Evidence for Evolution
... Earth is 4.6 billion years old and the oldest evidence of life is 3.6 billion years old. If this mechanism of change has been shaping the organisms on this planet, then there should be evidence of it occurring 5 major types of evidence used to support the theory of evolution. ...
... Earth is 4.6 billion years old and the oldest evidence of life is 3.6 billion years old. If this mechanism of change has been shaping the organisms on this planet, then there should be evidence of it occurring 5 major types of evidence used to support the theory of evolution. ...
Class Notes - North Star Academy
... BOTH: mate and lay eggs, when eggs hatch both species are on their own SNAIL: leaves its eggs PYTHON: stays until eggs hatch, lives much longer ...
... BOTH: mate and lay eggs, when eggs hatch both species are on their own SNAIL: leaves its eggs PYTHON: stays until eggs hatch, lives much longer ...
Differences in the concept of fitness between artificial
... of teams in the generation 999 that contributed both agents to the last 1000th generation. Each agent was assigned one performance point by default, and then could transfer it to its partner in the team. The team displayed reproductive division of labor when one agent he other agent was altruistic, ...
... of teams in the generation 999 that contributed both agents to the last 1000th generation. Each agent was assigned one performance point by default, and then could transfer it to its partner in the team. The team displayed reproductive division of labor when one agent he other agent was altruistic, ...
Population Evolution
... 1. Over production. Most organisms produce more offspring than can survive. 2. Competition. Organisms compete for food and resources. 3. Variation. There is variation among individuals of a species. 4. Adaptation. Individuals with traits best suited to the environment will survive. ...
... 1. Over production. Most organisms produce more offspring than can survive. 2. Competition. Organisms compete for food and resources. 3. Variation. There is variation among individuals of a species. 4. Adaptation. Individuals with traits best suited to the environment will survive. ...
Unit A: Biodiversity Science 9 Study Guide
... One organism benefits, while the other is harmed i.e. a mosquito and a human 7. What are niches? A niche describes the role of an organism within its ecosystem This includes what it eats and what eats it (where it fits on the food pyramid), its habitat, nesting site, or range, and how it affects the ...
... One organism benefits, while the other is harmed i.e. a mosquito and a human 7. What are niches? A niche describes the role of an organism within its ecosystem This includes what it eats and what eats it (where it fits on the food pyramid), its habitat, nesting site, or range, and how it affects the ...
Tree of Life – Evolution and Darwin CS
... On his return to England in 1836, Darwin tried to solve the riddles of these observations and the puzzle of how species evolve. He proposed a theory of evolution occurring by the process of natural selection. The theory proposedthat animals (or plants) were more likely to survive if they adaptedto t ...
... On his return to England in 1836, Darwin tried to solve the riddles of these observations and the puzzle of how species evolve. He proposed a theory of evolution occurring by the process of natural selection. The theory proposedthat animals (or plants) were more likely to survive if they adaptedto t ...
Evolution-Natural and Artificial John Maynard Smith
... Time for natural Selection(1/2) • Has there been time for natural selection to produce the complex creatures we see around us? – The genome of higher animals and plants contains 108 to 109 base pairs of informative DNA. – This is enough, together with the environment and the laws of physics and che ...
... Time for natural Selection(1/2) • Has there been time for natural selection to produce the complex creatures we see around us? – The genome of higher animals and plants contains 108 to 109 base pairs of informative DNA. – This is enough, together with the environment and the laws of physics and che ...
Evolution by Natural Selection
... What did he say? 3. Selection: In an environment, having a particular trait can make individuals more or less likely to survive and have successful reproduction. So, some individuals leave more offspring than others. 4. Adaptation: Over time, those traits that improve survival and reproduction ...
... What did he say? 3. Selection: In an environment, having a particular trait can make individuals more or less likely to survive and have successful reproduction. So, some individuals leave more offspring than others. 4. Adaptation: Over time, those traits that improve survival and reproduction ...
50. and 51. Natural Selection
... many ways to help it survive in its environment. It has good eyesight, which allows it to see and catch bugs in the air. It has bristles near its beak that allow it to sense nearby insects and quickly snap them up. The great crested flycatcher has also adapted so that it instinctively knows where to ...
... many ways to help it survive in its environment. It has good eyesight, which allows it to see and catch bugs in the air. It has bristles near its beak that allow it to sense nearby insects and quickly snap them up. The great crested flycatcher has also adapted so that it instinctively knows where to ...
Population Genetics - wlhs.wlwv.k12.or.us
... 2) No mutation 3) No gene flow (no immigration or emigration) 4) Random mating (no mating preference for particular phenotype) 5) No natural selection (all genotypes have an = chance of surviving & reproducing) ...
... 2) No mutation 3) No gene flow (no immigration or emigration) 4) Random mating (no mating preference for particular phenotype) 5) No natural selection (all genotypes have an = chance of surviving & reproducing) ...
Population Genetics - wlhs.wlwv.k12.or.us
... 2) No mutation 3) No gene flow (no immigration or emigration) 4) Random mating (no mating preference for particular phenotype) 5) No natural selection (all genotypes have an = chance of surviving & reproducing) ...
... 2) No mutation 3) No gene flow (no immigration or emigration) 4) Random mating (no mating preference for particular phenotype) 5) No natural selection (all genotypes have an = chance of surviving & reproducing) ...
Biology Pre-Learning Check
... 15. ______ Parts on an organism that are similar to parts on another organism although they do not share a common ancestor; e.g. wings on birds and wings on insects 16. ______ A trait that helps an organism survive its environment 17. ______ How well an organisms fits into/survives in its environmen ...
... 15. ______ Parts on an organism that are similar to parts on another organism although they do not share a common ancestor; e.g. wings on birds and wings on insects 16. ______ A trait that helps an organism survive its environment 17. ______ How well an organisms fits into/survives in its environmen ...
Name: Evolution: the Process Date: Taxonomy—Naming and
... o Successful adaptations enable organisms to become better suited to their environment, better able to survive and reproduce: “Survival of the Fittest” o Certain adaptive traits increase an organism’s chance of survival, and therefore the chance to pass on its favourable traits to its offspring—and ...
... o Successful adaptations enable organisms to become better suited to their environment, better able to survive and reproduce: “Survival of the Fittest” o Certain adaptive traits increase an organism’s chance of survival, and therefore the chance to pass on its favourable traits to its offspring—and ...
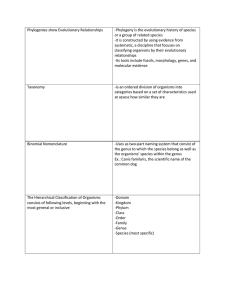
Phylogenies show Evolutionary Relationships
... determine evolutionary relationships -The more alike the DNA sequences of two organisms the more closely related they are evolutionarily- so the closer they are on the phylogenetic tree ...
... determine evolutionary relationships -The more alike the DNA sequences of two organisms the more closely related they are evolutionarily- so the closer they are on the phylogenetic tree ...
Chapter 14
... has split now that genes cannot flow between the populations. http://evolution.berkeley.edu ...
... has split now that genes cannot flow between the populations. http://evolution.berkeley.edu ...
Evolution - FroggiWik
... • Lamarck believed that changes in the environment caused the organisms behavior to change, leading to greater use or disuse of a structure or organ. • The structure would then become larger or smaller as a result and the organism could pass the change to its’ offspring. • Lamarck’s theory became k ...
... • Lamarck believed that changes in the environment caused the organisms behavior to change, leading to greater use or disuse of a structure or organ. • The structure would then become larger or smaller as a result and the organism could pass the change to its’ offspring. • Lamarck’s theory became k ...
When looking at the fossil record, similarities in anatomical
... C natural selection D vestigial structures 20 Looking through the fossil record, there are times when numerous fossils look to just appear all at the same time, with similar characteristics. What is a good explanation for this? A A change in the environment occurred, and animals choose to express di ...
... C natural selection D vestigial structures 20 Looking through the fossil record, there are times when numerous fossils look to just appear all at the same time, with similar characteristics. What is a good explanation for this? A A change in the environment occurred, and animals choose to express di ...
Class Review Guide for test
... • Comparing the survivability of traits between populations in different environments; • Comparing evolutionary mechanisms illustrated in a variety of populations; • Using mathematical reasoning related to Hardy-Weinberg’s Law to explain or predict changes in a population; • Given data and/or a scen ...
... • Comparing the survivability of traits between populations in different environments; • Comparing evolutionary mechanisms illustrated in a variety of populations; • Using mathematical reasoning related to Hardy-Weinberg’s Law to explain or predict changes in a population; • Given data and/or a scen ...
Slides - Michigan State University
... species, allows for the determination of the source of an infectious agents • Example: Doctor who ...
... species, allows for the determination of the source of an infectious agents • Example: Doctor who ...
Evolution Powerpoint
... • Refers to the process in which populations gradually change over time. • CHARLES DARWIN… • Developed a theory of how evolution takes place. ...
... • Refers to the process in which populations gradually change over time. • CHARLES DARWIN… • Developed a theory of how evolution takes place. ...
Variationand geneticdrift12
... gene pool increases the chance that at least some members will survive and reproduce when environmental conditions change ...
... gene pool increases the chance that at least some members will survive and reproduce when environmental conditions change ...
Darwin`s Theory of Evolution
... Darwin devoted much of On The Origin of Species to exploring adaptations of organisms to their environment Darwin discussed many examples of artificial selection, in which humans have modified species through selection and breeding Darwin reasoned that o Organisms with traits that increased their ch ...
... Darwin devoted much of On The Origin of Species to exploring adaptations of organisms to their environment Darwin discussed many examples of artificial selection, in which humans have modified species through selection and breeding Darwin reasoned that o Organisms with traits that increased their ch ...
Koinophilia

Koinophilia is an evolutionary hypothesis concerning sexual selection which proposes that animals seeking mate preferentially choose individuals with a minimum of unusual features. Koinophilia intends to explain the clustering of organisms into species and other issues described by Darwin's Dilemma. The term derives from the Greek, koinos, ""the usual"", and philos, ""fondness"".Natural selection causes beneficial inherited features to become more common and eventually replace their disadvantageous counterparts. A sexually-reproducing animal would be expected to avoid individuals with unusual features, and to prefer to mate with individuals displaying a predominance of common or average features. This means that mates displaying mutant features are also avoided. This is advantageous because most mutations that manifest themselves as changes in appearance, functionality or behavior, are disadvantageous. Because it is impossible to judge whether a new mutation is beneficial or not, koinophilic animals avoid them all, at the cost of avoiding the occasional beneficial mutation. Thus, koinophilia, although not infallible in its ability to distinguish fit from unfit mates, is a good strategy when choosing a mate. A koinophilic choice ensures that offspring are likely to inherit features that have been successful in the past.Koinophilia differs from assortative mating, where ""like prefers like"". If like preferred like, leucistic animals (such as white peacocks) would be sexually attracted to one another, and a leucistic subspecies would come into being. Koinophilia predicts that this is unlikely because leucistic animals are attracted to the average in the same way as other animals. Since non-leucistic animals are not attracted by leucism, few leucistic individuals find mates, and leucistic lineages will rarely form.Koinophilia provides simple explanations for the rarity of speciation (in particular Darwin's Dilemma), evolutionary stasis, punctuated equilibria, and the evolution of cooperation. Koinophilia might also contribute to the maintenance of sexual reproduction, preventing its reversion to the much simpler and inherently more advantageous asexual form of reproduction.The koinophilia hypothesis is supported by research into the physical attractiveness of human faces by Judith Langlois and her co-workers. They found that the average of two human faces was more attractive than either of the faces from which that average was derived. The more faces (of the same gender and age) that were used in the averaging process the more attractive and appealing the average face became. This work into averageness supports koinophilia as an explanation of what constitutes a beautiful face, and how the individuality of a face is recognized.