Grade: 3rd Activity #: 1 Activity Title: Studying Rocks and Minerals
... that do dissolve rapidly are therefore considered soluble and this can be diagnostic. Solubility is not just limited to water. Many acids are capable of dissolving minerals where water has no effect. Of course, identification of minerals using solubility is a test that could destroy the specimen, if ...
... that do dissolve rapidly are therefore considered soluble and this can be diagnostic. Solubility is not just limited to water. Many acids are capable of dissolving minerals where water has no effect. Of course, identification of minerals using solubility is a test that could destroy the specimen, if ...
Guided Notes on Volcanoes
... • Convergence causes the crust to descend into the mantle and melt. The magma generated is forced upward and forms volcanoes when it reaches the surface. ...
... • Convergence causes the crust to descend into the mantle and melt. The magma generated is forced upward and forms volcanoes when it reaches the surface. ...
Jeopardy
... During the rock cycle, a collision between two continental plates could force one plate down toward the heat of the mantle, producing this type of rock. ...
... During the rock cycle, a collision between two continental plates could force one plate down toward the heat of the mantle, producing this type of rock. ...
... presence of an anorthositic highland crust and of samples enriched in incompatible elements K, REE, and P (KREEP) give strong support to the magma ocean concept (e.g. Warren, 1985). The Moon’s relative small pressure range and dry magma ocean composition increased the stability range of plagioclase ...
igneous rocks - Math/Science Nucleus
... large or small magma chambers inside the crust and upper mantle of the Earth. These chambers never reach the surface, unless they have cooled and the surface rocks are eroded away. The term pluton refers to large and small chambers. A batholith is the largest chamber, while a laccolith is a smaller ...
... large or small magma chambers inside the crust and upper mantle of the Earth. These chambers never reach the surface, unless they have cooled and the surface rocks are eroded away. The term pluton refers to large and small chambers. A batholith is the largest chamber, while a laccolith is a smaller ...
41. Comparison of the Chemical and Magnetic Stratigraphy of DSDP
... Deep drilling into oceanic basement at Sites 332 (36° 53 'N, 33° 39 "W; 583 m) and 395 (22 ° 45 'N, 46 ° 05 'W; 572 m) provides an opportunity to compare the origin of a major portion of Layer 2 at two places on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. The sites are similar in that basement at each consists dominant ...
... Deep drilling into oceanic basement at Sites 332 (36° 53 'N, 33° 39 "W; 583 m) and 395 (22 ° 45 'N, 46 ° 05 'W; 572 m) provides an opportunity to compare the origin of a major portion of Layer 2 at two places on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. The sites are similar in that basement at each consists dominant ...
Did mantle plume magmatism help trigger the Great Oxidation Event?
... by the Matachewan LIP, we can calculate that the number of moles of O2 produced by these reactions would have 7.72 × 1016. This equates to a mass of O2 of 2.47 × 1015 kg. The mass of the modern atmosphere is approximately 5.15 × 1018 kg (Trenberth and Smith, 2005) of which 23% (1.18 × 1018 kg) is O2 ...
... by the Matachewan LIP, we can calculate that the number of moles of O2 produced by these reactions would have 7.72 × 1016. This equates to a mass of O2 of 2.47 × 1015 kg. The mass of the modern atmosphere is approximately 5.15 × 1018 kg (Trenberth and Smith, 2005) of which 23% (1.18 × 1018 kg) is O2 ...
Geology and Nonrenewable Mineral Resources - Baxley
... no new discoveries; rising prices Recycle; increase reserves by improved mining technology, higher prices, and new discoveries ...
... no new discoveries; rising prices Recycle; increase reserves by improved mining technology, higher prices, and new discoveries ...
Yellowstone Geologic History
... Yellowstone contains over 10,000 thermal features, and between 300 and 500 active geysers. Conservatively more than 55% of the world's geysers reside in Yellowstone National Park. The park's thermal features lie in the only essentially-undisturbed geyser basin in the world. Unlike Iceland or New Zea ...
... Yellowstone contains over 10,000 thermal features, and between 300 and 500 active geysers. Conservatively more than 55% of the world's geysers reside in Yellowstone National Park. The park's thermal features lie in the only essentially-undisturbed geyser basin in the world. Unlike Iceland or New Zea ...
An Overview of Yellowstone Geologic History
... Yellowstone contains over 10,000 thermal features, and between 300 and 500 active geysers. Conservatively more than 55% of the world's geysers reside in Yellowstone National Park. The park's thermal features lie in the only essentially-undisturbed geyser basin in the world. Unlike Iceland or New Zea ...
... Yellowstone contains over 10,000 thermal features, and between 300 and 500 active geysers. Conservatively more than 55% of the world's geysers reside in Yellowstone National Park. The park's thermal features lie in the only essentially-undisturbed geyser basin in the world. Unlike Iceland or New Zea ...
NWGS Pasco Basin
... and solidification of each flow and result from variations in cooling rates, degassing, thermal contraction, and interaction with surface water. They are distinct from features formed by tectonic processes. Columbia River Basalt Group flows typically consist of a flow top, a dense, flow interior, and a fl ...
... and solidification of each flow and result from variations in cooling rates, degassing, thermal contraction, and interaction with surface water. They are distinct from features formed by tectonic processes. Columbia River Basalt Group flows typically consist of a flow top, a dense, flow interior, and a fl ...
PDF sample
... up the Earth’s crust, or outer layer, are slowly crunching together with enormous force. The Atlantic is getting wider, pushing the Americas further west. Yet the Earth is not getting any bigger because as the American plates crash into the Pacific plates, the thinner, denser ocean plates are driven ...
... up the Earth’s crust, or outer layer, are slowly crunching together with enormous force. The Atlantic is getting wider, pushing the Americas further west. Yet the Earth is not getting any bigger because as the American plates crash into the Pacific plates, the thinner, denser ocean plates are driven ...
Chapter 16
... Natural Hazards: Volcanic Eruptions Impacts: • Ejects – hot ash, hot gases, lava, chunks of rocks. • Mudflows • Acid Rain • Earthquakes Some eruptions violent, others not so violent ...
... Natural Hazards: Volcanic Eruptions Impacts: • Ejects – hot ash, hot gases, lava, chunks of rocks. • Mudflows • Acid Rain • Earthquakes Some eruptions violent, others not so violent ...
Geology of the Seal Rock Area
... (Figure 5). At the seaward edge of the basin, silt, sand and gravel formed deltas near river mouths, with mud and clay settling farther from shore. Rivers brought pumice and other volcanic material into the sea from ongoing eruptions in the nearby western Cascades. These sediments were likewise comp ...
... (Figure 5). At the seaward edge of the basin, silt, sand and gravel formed deltas near river mouths, with mud and clay settling farther from shore. Rivers brought pumice and other volcanic material into the sea from ongoing eruptions in the nearby western Cascades. These sediments were likewise comp ...
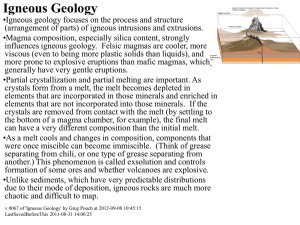
Igneous Geology - Illinois Wesleyan University
... of square kilometers. Basalt flows like this frequently show columnar jointing. (see text). –There are not any currently active regions of flood basalts. •Falls are extensive layers of ash and other debris, usually transported by air and are often very violent. Typical of granite/rhyolite. They can ...
... of square kilometers. Basalt flows like this frequently show columnar jointing. (see text). –There are not any currently active regions of flood basalts. •Falls are extensive layers of ash and other debris, usually transported by air and are often very violent. Typical of granite/rhyolite. They can ...
Rocks and Minerals Readings
... Igneous Rocks Igneous rocks are formed from melted rock that has cooled and solidified. Igneous rocks are the most abundant type of rock on Earth. Igneous rocks are classified by their chemical composition (amount of silica) and crystal size (extrusive or intrusive). Rocks melt when they are buried ...
... Igneous Rocks Igneous rocks are formed from melted rock that has cooled and solidified. Igneous rocks are the most abundant type of rock on Earth. Igneous rocks are classified by their chemical composition (amount of silica) and crystal size (extrusive or intrusive). Rocks melt when they are buried ...
Ch7_Metamorphism
... C) He will continue to change with new external conditions (increased heat and pressure will cause further change) ...
... C) He will continue to change with new external conditions (increased heat and pressure will cause further change) ...
Lesson 1: Minerals and Rocks
... sedimentary rock differ from those of metamorphic rock? Sedimentary rocks are formed when loose pieces of rocks and minerals are squeezed and cemented together; metamorphic rocks develop from other rocks when great heat and pressure change the original structure, texture, and composition. ...
... sedimentary rock differ from those of metamorphic rock? Sedimentary rocks are formed when loose pieces of rocks and minerals are squeezed and cemented together; metamorphic rocks develop from other rocks when great heat and pressure change the original structure, texture, and composition. ...
Gabbroic Pegmatite Intrusions, Iberia Abyssal
... Exclusive of rodingitization, the main pegmatite contains 40–70% calcic andesine, 25–35% kaersutitic amphibole (Mg# 60–70), 5–25% augite (Mg# 70–80) and 1–2% ilmenite. The dikelets are more magnesian (Mg# up to 82 in kaersutite and 88 in augite). Most indications are that the high Mg#s in the dikele ...
... Exclusive of rodingitization, the main pegmatite contains 40–70% calcic andesine, 25–35% kaersutitic amphibole (Mg# 60–70), 5–25% augite (Mg# 70–80) and 1–2% ilmenite. The dikelets are more magnesian (Mg# up to 82 in kaersutite and 88 in augite). Most indications are that the high Mg#s in the dikele ...
Geology and petrography of Adolerite dyke, Hyderabad granitic
... the Eastern Dharwar Craton (EDC) , is considered as largest granitic pluton of Indian subcontinent. (S.B. Singh, et.al).Region of this batholithic craton is composed with granitic gneisses and unclassified granites. This region was apparently formed due to extensive lower crustal remelting of permob ...
... the Eastern Dharwar Craton (EDC) , is considered as largest granitic pluton of Indian subcontinent. (S.B. Singh, et.al).Region of this batholithic craton is composed with granitic gneisses and unclassified granites. This region was apparently formed due to extensive lower crustal remelting of permob ...
Magnesium-rich Basalts on Mercury
... liquidus temperatures and low viscosities (relative to typical values of lavas on Earth) lead Stockstill-Cahill and colleagues to predict that the Mg-rich lavas originated from high temperature (>1500 o C) source regions in the mantle and if not cooled before reaching the surface would have erupted ...
... liquidus temperatures and low viscosities (relative to typical values of lavas on Earth) lead Stockstill-Cahill and colleagues to predict that the Mg-rich lavas originated from high temperature (>1500 o C) source regions in the mantle and if not cooled before reaching the surface would have erupted ...
Tertiary Igneous Chronology of the Great Basin of Western United
... TECTONIC SETTING The older igneous rocks (high-K andesites and rhyolite ash-flow tuffs) were extruded on an erosion surface of low to moderate relief in a region that had been tectonically stable for many millions of years. Eruption was not accompanied by any marked increase in tectonism, except in ...
... TECTONIC SETTING The older igneous rocks (high-K andesites and rhyolite ash-flow tuffs) were extruded on an erosion surface of low to moderate relief in a region that had been tectonically stable for many millions of years. Eruption was not accompanied by any marked increase in tectonism, except in ...
Basalt

Basalt (pronounced /bəˈsɔːlt/, /ˈbæsɒlt/, /ˈbæsɔːlt/, or /ˈbeɪsɔːlt/)is a common extrusive igneous (volcanic) rock formed from the rapid cooling of basaltic lava exposed at or very near the surface of a planet or moon. Flood basalt describes the formation in a series of lava basalt flows.