Bargaining games
... In round 4, 1 gets 0 if they reject the offer, so they accept any non-negative offer, so 2 offers them y2 = 0. This gives 2 a round 4 payoff of δ3S. In round 3, 1 must make an offer that leaves 2 indifferent between accepting that offer and rejecting the offer (which gives δ3S). So 1 will offer x2 = ...
... In round 4, 1 gets 0 if they reject the offer, so they accept any non-negative offer, so 2 offers them y2 = 0. This gives 2 a round 4 payoff of δ3S. In round 3, 1 must make an offer that leaves 2 indifferent between accepting that offer and rejecting the offer (which gives δ3S). So 1 will offer x2 = ...
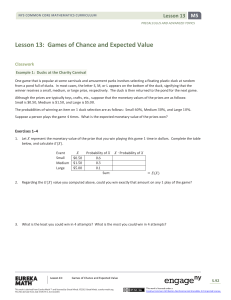
Lesson 13: Games of Chance and Expected Value
... When this value is positive, the player can expect to come out ahead in the long run. However, in most games of chance, this value is negative and represents how much the group operating the game takes in on average per game. From a player’s perspective, a negative expected value means that the play ...
... When this value is positive, the player can expect to come out ahead in the long run. However, in most games of chance, this value is negative and represents how much the group operating the game takes in on average per game. From a player’s perspective, a negative expected value means that the play ...
An Approach to Bounded Rationality
... as prisoner’s dilemma, e.g. [2, 3, 4, 5]). This paper focuses on the strategic aspects of decisionmaking in complex multi-agent environments, i.e., on how a player should choose among strategies of varying complexity, given that its opponents are making similar decisions. Our model applies to genera ...
... as prisoner’s dilemma, e.g. [2, 3, 4, 5]). This paper focuses on the strategic aspects of decisionmaking in complex multi-agent environments, i.e., on how a player should choose among strategies of varying complexity, given that its opponents are making similar decisions. Our model applies to genera ...
Alpha-Beta Example
... – Solution is strategy (strategy specifies move for every possible opponent reply). – Time limits force an approximate solution – Evaluation function: evaluate “goodness” of game position – Examples: chess, checkers, Othello, backgammon ...
... – Solution is strategy (strategy specifies move for every possible opponent reply). – Time limits force an approximate solution – Evaluation function: evaluate “goodness” of game position – Examples: chess, checkers, Othello, backgammon ...
Target (R)
... Consider the random player as an adversary. Then there is a choice of successors such that the play will reach the target. The probability of the choice of successors is at least (1/2)n . ...
... Consider the random player as an adversary. Then there is a choice of successors such that the play will reach the target. The probability of the choice of successors is at least (1/2)n . ...
Understanding Fun - Personal Web Pages
... interactive storytelling can differ critically from traditional linear modes ...
... interactive storytelling can differ critically from traditional linear modes ...
1.6 Non-cooperative Games in wireless networks
... In a game strategic there are different actors who have to make decisions on how to act upon certain rules and have certain preferences over out comes. This means for example that a situation when two friends are deciding on where to eat and they both have a favorite restaurant can be modeled as a s ...
... In a game strategic there are different actors who have to make decisions on how to act upon certain rules and have certain preferences over out comes. This means for example that a situation when two friends are deciding on where to eat and they both have a favorite restaurant can be modeled as a s ...
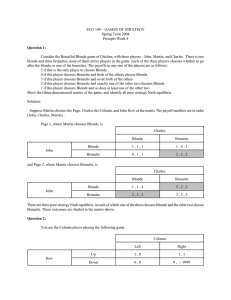
Prcpt04.pdf
... This is like the game on p.141 of the textbook. The game is dominance solvable - Up is Row’s dominant strategy, so Column should choose Right. This is the only Nash equilibrium. But it is risky - if Row has misunderstood the game, or his hand trembles when he is making the choice, then Right may get ...
... This is like the game on p.141 of the textbook. The game is dominance solvable - Up is Row’s dominant strategy, so Column should choose Right. This is the only Nash equilibrium. But it is risky - if Row has misunderstood the game, or his hand trembles when he is making the choice, then Right may get ...
Algorithmic Game Theory and Applications Lecture 10: Games in
... If the extensive game G is finite, i.e., tree T is finite, then the strategic game ΓG is also finite. Thus, all the theory we developed for finite strategic games also applies to finite extensive games. Unfortunately, the strategic game ΓG is generally exponentially bigger than G. Note that the numb ...
... If the extensive game G is finite, i.e., tree T is finite, then the strategic game ΓG is also finite. Thus, all the theory we developed for finite strategic games also applies to finite extensive games. Unfortunately, the strategic game ΓG is generally exponentially bigger than G. Note that the numb ...
KONANE HAS INFINITE NIM-DIMENSION Carlos Pereira
... In combinatorial game theory, games can be expressed recursively as G = {GL | GR } where GL are the Left options and GR are the Right options of G. An example of a combinatorial game is the classic game of nim, first studied by C. Bouton [3]. This game is played with piles of stones. On his turn, ea ...
... In combinatorial game theory, games can be expressed recursively as G = {GL | GR } where GL are the Left options and GR are the Right options of G. An example of a combinatorial game is the classic game of nim, first studied by C. Bouton [3]. This game is played with piles of stones. On his turn, ea ...
The Chooser-Picker 7-in-a-row game
... ~These games are close to each other. If we believe that Breaker If there is odd number of vertexes, then the last one goes to Chooser by wins the game, then the Chooser-Picker version can be analyzed ...
... ~These games are close to each other. If we believe that Breaker If there is odd number of vertexes, then the last one goes to Chooser by wins the game, then the Chooser-Picker version can be analyzed ...
Decision-making Situations
... If each value in a row (say R1) is greater than, or equal to, the corresponding value in another row (say R2), then R1 dominates R2 If each value in a column (say C1) is smaller than, or equal to, the corresponding value in another column (say C2), then C1 dominates C2 A linear combination of ...
... If each value in a row (say R1) is greater than, or equal to, the corresponding value in another row (say R2), then R1 dominates R2 If each value in a column (say C1) is smaller than, or equal to, the corresponding value in another column (say C2), then C1 dominates C2 A linear combination of ...
THE NUCLEOLUS AND THE SHAPLEY VALUE
... where x(S ) = i∈S xi . Let e(x) be the 2n -dimensional vector of excesses, the components of which are arranged in the non-increasing order, that is, el (x) ≥ el+1 (x), l = 1, . . . , 2n−1 . We say e(x) is lexicographically less than e(y) if el (x) < el (y) for the smallest l for which el (x) , el ( ...
... where x(S ) = i∈S xi . Let e(x) be the 2n -dimensional vector of excesses, the components of which are arranged in the non-increasing order, that is, el (x) ≥ el+1 (x), l = 1, . . . , 2n−1 . We say e(x) is lexicographically less than e(y) if el (x) < el (y) for the smallest l for which el (x) , el ( ...