mam.evolution
... collapse into a explosion of that electrons and compact object an M > 8 Msun protons combine to form supported by star blows stable neutrons away its outer neutron degeneracy throughout the object. pressure. layers. Typical size: R ~ 10 km Mass: M ~ 1.4 – 3 Msun Density: r ~ 1014 g/cm3 ...
... collapse into a explosion of that electrons and compact object an M > 8 Msun protons combine to form supported by star blows stable neutrons away its outer neutron degeneracy throughout the object. pressure. layers. Typical size: R ~ 10 km Mass: M ~ 1.4 – 3 Msun Density: r ~ 1014 g/cm3 ...
Nucleosynthesis in asymptotic giant branch stars
... capture and branching to more neutron rich nuclei is inhibited. However, branching along the s-process path can be demonstrated using the Zirconium isotopes (Zr) with mass numbers A=90 to 96. Along this path, the isotope 93 Zr has a relatively long half-lifetime of 1.5 My, while 95 Zr has a half-lif ...
... capture and branching to more neutron rich nuclei is inhibited. However, branching along the s-process path can be demonstrated using the Zirconium isotopes (Zr) with mass numbers A=90 to 96. Along this path, the isotope 93 Zr has a relatively long half-lifetime of 1.5 My, while 95 Zr has a half-lif ...
3D GR Hydrodynamic Simulations of Binary Neutron Star
... 1) Capture fluxes on coarse and fine grid AMR boundary 2) Integrate both until coarse and fine grid are aligned in time again 3) Restrict integrated coarse grid flux onto fine grid boundary 4) Difference between integrated coarse grid flux and fine grid flux is correction ...
... 1) Capture fluxes on coarse and fine grid AMR boundary 2) Integrate both until coarse and fine grid are aligned in time again 3) Restrict integrated coarse grid flux onto fine grid boundary 4) Difference between integrated coarse grid flux and fine grid flux is correction ...
The Sun: Our Nearest Star
... Fusion Reactions in Stars Where do elements with Z > 26 come from ? s-Process Nucleosynthesis One way is by s-process, s- for “slow”. Free neutrons do not feel Coulomb Barrier and collide with nuclei. Occasionally they stick, making larger nuclei. If neutron flux is not too great, these heavier n ...
... Fusion Reactions in Stars Where do elements with Z > 26 come from ? s-Process Nucleosynthesis One way is by s-process, s- for “slow”. Free neutrons do not feel Coulomb Barrier and collide with nuclei. Occasionally they stick, making larger nuclei. If neutron flux is not too great, these heavier n ...
Model Solutions
... both the stars are at same distance and have same mass, then star A will appear brighter if it is intrinsically bright i.e. it is hotter (blue is hotter than yellow) than star B. the size and the mass of the star does not explicitly explain the brightness of a star. A star B having smaller radius th ...
... both the stars are at same distance and have same mass, then star A will appear brighter if it is intrinsically bright i.e. it is hotter (blue is hotter than yellow) than star B. the size and the mass of the star does not explicitly explain the brightness of a star. A star B having smaller radius th ...
Ch. 14 Formation of Stars
... energy so that it neither expands or contracts too much? • If the star begins producing more energy, then it expands. This results in a lower central temperature and density and slows nuclear fusion until the star regained stability. • The same process works in reverse: if less energy were generated ...
... energy so that it neither expands or contracts too much? • If the star begins producing more energy, then it expands. This results in a lower central temperature and density and slows nuclear fusion until the star regained stability. • The same process works in reverse: if less energy were generated ...
Name Date Life and Death of a Star 2015 1. In the main
... B. how they generate energy C. their brightness 41. A magnetar is a type of pulsar that generates energy by A. an extremely strong magnetic field B. rotation C. gravitational contraction 42. Our sun will eventually become a supernova. A. TRUE B. FALSE 43. "High mass stars" eventually become SUPERGIA ...
... B. how they generate energy C. their brightness 41. A magnetar is a type of pulsar that generates energy by A. an extremely strong magnetic field B. rotation C. gravitational contraction 42. Our sun will eventually become a supernova. A. TRUE B. FALSE 43. "High mass stars" eventually become SUPERGIA ...
Lecture 15: The Main Sequence
... More massive main-sequence stars need higher pressures to support themselves against gravitational collapse. Higher pressure=higher temperatures. The higher temperatures lead to greater rates of nuclear fusion which means higher luminosity. ...
... More massive main-sequence stars need higher pressures to support themselves against gravitational collapse. Higher pressure=higher temperatures. The higher temperatures lead to greater rates of nuclear fusion which means higher luminosity. ...
Accretion Disk
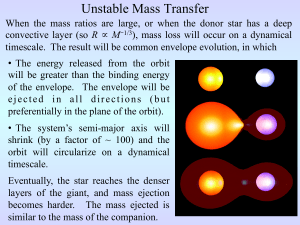
... timescale. The result will be common envelope evolution, in which • The energy released from the orbit will be greater than the binding energy of the envelope. The envelope will be ejected in all directions (but preferentially in the plane of the orbit). • The system’s semi-major axis will shrink ...
... timescale. The result will be common envelope evolution, in which • The energy released from the orbit will be greater than the binding energy of the envelope. The envelope will be ejected in all directions (but preferentially in the plane of the orbit). • The system’s semi-major axis will shrink ...
File - YEAR 11 EBSS PHYSICS DETAILED STUDIES
... But how is the mass turned into energy? This is done at the center, or core, of the sun, and is achieved through the process known as nuclear fusion. A nuclear fusion reaction occurs when two nuclei (hydrogen nuclei in the case of our sun) fuse together creating a new nucleus (helium), this re ...
... But how is the mass turned into energy? This is done at the center, or core, of the sun, and is achieved through the process known as nuclear fusion. A nuclear fusion reaction occurs when two nuclei (hydrogen nuclei in the case of our sun) fuse together creating a new nucleus (helium), this re ...
Chapter 13 The Life of a Star The Life of a Star Mass Is the Key The
... • Formation of heavy elements by nuclear burning processes is called nucleosynthesis • It is proposed that all elements in the universe heavier than helium were created by massive stars ...
... • Formation of heavy elements by nuclear burning processes is called nucleosynthesis • It is proposed that all elements in the universe heavier than helium were created by massive stars ...
B - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... C. The more massive star captured the other one into orbit some time after the two stars had formed D. Stars evolve differently in binary star systems, with less massive stars evolving f faster than more massive stars 18. How many properties of the matter inside a black hole can be measured from out ...
... C. The more massive star captured the other one into orbit some time after the two stars had formed D. Stars evolve differently in binary star systems, with less massive stars evolving f faster than more massive stars 18. How many properties of the matter inside a black hole can be measured from out ...
Chapter 13
... History of Stellar Evolution Theories • Aristotle wrote more than 2000 years ago that stars are heated by their passage through the heavens, but never considered that they evolved • In the 18th century, Immanuel Kant described the Sun as a fiery sphere, formed from the gases gravitated to the cente ...
... History of Stellar Evolution Theories • Aristotle wrote more than 2000 years ago that stars are heated by their passage through the heavens, but never considered that they evolved • In the 18th century, Immanuel Kant described the Sun as a fiery sphere, formed from the gases gravitated to the cente ...
Nuclear fusion in stars
... In such conditions, photon-photon interactions produce e--e+ pairs and neutrinos, which carry away core energy cooling it in a runaway process leading up to core collapse ! by the core bounce cause detonation of Heat pulse caused successive shells of the star and a catastrophic ...
... In such conditions, photon-photon interactions produce e--e+ pairs and neutrinos, which carry away core energy cooling it in a runaway process leading up to core collapse ! by the core bounce cause detonation of Heat pulse caused successive shells of the star and a catastrophic ...
Thermal emission and internal heating processes in millisecond
... • Observed UV emission of PSR J0437-4715 may be due to rotochemical heating • The same emission can be used to constrain |dG/dt|: – competitive with best existing constraints if fast cooling processes could be ruled out ...
... • Observed UV emission of PSR J0437-4715 may be due to rotochemical heating • The same emission can be used to constrain |dG/dt|: – competitive with best existing constraints if fast cooling processes could be ruled out ...
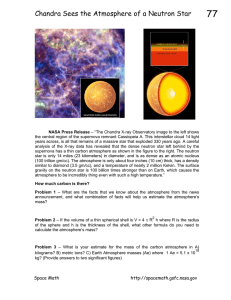
Chandra Sees the Atmosphere of a Neutron Star - Chandra X
... the central region of the supernova remnant Cassiopeia A. This interstellar cloud 14 light years across, is all that remains of a massive star that exploded 330 years ago. A careful analysis of the X-ray data has revealed that the dense neutron star left behind by the supernova has a thin carbon atm ...
... the central region of the supernova remnant Cassiopeia A. This interstellar cloud 14 light years across, is all that remains of a massive star that exploded 330 years ago. A careful analysis of the X-ray data has revealed that the dense neutron star left behind by the supernova has a thin carbon atm ...
Properties of Stars
... A Hertzsprung–Russell diagram shows the relationship between the absolute magnitude and temperature of stars. A main-sequence star is a star that falls into the main sequence category on the H–R diagram. This category contains the majority of stars and runs diagonally from the upper left to the ...
... A Hertzsprung–Russell diagram shows the relationship between the absolute magnitude and temperature of stars. A main-sequence star is a star that falls into the main sequence category on the H–R diagram. This category contains the majority of stars and runs diagonally from the upper left to the ...
lecture24
... he can use to temporarily stop his descent into the black hole. With visions of heroism in your head, you tie a rope to your waist and jump out of your spaceship to go and rescue him. How does time appear (to you) to progress for you and your friend as you approach him? 1) Your own time seems to run ...
... he can use to temporarily stop his descent into the black hole. With visions of heroism in your head, you tie a rope to your waist and jump out of your spaceship to go and rescue him. How does time appear (to you) to progress for you and your friend as you approach him? 1) Your own time seems to run ...
Unit 3 - Lesson 8.9 Life of Stars Challenge
... These large stars have diameters between 10X and 100X that of the Sun. If the star is a Super Giant, their diameters can be up to 1000X of the Sun. A late-life stage sub-species star that emits a beam of electromagnetic radiation that can be only seen when the beam of emission is pointing toward the ...
... These large stars have diameters between 10X and 100X that of the Sun. If the star is a Super Giant, their diameters can be up to 1000X of the Sun. A late-life stage sub-species star that emits a beam of electromagnetic radiation that can be only seen when the beam of emission is pointing toward the ...
PHYSICS 113 Practice Questions #2
... b. a small disk of gas and dust surrounding a single star that was recently formed c. a cloud o f gas and du st illuminated by th e light of newly form ed stars within it d. the remnant of a star that exploded several thousand years ago e. an illusion caused by activity in the Earth's upper atmosphe ...
... b. a small disk of gas and dust surrounding a single star that was recently formed c. a cloud o f gas and du st illuminated by th e light of newly form ed stars within it d. the remnant of a star that exploded several thousand years ago e. an illusion caused by activity in the Earth's upper atmosphe ...
Ch12&13 Life and Death of Stars
... • The first neutron stars were discovered using radio telescopes that found very regular pulses of radio emission coming from a single part of the sky. ...
... • The first neutron stars were discovered using radio telescopes that found very regular pulses of radio emission coming from a single part of the sky. ...
P-nuclei
p-Nuclei (p stands for proton-rich) are certain proton-rich, naturally occurring isotopes of some elements between selenium and mercury which cannot be produced in either s- or r-process.