Applied Animal Breeding and Gene
... The examination of most animal species reveals the existence of phenotype difference between individuals for example in cattle there are obvious difference in coat colours and the presence and absence of horns. If cattle are weighed or if milk production is recorded there will be difference in perfo ...
... The examination of most animal species reveals the existence of phenotype difference between individuals for example in cattle there are obvious difference in coat colours and the presence and absence of horns. If cattle are weighed or if milk production is recorded there will be difference in perfo ...
- Journal of Clinical Neurology
... A4295V HgaI restriction enzyme analysis was performed for screening the R2435H mutation, as described previously.20 For screening the A4295V mutation using direct sequencing, a 598-bp product in exon 91 of RYR1 was amplified by PCR using forward (5’-tgtagctgccactgcgctgtcg-3’) and reverse (5’tgccagga ...
... A4295V HgaI restriction enzyme analysis was performed for screening the R2435H mutation, as described previously.20 For screening the A4295V mutation using direct sequencing, a 598-bp product in exon 91 of RYR1 was amplified by PCR using forward (5’-tgtagctgccactgcgctgtcg-3’) and reverse (5’tgccagga ...
as a PDF
... However, the differences are mostly restricted to the level of expression and tissue-specificity rather than gender-specific expression [18]. Only few genes are known to be specifically transcribed in only one sex (e.g., cwp genes [19]; lov-1 and pkd-2 [20]). It is therefore likely that the extensiv ...
... However, the differences are mostly restricted to the level of expression and tissue-specificity rather than gender-specific expression [18]. Only few genes are known to be specifically transcribed in only one sex (e.g., cwp genes [19]; lov-1 and pkd-2 [20]). It is therefore likely that the extensiv ...
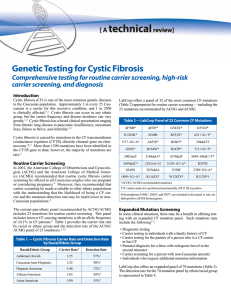
Genetic Testing for Cystic Fibrosis
... in the Caucasian population. Approximately 1 in every 25 Caucasians is a carrier for this recessive condition, and 1 in 2500 is clinically affected.1-2 Cystic fibrosis can occur in any ethnic group, but the carrier frequency and disease incidence can vary greatly.1-2 Cystic fibrosis has a broad clin ...
... in the Caucasian population. Approximately 1 in every 25 Caucasians is a carrier for this recessive condition, and 1 in 2500 is clinically affected.1-2 Cystic fibrosis can occur in any ethnic group, but the carrier frequency and disease incidence can vary greatly.1-2 Cystic fibrosis has a broad clin ...
The Close Relationship Between the A and B Genomes in Avena L
... morphology of the genus Aena, did not support the autoploid origin of the barbata group tetraploids from the strigosa group of diploids as previously suggested by Oinuma (1952). Karyotypic observation confirmed the presence of an A. strigosa chromosome set (As genome) in the barbata group tetraploi ...
... morphology of the genus Aena, did not support the autoploid origin of the barbata group tetraploids from the strigosa group of diploids as previously suggested by Oinuma (1952). Karyotypic observation confirmed the presence of an A. strigosa chromosome set (As genome) in the barbata group tetraploi ...
Reproduction and the pheromonal regulation of sex type in fern
... gametophyte will reproduce, self-fertilization of a hermaphrodite (which is genetically similar to a doubled haploid in angiosperms) results in a completely homozygous sporophyte. Given that this absolute inbreeding could have negative consequences to the individual and reduce genetic variation in p ...
... gametophyte will reproduce, self-fertilization of a hermaphrodite (which is genetically similar to a doubled haploid in angiosperms) results in a completely homozygous sporophyte. Given that this absolute inbreeding could have negative consequences to the individual and reduce genetic variation in p ...
A comparison of methods for haplotype inference
... regulatory RNA molecule (see e.g., Alberts et al,. 2008). The location of a gene on a chromosome is called the locus. The alternative forms of a gene at a locus are called alleles. Since DNA replication is not a perfect process, mutations arise, and as a consequence different versions of a gene can ...
... regulatory RNA molecule (see e.g., Alberts et al,. 2008). The location of a gene on a chromosome is called the locus. The alternative forms of a gene at a locus are called alleles. Since DNA replication is not a perfect process, mutations arise, and as a consequence different versions of a gene can ...
Geospiza ground finches ( Mechanical stress, fracture risk and beak
... One contribution of 13 to a Theme Issue ‘Darwin’s Galápagos finches in modern evolutionary biology’. ...
... One contribution of 13 to a Theme Issue ‘Darwin’s Galápagos finches in modern evolutionary biology’. ...
Nature Genetics: doi:10.1038/ng.3304
... (http://pfam.sanger.ac.uk/family/duf908) (Supplementary Figure 8, bottom right). Five missense mutations elsewhere in the protein were previously reported in pedigrees segregating X-linked mental retardation or autistic spectrum disorder4-6. In two of these pedigrees, female carriers were reported t ...
... (http://pfam.sanger.ac.uk/family/duf908) (Supplementary Figure 8, bottom right). Five missense mutations elsewhere in the protein were previously reported in pedigrees segregating X-linked mental retardation or autistic spectrum disorder4-6. In two of these pedigrees, female carriers were reported t ...
Divergent evolution of molecular markers during laboratory
... Several recent empirical studies in laboratory populations have focused on how different population sizes affect the rates of genetic diversity decline (e.g. see England et al. 2003; Montgomery et al. 2000; Rodrı́guez-Ramilo et al. 2006). Fewer studies in laboratory populations have analysed the lon ...
... Several recent empirical studies in laboratory populations have focused on how different population sizes affect the rates of genetic diversity decline (e.g. see England et al. 2003; Montgomery et al. 2000; Rodrı́guez-Ramilo et al. 2006). Fewer studies in laboratory populations have analysed the lon ...
(political) origin of “corporate governance” species
... governance arrangements inside the firm among constituents (in particular, managers, owners, and workers) interact deeply with a nation’s politics (cf. Roe 2003). In this respect, party systems, political institutions, political orientations of governments, distributional coalitions, ideologies, an ...
... governance arrangements inside the firm among constituents (in particular, managers, owners, and workers) interact deeply with a nation’s politics (cf. Roe 2003). In this respect, party systems, political institutions, political orientations of governments, distributional coalitions, ideologies, an ...
Practice Questions, Lectures 6-13 (259 KB pdf file)
... From the fossil record she knows that species a and c diverged 20 Myr. ago. If the rate of nucleotide substitutions is constant over years and among lineages, how long ago did species c and d diverge? ...
... From the fossil record she knows that species a and c diverged 20 Myr. ago. If the rate of nucleotide substitutions is constant over years and among lineages, how long ago did species c and d diverge? ...
Combining Whole-exome and RNA-Seq Data Improves the Quality
... Figure 6: Mutation rate detected in WES and RNA-Seq data across analyzed cancer types. The mutation rate is higher in WES than in RNA-Seq for 71 models. The mutation rate is calculated from mutations found in target regions of WES and in expressed transcripts of RNA-Seq respectively. Top-right figur ...
... Figure 6: Mutation rate detected in WES and RNA-Seq data across analyzed cancer types. The mutation rate is higher in WES than in RNA-Seq for 71 models. The mutation rate is calculated from mutations found in target regions of WES and in expressed transcripts of RNA-Seq respectively. Top-right figur ...
Influence of Mutation Type and Location on Phenotype
... MECP2 gene that encodes the methyl-CpG-binding protein 2 (MeCP2). In this study we correlated mutation type and location with the severity of the phenotype in 123 girls with RTT. The ability to sit, walk, speak, hand function, head growth, occurrence of epilepsy and a combined severity score were as ...
... MECP2 gene that encodes the methyl-CpG-binding protein 2 (MeCP2). In this study we correlated mutation type and location with the severity of the phenotype in 123 girls with RTT. The ability to sit, walk, speak, hand function, head growth, occurrence of epilepsy and a combined severity score were as ...
(1904–2005) Ernst Mayr and the integration of geographic and
... expose populations to divergent natural selection will accelerate genetic divergence, and thus the process of by-product speciation. Speciation is accelerated because ecological traits under divergent selection, or traits that are genetically-correlated with such traits, can incidentally affect repr ...
... expose populations to divergent natural selection will accelerate genetic divergence, and thus the process of by-product speciation. Speciation is accelerated because ecological traits under divergent selection, or traits that are genetically-correlated with such traits, can incidentally affect repr ...
A Unified Approach to the Evolutionary Consequences of Genetic
... values that occur during transmission from parent to offspring (henceforth termed “reproductive transmission”), reflecting the transmission rules for the factor in question (table 1). The term E(bDg b) is the fecundity-weighted expected change from parent to offspring in the genetic component. Thus, ...
... values that occur during transmission from parent to offspring (henceforth termed “reproductive transmission”), reflecting the transmission rules for the factor in question (table 1). The term E(bDg b) is the fecundity-weighted expected change from parent to offspring in the genetic component. Thus, ...
Doubling Down on Genomes: Polyploidy and Crop Plants
... detailed the loss and gain of restriction fragments in newly synthesized allopolyploids mimicking natural B. rapa and B. juncea (Song et al., 1995). This study was important as Song and colleagues (1995) were able to use the precise progenitors of the allopolyploids, rather than close relatives, to ...
... detailed the loss and gain of restriction fragments in newly synthesized allopolyploids mimicking natural B. rapa and B. juncea (Song et al., 1995). This study was important as Song and colleagues (1995) were able to use the precise progenitors of the allopolyploids, rather than close relatives, to ...
View - OhioLINK Electronic Theses and Dissertations Center
... Centrosomes are highly conserved organelles that are composed of two microtubule-based centrioles surrounded by an amorphous protein cloud of pericentriolar material (PCM), which is able to nucleate astral microtubules. They serve as microtubule organizing centers during cell division and are import ...
... Centrosomes are highly conserved organelles that are composed of two microtubule-based centrioles surrounded by an amorphous protein cloud of pericentriolar material (PCM), which is able to nucleate astral microtubules. They serve as microtubule organizing centers during cell division and are import ...
A Survey of Diversity-Oriented Optimization 1 Introduction - IC
... variables (causes) to output variables (effects). When performing model-based fault diagnosis, it can be of crucial importance to find all possible causes to a measured effect. If there are different possible causes, this indicates that further data is needed to identify the true cause. This aspect ...
... variables (causes) to output variables (effects). When performing model-based fault diagnosis, it can be of crucial importance to find all possible causes to a measured effect. If there are different possible causes, this indicates that further data is needed to identify the true cause. This aspect ...
Reprint
... values that occur during transmission from parent to offspring (henceforth termed “reproductive transmission”), reflecting the transmission rules for the factor in question (table 1). The term E(bDg b) is the fecundity-weighted expected change from parent to offspring in the genetic component. Thus, ...
... values that occur during transmission from parent to offspring (henceforth termed “reproductive transmission”), reflecting the transmission rules for the factor in question (table 1). The term E(bDg b) is the fecundity-weighted expected change from parent to offspring in the genetic component. Thus, ...
Chapter 23 PowerPoint - The Evolution of Populations
... other loci • We can assume the locus that causes phenylketonuria (PKU) is in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium given that: – The PKU gene mutation rate is low – Mate selection is random with respect to whether or not an individual is a carrier for the PKU allele Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education Inc., pub ...
... other loci • We can assume the locus that causes phenylketonuria (PKU) is in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium given that: – The PKU gene mutation rate is low – Mate selection is random with respect to whether or not an individual is a carrier for the PKU allele Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education Inc., pub ...
Genetic Disorders
... normal dominant allele as R. Although any mating in which each parent has at least one recessive allele can ...
... normal dominant allele as R. Although any mating in which each parent has at least one recessive allele can ...
Candidate gene analysis of thyroid hormone receptors
... examined TRa and TRb for linkage to DNA markers that ¯ank a major-eect locus for metamorphic failure in A. mexicanum (Voss and Shaer, 1997). If TRa or TRb are linked to these ¯anking DNA markers, this would be consistent with a causal relationship between TRs and metamorphic failure that could be ...
... examined TRa and TRb for linkage to DNA markers that ¯ank a major-eect locus for metamorphic failure in A. mexicanum (Voss and Shaer, 1997). If TRa or TRb are linked to these ¯anking DNA markers, this would be consistent with a causal relationship between TRs and metamorphic failure that could be ...
Case Report: Achondroplasia
... Achondroplasia is the most common form of skeletal dysplasia, affecting growth of tubular bones, spine and skull. Achondroplasia is an autosomal dominant disorder with complete penetration. The gene of Achon-droplasia was localized to 4p16.3[4,5]. Subsequently mu-tation of fibroblast growth factor r ...
... Achondroplasia is the most common form of skeletal dysplasia, affecting growth of tubular bones, spine and skull. Achondroplasia is an autosomal dominant disorder with complete penetration. The gene of Achon-droplasia was localized to 4p16.3[4,5]. Subsequently mu-tation of fibroblast growth factor r ...
Koinophilia

Koinophilia is an evolutionary hypothesis concerning sexual selection which proposes that animals seeking mate preferentially choose individuals with a minimum of unusual features. Koinophilia intends to explain the clustering of organisms into species and other issues described by Darwin's Dilemma. The term derives from the Greek, koinos, ""the usual"", and philos, ""fondness"".Natural selection causes beneficial inherited features to become more common and eventually replace their disadvantageous counterparts. A sexually-reproducing animal would be expected to avoid individuals with unusual features, and to prefer to mate with individuals displaying a predominance of common or average features. This means that mates displaying mutant features are also avoided. This is advantageous because most mutations that manifest themselves as changes in appearance, functionality or behavior, are disadvantageous. Because it is impossible to judge whether a new mutation is beneficial or not, koinophilic animals avoid them all, at the cost of avoiding the occasional beneficial mutation. Thus, koinophilia, although not infallible in its ability to distinguish fit from unfit mates, is a good strategy when choosing a mate. A koinophilic choice ensures that offspring are likely to inherit features that have been successful in the past.Koinophilia differs from assortative mating, where ""like prefers like"". If like preferred like, leucistic animals (such as white peacocks) would be sexually attracted to one another, and a leucistic subspecies would come into being. Koinophilia predicts that this is unlikely because leucistic animals are attracted to the average in the same way as other animals. Since non-leucistic animals are not attracted by leucism, few leucistic individuals find mates, and leucistic lineages will rarely form.Koinophilia provides simple explanations for the rarity of speciation (in particular Darwin's Dilemma), evolutionary stasis, punctuated equilibria, and the evolution of cooperation. Koinophilia might also contribute to the maintenance of sexual reproduction, preventing its reversion to the much simpler and inherently more advantageous asexual form of reproduction.The koinophilia hypothesis is supported by research into the physical attractiveness of human faces by Judith Langlois and her co-workers. They found that the average of two human faces was more attractive than either of the faces from which that average was derived. The more faces (of the same gender and age) that were used in the averaging process the more attractive and appealing the average face became. This work into averageness supports koinophilia as an explanation of what constitutes a beautiful face, and how the individuality of a face is recognized.