Darwin and Divinity - The Clergy Letter Project
... traits that are suited to the survival of a species within particular habitat. So, stubbybeaked finches on a particular island in the Galapagos did a lot better than longer-beaked finches on the next island over – better for cracking a particular seed. Stubby-beaked finches mated and over time you e ...
... traits that are suited to the survival of a species within particular habitat. So, stubbybeaked finches on a particular island in the Galapagos did a lot better than longer-beaked finches on the next island over – better for cracking a particular seed. Stubby-beaked finches mated and over time you e ...
Jeopardy - demascalchemistry
... Natural selection _________. a. results in evolutionary adaptation b. is the result of sampling error c. does not affect allelic frequencies d. prepares organisms for future changes in the environment BACK TO GAME ...
... Natural selection _________. a. results in evolutionary adaptation b. is the result of sampling error c. does not affect allelic frequencies d. prepares organisms for future changes in the environment BACK TO GAME ...
File
... Analyze and interpret data to explain patterns in biodiversity that result from speciation. (Biodiversity & Speciation) Describe the different types of evidence used to show evolution. (Evidence for Evolution) Discuss evidence that supports the claim that all living organisms are related by wa ...
... Analyze and interpret data to explain patterns in biodiversity that result from speciation. (Biodiversity & Speciation) Describe the different types of evidence used to show evolution. (Evidence for Evolution) Discuss evidence that supports the claim that all living organisms are related by wa ...
evolution 4a - Hicksville Public Schools
... The gene pool remains the same from generation to generation. 1) The population must be large. In a small population, alleles of low frequency may be lost due to genetic drift. 2)Individuals must not migrate into or out of a population. 3)Mutations must not occur. 4)Reproduction must be completely r ...
... The gene pool remains the same from generation to generation. 1) The population must be large. In a small population, alleles of low frequency may be lost due to genetic drift. 2)Individuals must not migrate into or out of a population. 3)Mutations must not occur. 4)Reproduction must be completely r ...
Week 8, Class 2
... Between Mutation & Selection • Lamarkian: the origin of variation depends on selection. Variation arises (through mutation) in response to challenges. • Darwinian: the origin of variation is independent of selection. Variation exists in a population and some traits are passed down due to their highe ...
... Between Mutation & Selection • Lamarkian: the origin of variation depends on selection. Variation arises (through mutation) in response to challenges. • Darwinian: the origin of variation is independent of selection. Variation exists in a population and some traits are passed down due to their highe ...
#5 -Evidence for Evolution Notes
... are more likely to share a common ancestor. (ex. Mara- same niche as English rabbit, but more closely related to S. Amer. Animals than rabbit because they shared a common ancestor) ...
... are more likely to share a common ancestor. (ex. Mara- same niche as English rabbit, but more closely related to S. Amer. Animals than rabbit because they shared a common ancestor) ...
Chapter 2 - Test Bank 1
... 2. One kind of genetic drift, the founder effect, occurs when a population splits. 3. Especially if a new population contains a small number of individuals, it is unlikely that its gene frequencies will be representative of the larger population. 3. Gene Flow 1. Gene flow, the introduction of new al ...
... 2. One kind of genetic drift, the founder effect, occurs when a population splits. 3. Especially if a new population contains a small number of individuals, it is unlikely that its gene frequencies will be representative of the larger population. 3. Gene Flow 1. Gene flow, the introduction of new al ...
Question 3: What factors affect allele frequencies? Population
... The change in allele frequencies can be beneficial or disadvantageous to the population or species of the organism. It can be beneficial if it helps the organism survive in extreme condition and can be harmful if they make a population die easily when environmental changes occur. It is also importan ...
... The change in allele frequencies can be beneficial or disadvantageous to the population or species of the organism. It can be beneficial if it helps the organism survive in extreme condition and can be harmful if they make a population die easily when environmental changes occur. It is also importan ...
Darwin`s Second Idea – Natural Selection
... doubt the idea that all organisms have evolved from a single common ancestor.” -- Steve Meyer & John Campbell* San Francisco Chronicle, December ...
... doubt the idea that all organisms have evolved from a single common ancestor.” -- Steve Meyer & John Campbell* San Francisco Chronicle, December ...
Key Stage 4
... 2. Below is an evolutionary tree, when did squirrel monkeys, vervet monkeys, chimpanzees and humans all have a common ancestor? ...
... 2. Below is an evolutionary tree, when did squirrel monkeys, vervet monkeys, chimpanzees and humans all have a common ancestor? ...
Evolution Notes (March 14th to March 17th)
... • What are two sources of heritable variation? Explain how these sources create variation. • How are allele frequencies related to gene pools? ...
... • What are two sources of heritable variation? Explain how these sources create variation. • How are allele frequencies related to gene pools? ...
Olearia macdonnellensis - Northern Territory Government
... Olearia macdonnellensis would be particularly affected if, like many of its congeners, it has a light requirement for germination. Buffel Grass would additionally result in increased fire frequency and severity at badly infested sites. The specific threats posed by climate change to macdonnellensis ...
... Olearia macdonnellensis would be particularly affected if, like many of its congeners, it has a light requirement for germination. Buffel Grass would additionally result in increased fire frequency and severity at badly infested sites. The specific threats posed by climate change to macdonnellensis ...
DARWINIAN EVOLUTION e13 Sexual selection differential
... local and systemic signals. Early in fetal life, the reproductive system consists of an indifferent gonad that is indistinguishable by morphological criteria between the sexes. Adjacent to the gonads are two simple ducts: the Müllerian and the Wolffian. The development of the female requires Wnt-4, ...
... local and systemic signals. Early in fetal life, the reproductive system consists of an indifferent gonad that is indistinguishable by morphological criteria between the sexes. Adjacent to the gonads are two simple ducts: the Müllerian and the Wolffian. The development of the female requires Wnt-4, ...
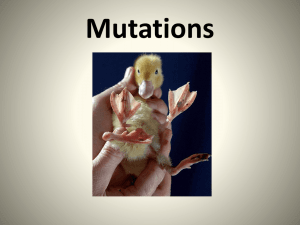
Mutations
... -mutations which occur in the sperm or the egg. If fertilized this mistake would be passed on to the child. Example: Sickle cell anemia ...
... -mutations which occur in the sperm or the egg. If fertilized this mistake would be passed on to the child. Example: Sickle cell anemia ...
Say 2 significant things about these terms:
... 16. Occur at loci 17. Are inherited from both parents 18. Are alternative version of genes 19. Code for amino acids Evolution: 20. Occurs through changes in gene frequencies in a population 21. Was first explined by Darwin through descent with modification 22. Artificial selection refutes it 23. It ...
... 16. Occur at loci 17. Are inherited from both parents 18. Are alternative version of genes 19. Code for amino acids Evolution: 20. Occurs through changes in gene frequencies in a population 21. Was first explined by Darwin through descent with modification 22. Artificial selection refutes it 23. It ...
File
... books ever written. The two critical ideas he developed in it are: The fact that evolution occurs. The theory of natural selection is the driving force or mechanism behind the process of evolution. Darwin began developing these ideas as a result of his experiences during a fiveyear voyage on the ...
... books ever written. The two critical ideas he developed in it are: The fact that evolution occurs. The theory of natural selection is the driving force or mechanism behind the process of evolution. Darwin began developing these ideas as a result of his experiences during a fiveyear voyage on the ...
evolution - kendricknovak
... • Drew and made observations while in the Galapagos • Back in England he looked at his findings – Tortoises and Finches ...
... • Drew and made observations while in the Galapagos • Back in England he looked at his findings – Tortoises and Finches ...
• - cloudfront.net
... 34. What makes a cell specialized in a multicellular organism? Why do specialized cells regulate the expression of genes? 35. Is gene regulation more complex in prokaryotes or eukaryotes? 36. Cell specialization that occurs during embryonic development is called… Chapters 15-17: Evolution 37. Define ...
... 34. What makes a cell specialized in a multicellular organism? Why do specialized cells regulate the expression of genes? 35. Is gene regulation more complex in prokaryotes or eukaryotes? 36. Cell specialization that occurs during embryonic development is called… Chapters 15-17: Evolution 37. Define ...
LS50B Concept questions: end of section 6: Solutions
... tools have been developed that makes certain types of experimental tests possible in some model organisms but not in other organisms and because they have been chosen for certain characteristics that make them amenable to rearing in the lab. However, model organisms represent only a very tiny fracti ...
... tools have been developed that makes certain types of experimental tests possible in some model organisms but not in other organisms and because they have been chosen for certain characteristics that make them amenable to rearing in the lab. However, model organisms represent only a very tiny fracti ...
Genetic Drift
... Consider, for example, humans. In West Africa, where malaria is prevalent, the Duffy antigen provides some resistance to the disease, and this allele is thus present in nearly all of the West African population. In contrast, Europeans have either the allele Fya or Fyb, because malaria is almost ...
... Consider, for example, humans. In West Africa, where malaria is prevalent, the Duffy antigen provides some resistance to the disease, and this allele is thus present in nearly all of the West African population. In contrast, Europeans have either the allele Fya or Fyb, because malaria is almost ...
Natural Selection and Evidence to Support Evolution
... automatic change in population • Due to variation that already exist in a population a change in the environment is going to cause the more beneficial trait to become more dominant • Changes in physical appearance (phenotype) occur when there is a change in the genotype (mutation) and the environmen ...
... automatic change in population • Due to variation that already exist in a population a change in the environment is going to cause the more beneficial trait to become more dominant • Changes in physical appearance (phenotype) occur when there is a change in the genotype (mutation) and the environmen ...
Life Science 7a notes 4
... All organisms have a certain amount of living space needed for them to survive. - They must get the needs of life (water, food, mates) from their living space. - Members of a community compete for living space and sometimes organisms don’t survive. - Stronger animals will prey on weaker animals. Hum ...
... All organisms have a certain amount of living space needed for them to survive. - They must get the needs of life (water, food, mates) from their living space. - Members of a community compete for living space and sometimes organisms don’t survive. - Stronger animals will prey on weaker animals. Hum ...
Koinophilia

Koinophilia is an evolutionary hypothesis concerning sexual selection which proposes that animals seeking mate preferentially choose individuals with a minimum of unusual features. Koinophilia intends to explain the clustering of organisms into species and other issues described by Darwin's Dilemma. The term derives from the Greek, koinos, ""the usual"", and philos, ""fondness"".Natural selection causes beneficial inherited features to become more common and eventually replace their disadvantageous counterparts. A sexually-reproducing animal would be expected to avoid individuals with unusual features, and to prefer to mate with individuals displaying a predominance of common or average features. This means that mates displaying mutant features are also avoided. This is advantageous because most mutations that manifest themselves as changes in appearance, functionality or behavior, are disadvantageous. Because it is impossible to judge whether a new mutation is beneficial or not, koinophilic animals avoid them all, at the cost of avoiding the occasional beneficial mutation. Thus, koinophilia, although not infallible in its ability to distinguish fit from unfit mates, is a good strategy when choosing a mate. A koinophilic choice ensures that offspring are likely to inherit features that have been successful in the past.Koinophilia differs from assortative mating, where ""like prefers like"". If like preferred like, leucistic animals (such as white peacocks) would be sexually attracted to one another, and a leucistic subspecies would come into being. Koinophilia predicts that this is unlikely because leucistic animals are attracted to the average in the same way as other animals. Since non-leucistic animals are not attracted by leucism, few leucistic individuals find mates, and leucistic lineages will rarely form.Koinophilia provides simple explanations for the rarity of speciation (in particular Darwin's Dilemma), evolutionary stasis, punctuated equilibria, and the evolution of cooperation. Koinophilia might also contribute to the maintenance of sexual reproduction, preventing its reversion to the much simpler and inherently more advantageous asexual form of reproduction.The koinophilia hypothesis is supported by research into the physical attractiveness of human faces by Judith Langlois and her co-workers. They found that the average of two human faces was more attractive than either of the faces from which that average was derived. The more faces (of the same gender and age) that were used in the averaging process the more attractive and appealing the average face became. This work into averageness supports koinophilia as an explanation of what constitutes a beautiful face, and how the individuality of a face is recognized.