzle; they are observed as single stars, and as both close and wide binaries. They are widely regarded to be core-helium burners; the majority have hydrogen-rich atmospheres, but this is only a thin veneer, since they b ...
Targetry Program in the US - NuFact09
... Both target-in and target-out data showed smaller signals, relative to the pump bunches, for probe bunches delayed by 40, 350 and 700 s. We therefore report a corrected probe/pump ratio: Probe target in -Probe target out Pump target in -Pump target out ...
... Both target-in and target-out data showed smaller signals, relative to the pump bunches, for probe bunches delayed by 40, 350 and 700 s. We therefore report a corrected probe/pump ratio: Probe target in -Probe target out Pump target in -Pump target out ...
Population synthesis of Be/white dwarf binaries in the Galaxy
... of short period Be binaries. According to our calculations the number of binary systems containing a Be star paired with a white dwarf in the Galaxy is very large – 70% of all Be stars formed as a result of binary evolution must have a white dwarf as a companion. Based on our calculations we conclud ...
... of short period Be binaries. According to our calculations the number of binary systems containing a Be star paired with a white dwarf in the Galaxy is very large – 70% of all Be stars formed as a result of binary evolution must have a white dwarf as a companion. Based on our calculations we conclud ...
PDF only - at www.arxiv.org.
... The resulting fluxes in photons cm-2 s-1 are then divided by the ISM UV flux of 108 photons cm-2 s-1 (BoechatRoberty et al., 2009), giving the estimated multiplicative correction factor, C. By using a black body model for the UV region of a Sun-like star, which is the case of HD 209458, the resultin ...
... The resulting fluxes in photons cm-2 s-1 are then divided by the ISM UV flux of 108 photons cm-2 s-1 (BoechatRoberty et al., 2009), giving the estimated multiplicative correction factor, C. By using a black body model for the UV region of a Sun-like star, which is the case of HD 209458, the resultin ...
P-nuclei
p-Nuclei (p stands for proton-rich) are certain proton-rich, naturally occurring isotopes of some elements between selenium and mercury which cannot be produced in either s- or r-process.