Human Genetic Disorders - Madison Central High School
... not usually have symptoms of the disease ...
... not usually have symptoms of the disease ...
Many islands in the Indian and Pacific oceans have or used to have
... Lamarck’s explanation of the evolution of the long legs of wading birds. Change occurs because an animal passes on to its offspring changes it acquires during its lifetime. The long legs of wading birds arose when those animals’ ancestors responded to a need to feed on fish. In their attempt to get ...
... Lamarck’s explanation of the evolution of the long legs of wading birds. Change occurs because an animal passes on to its offspring changes it acquires during its lifetime. The long legs of wading birds arose when those animals’ ancestors responded to a need to feed on fish. In their attempt to get ...
File - Covenant Science Stuff
... a. had a brain volume of around 940 cc and b. was the first hominin to leave Africa. 6. The oldest known fossils of hominins outside of Africa are about 1.8 million years old. 7. Homo neanderthalensis, commonly called Neanderthals a. lived in Europe from about 350,000 to 28,000 years ago when they w ...
... a. had a brain volume of around 940 cc and b. was the first hominin to leave Africa. 6. The oldest known fossils of hominins outside of Africa are about 1.8 million years old. 7. Homo neanderthalensis, commonly called Neanderthals a. lived in Europe from about 350,000 to 28,000 years ago when they w ...
Non-Random Mating
... becomes small, close relatives end up mating with one another, and those relatives likely carry the same recessive deleterious alleles. When the relatives mate, the offspring may inherit two copies of the same recessive deleterious allele and suffer the consequences of expressing the deleterious all ...
... becomes small, close relatives end up mating with one another, and those relatives likely carry the same recessive deleterious alleles. When the relatives mate, the offspring may inherit two copies of the same recessive deleterious allele and suffer the consequences of expressing the deleterious all ...
Keywords Lectures 7 and 8
... Although the frequencies of mutants are initially rare, and most are lost from the population, nevertheless some increase in frequency due to genetic drift effects and also selection (see below and later lecture on molecular evolution). migration: is the movement of individuals from one population i ...
... Although the frequencies of mutants are initially rare, and most are lost from the population, nevertheless some increase in frequency due to genetic drift effects and also selection (see below and later lecture on molecular evolution). migration: is the movement of individuals from one population i ...
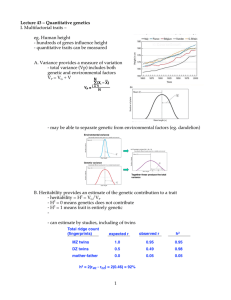
1 Lecture 43 â Quantitative genetics I. Multifactorial traits â eg
... - may be able to separate genetic from environmental factors (eg. dandelion) ...
... - may be able to separate genetic from environmental factors (eg. dandelion) ...
Why organisms age: Evolution of senescence under positive
... fitness [27]. Nevertheless, it should be stressed that AP alleles can be very rare and the absence of such alleles in the mutation accumulation experiments does not necessarily contradict AP theory [28]. It is therefore particularly interesting to look at long-term selection studies that apply selec ...
... fitness [27]. Nevertheless, it should be stressed that AP alleles can be very rare and the absence of such alleles in the mutation accumulation experiments does not necessarily contradict AP theory [28]. It is therefore particularly interesting to look at long-term selection studies that apply selec ...
Natural Selection Notes
... Does every organism get a chance to pass on it’s genes? Why / why not? What could this have to do with evolution? ...
... Does every organism get a chance to pass on it’s genes? Why / why not? What could this have to do with evolution? ...
Test Info Sheet
... ultrasound in fetuses of families with no family history and mutation detection has identified ITGB4 or ITGA6 mutations,10-13 although this has not been described in EB cases with plectin defects. In one rare case, EB-PA with desquamative enteropathy but without skin disease has been reported.14 Inh ...
... ultrasound in fetuses of families with no family history and mutation detection has identified ITGB4 or ITGA6 mutations,10-13 although this has not been described in EB cases with plectin defects. In one rare case, EB-PA with desquamative enteropathy but without skin disease has been reported.14 Inh ...
Darwin`s Finches
... supply of small seeds. Thus, natural selection began to favor birds that could also cope with larger seeds and with other food resources. In time, the bird’s bill sizes changed through the process of natural selection as each population began to adapt more closely to the different kinds of food foun ...
... supply of small seeds. Thus, natural selection began to favor birds that could also cope with larger seeds and with other food resources. In time, the bird’s bill sizes changed through the process of natural selection as each population began to adapt more closely to the different kinds of food foun ...
Sequence variation: Looking for effects of
... Drosophila [2]; it is not known whether this is true for the fluctuating fitness model. These considerations raise two questions: Are such patterns general? And how can we test between different possible explanations of the patterns? Surveys of DNA sequence variation are rapidly being extended beyon ...
... Drosophila [2]; it is not known whether this is true for the fluctuating fitness model. These considerations raise two questions: Are such patterns general? And how can we test between different possible explanations of the patterns? Surveys of DNA sequence variation are rapidly being extended beyon ...
CHAPTER 25
... This may make it more difficult for the species to respond in a positive way to changes in the environment. Species that are approaching extinction also face a bottleneck as their numbers decrease. The loss of genetic diversity may make it even more difficult for the species to rebound. C21. Answer: ...
... This may make it more difficult for the species to respond in a positive way to changes in the environment. Species that are approaching extinction also face a bottleneck as their numbers decrease. The loss of genetic diversity may make it even more difficult for the species to rebound. C21. Answer: ...
Molecular Biology Primer 3
... physical trait – which means that sometimes genes can be passed down to the next generation even if a parent does not physically express the gene. • Balanced Polymorphism is the ability of natural selection to preserve genetic variation. For example, natural selection in one species of finch keeps b ...
... physical trait – which means that sometimes genes can be passed down to the next generation even if a parent does not physically express the gene. • Balanced Polymorphism is the ability of natural selection to preserve genetic variation. For example, natural selection in one species of finch keeps b ...
Reproduction in Plants and Animals
... tiny insects eating some of his plants. The gardener isn’t worried—a few insects are not a concern. But when he comes back several weeks later, his plants are covered in these small insects. There are at least ten times as many insects as there were several weeks ago! Where did all of these insects ...
... tiny insects eating some of his plants. The gardener isn’t worried—a few insects are not a concern. But when he comes back several weeks later, his plants are covered in these small insects. There are at least ten times as many insects as there were several weeks ago! Where did all of these insects ...
Conceptual Questions C1. Answer: A gene pool is all of the genes
... make it more difficult for the species to respond in a positive way to changes in the environment. Species that are approaching extinction also face a bottleneck as their numbers decrease. The loss of genetic diversity may make it even more difficult for the species to rebound. C21. Answer: When two ...
... make it more difficult for the species to respond in a positive way to changes in the environment. Species that are approaching extinction also face a bottleneck as their numbers decrease. The loss of genetic diversity may make it even more difficult for the species to rebound. C21. Answer: When two ...
T3 Scopes Weeks 1-9
... B Water trapped behind the dam causes the marine ecosystem to move inland. C The flooding in August through November causes marine life to be destroyed. D The water temperature of the sea has increased 8-2 (12A) In a forest community, a shelf fungus and a slug live on the side of a decaying tree tru ...
... B Water trapped behind the dam causes the marine ecosystem to move inland. C The flooding in August through November causes marine life to be destroyed. D The water temperature of the sea has increased 8-2 (12A) In a forest community, a shelf fungus and a slug live on the side of a decaying tree tru ...
Teacher notes and student sheets
... explains evolution is natural selection. There is always variation between individuals in the same species. Some individuals will have characteristics which give them a better chance of surviving in a particular environment. Those individuals that survive will reproduce and pass on their characteris ...
... explains evolution is natural selection. There is always variation between individuals in the same species. Some individuals will have characteristics which give them a better chance of surviving in a particular environment. Those individuals that survive will reproduce and pass on their characteris ...
Evolution Cards - Nuffield Foundation
... explains evolution is natural selection. There is always variation between individuals in the same species. Some individuals will have characteristics which give them a better chance of surviving in a particular environment. Those individuals that survive will reproduce and pass on their characteris ...
... explains evolution is natural selection. There is always variation between individuals in the same species. Some individuals will have characteristics which give them a better chance of surviving in a particular environment. Those individuals that survive will reproduce and pass on their characteris ...
LSE-03
... a) Define the following terms: i) Adaptive value ii) Selection coefficient iii) Genetic drift iv) Gene flow b) An allele has an adaptive value of 0.45. What is its Selection coefficient? c) Explain with the help of an example how genetic drift affects gene frequencies in populations. ...
... a) Define the following terms: i) Adaptive value ii) Selection coefficient iii) Genetic drift iv) Gene flow b) An allele has an adaptive value of 0.45. What is its Selection coefficient? c) Explain with the help of an example how genetic drift affects gene frequencies in populations. ...
Classification Chapter 18
... Limpets have an internal anatomy more like snails, which are MOLLUSKS. Because of these characteristics, scientists have concluded that barnacles are more closely related to crabs than to MOLLUSKS http://siena.earth.rochester.edu/ees207/Gastropoda/ ...
... Limpets have an internal anatomy more like snails, which are MOLLUSKS. Because of these characteristics, scientists have concluded that barnacles are more closely related to crabs than to MOLLUSKS http://siena.earth.rochester.edu/ees207/Gastropoda/ ...
Reproductive barriers between two sympatric beetle species
... reproductive isolation and (b) the inheritance mode of preference and hostspecific performance, using a joint-scaling test. Each species preferred almost exclusively its host plant, creating strong prezygotic isolation between them, and suggesting that speciation may occur at least partly in sympatr ...
... reproductive isolation and (b) the inheritance mode of preference and hostspecific performance, using a joint-scaling test. Each species preferred almost exclusively its host plant, creating strong prezygotic isolation between them, and suggesting that speciation may occur at least partly in sympatr ...
Koinophilia

Koinophilia is an evolutionary hypothesis concerning sexual selection which proposes that animals seeking mate preferentially choose individuals with a minimum of unusual features. Koinophilia intends to explain the clustering of organisms into species and other issues described by Darwin's Dilemma. The term derives from the Greek, koinos, ""the usual"", and philos, ""fondness"".Natural selection causes beneficial inherited features to become more common and eventually replace their disadvantageous counterparts. A sexually-reproducing animal would be expected to avoid individuals with unusual features, and to prefer to mate with individuals displaying a predominance of common or average features. This means that mates displaying mutant features are also avoided. This is advantageous because most mutations that manifest themselves as changes in appearance, functionality or behavior, are disadvantageous. Because it is impossible to judge whether a new mutation is beneficial or not, koinophilic animals avoid them all, at the cost of avoiding the occasional beneficial mutation. Thus, koinophilia, although not infallible in its ability to distinguish fit from unfit mates, is a good strategy when choosing a mate. A koinophilic choice ensures that offspring are likely to inherit features that have been successful in the past.Koinophilia differs from assortative mating, where ""like prefers like"". If like preferred like, leucistic animals (such as white peacocks) would be sexually attracted to one another, and a leucistic subspecies would come into being. Koinophilia predicts that this is unlikely because leucistic animals are attracted to the average in the same way as other animals. Since non-leucistic animals are not attracted by leucism, few leucistic individuals find mates, and leucistic lineages will rarely form.Koinophilia provides simple explanations for the rarity of speciation (in particular Darwin's Dilemma), evolutionary stasis, punctuated equilibria, and the evolution of cooperation. Koinophilia might also contribute to the maintenance of sexual reproduction, preventing its reversion to the much simpler and inherently more advantageous asexual form of reproduction.The koinophilia hypothesis is supported by research into the physical attractiveness of human faces by Judith Langlois and her co-workers. They found that the average of two human faces was more attractive than either of the faces from which that average was derived. The more faces (of the same gender and age) that were used in the averaging process the more attractive and appealing the average face became. This work into averageness supports koinophilia as an explanation of what constitutes a beautiful face, and how the individuality of a face is recognized.