Week 7: Igneous Rocks - Elderslie High School
... upper layers. This is known as the Law of ____________________________. 3. Order the steps involved in turning sediment into sedimentary rock _________ Sediment settles and is deposited into layers _________ Erosion transports the weathered material _________ Minerals dissolve, cementing sediment in ...
... upper layers. This is known as the Law of ____________________________. 3. Order the steps involved in turning sediment into sedimentary rock _________ Sediment settles and is deposited into layers _________ Erosion transports the weathered material _________ Minerals dissolve, cementing sediment in ...
Rocks and Minerals - Georgia Standards
... Sedimentary, igneous, metamorphic, rock composition, mineral formation, pressure, rock cycle, Minerals can be identified by their physical properties. Igneous rocks are dominated by silicate minerals. Rocks are composed of minerals. Minerals are the building blocks of rocks. The rock cycle explains ...
... Sedimentary, igneous, metamorphic, rock composition, mineral formation, pressure, rock cycle, Minerals can be identified by their physical properties. Igneous rocks are dominated by silicate minerals. Rocks are composed of minerals. Minerals are the building blocks of rocks. The rock cycle explains ...
lecture 01s - Kean University
... Plates move0ºrelative to each other at90º a very slow but continuous Average about 5 centimeters (2 inches) per year Seven major lithospheric plates Cooler, denser slabs of oceanic lithosphere descend into the mantle Seven or so smaller ones. Plates are in motion and change in shape and size Largest ...
... Plates move0ºrelative to each other at90º a very slow but continuous Average about 5 centimeters (2 inches) per year Seven major lithospheric plates Cooler, denser slabs of oceanic lithosphere descend into the mantle Seven or so smaller ones. Plates are in motion and change in shape and size Largest ...
Return
... and made today’s continents. Theory says all continents drifted apart and continue to do so. ...
... and made today’s continents. Theory says all continents drifted apart and continue to do so. ...
9 Early Earth
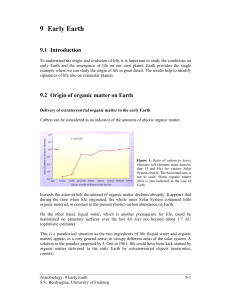
... analogous to sulfide deposits produced at present-day midocean ridges. To produce such deposits, the ocean-floor pressure should be higher than the critical pressure, which is equivalent to an ocean depth of about 3 km (Harrison 1999). Micrometeorites (dust particles less than a millimeter in size) ...
... analogous to sulfide deposits produced at present-day midocean ridges. To produce such deposits, the ocean-floor pressure should be higher than the critical pressure, which is equivalent to an ocean depth of about 3 km (Harrison 1999). Micrometeorites (dust particles less than a millimeter in size) ...
Introduction to Plate Tectonics
... drift and seafloor spreading into a coherent model; it has revolutionized geologists’ understanding of continents, ocean basins, mountains, and Earth history. Context: The theory of plate tectonics did not gain wide scientific interest until the 1960s. subduction Definition: When an oceanic plate co ...
... drift and seafloor spreading into a coherent model; it has revolutionized geologists’ understanding of continents, ocean basins, mountains, and Earth history. Context: The theory of plate tectonics did not gain wide scientific interest until the 1960s. subduction Definition: When an oceanic plate co ...
Paleozoic large igneous provinces of Northern Eurasia: Correlation
... 0921-8181/$ – see front matter © 2012 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved. ...
... 0921-8181/$ – see front matter © 2012 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved. ...
6-Plate Tectonics
... plates of India and Eurasia began to collide with each other. As a result, the shallow seabeds of the Tethys Sea rapidly folded and raised into longitudinal ridges and valleys. A second major phase occurred about 25 MY, and the last phase started about 800 TY. The former sea-bed was elevated to form ...
... plates of India and Eurasia began to collide with each other. As a result, the shallow seabeds of the Tethys Sea rapidly folded and raised into longitudinal ridges and valleys. A second major phase occurred about 25 MY, and the last phase started about 800 TY. The former sea-bed was elevated to form ...
Andy Modaff, Tony Schneider, Richie Moore, and
... receiving antenna which is then received by a computer. The information received determines the distance of precipitation relative to the location of the receiving antenna. A specific form of radar, called a Doppler radar, utilizes the Doppler effect. The Doppler effect is the change in pitch or fre ...
... receiving antenna which is then received by a computer. The information received determines the distance of precipitation relative to the location of the receiving antenna. A specific form of radar, called a Doppler radar, utilizes the Doppler effect. The Doppler effect is the change in pitch or fre ...
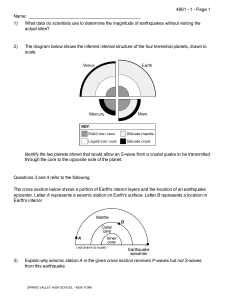
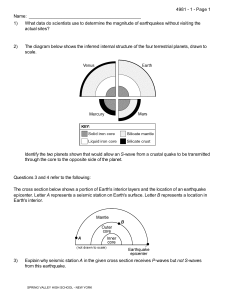
Name: 1) What data do scientists use to determine the magnitude of
... The Three Sisters are 10,000-foot volcanic mountain peaks in Oregon. Volcanic eruptions began building the Three Sisters from andesitic lava and cinders 700,000 years ago. The last major eruption occurred 2,000 years ago. West of the Three Sisters peaks, geologists have recently discovered that Eart ...
... The Three Sisters are 10,000-foot volcanic mountain peaks in Oregon. Volcanic eruptions began building the Three Sisters from andesitic lava and cinders 700,000 years ago. The last major eruption occurred 2,000 years ago. West of the Three Sisters peaks, geologists have recently discovered that Eart ...
Name: 1) What data do scientists use to determine the magnitude of
... The Three Sisters are 10,000-foot volcanic mountain peaks in Oregon. Volcanic eruptions began building the Three Sisters from andesitic lava and cinders 700,000 years ago. The last major eruption occurred 2,000 years ago. West of the Three Sisters peaks, geologists have recently discovered that Eart ...
... The Three Sisters are 10,000-foot volcanic mountain peaks in Oregon. Volcanic eruptions began building the Three Sisters from andesitic lava and cinders 700,000 years ago. The last major eruption occurred 2,000 years ago. West of the Three Sisters peaks, geologists have recently discovered that Eart ...
To get a better understanding of this whole process, I would like you
... 2. Explain the significance of paleomagnetic banding. Paleomagnetic banding shows that at one point, older rock further from the ridge had been formed at the divergent boundary- only way to explain the zebra like banding of alternating magnetic orientation of the sea floor. 3. Explain the process of ...
... 2. Explain the significance of paleomagnetic banding. Paleomagnetic banding shows that at one point, older rock further from the ridge had been formed at the divergent boundary- only way to explain the zebra like banding of alternating magnetic orientation of the sea floor. 3. Explain the process of ...
File
... Metamorphism of sedimentary rocks —shales undergo the most spectacular metamorphosis of all the rocks. The reason is that the clay minerals form at Earth surface temperature (T) (030 C) and pressure (P) (1 bar) by weathering of pre-existing rocks. Thus, clay minerals are grossly out of equilibriu ...
... Metamorphism of sedimentary rocks —shales undergo the most spectacular metamorphosis of all the rocks. The reason is that the clay minerals form at Earth surface temperature (T) (030 C) and pressure (P) (1 bar) by weathering of pre-existing rocks. Thus, clay minerals are grossly out of equilibriu ...
1 IDS 102 Plate Tectonics Questions Part I: Observations
... Part I: Observations- Four maps of world are positioned around the room. Answer the questions associated with each map and record your general observations about the maps. World topography- this map portrays the elevation of the Earth’s surface by color. See the scale along the side of the map for t ...
... Part I: Observations- Four maps of world are positioned around the room. Answer the questions associated with each map and record your general observations about the maps. World topography- this map portrays the elevation of the Earth’s surface by color. See the scale along the side of the map for t ...
hssv0301t_powerpres - Deer Creek High School
... • Volcanoes are often located near tectonic plate boundaries where plates are either colliding or separating from one another. • The majority of the world’s active volcanoes on land are located along tectonic plate boundaries that surround the Pacific Ocean. ...
... • Volcanoes are often located near tectonic plate boundaries where plates are either colliding or separating from one another. • The majority of the world’s active volcanoes on land are located along tectonic plate boundaries that surround the Pacific Ocean. ...
continental drift
... When ocean crust converges with continental crust, the more dense ocean crust subducts into a deep trench beneath the less dense continental crust. As the oceanic “slab” moves down into the mantle, it melts at about 100 km depth. The melted rock or magma moves up within the crust and eventually erup ...
... When ocean crust converges with continental crust, the more dense ocean crust subducts into a deep trench beneath the less dense continental crust. As the oceanic “slab” moves down into the mantle, it melts at about 100 km depth. The melted rock or magma moves up within the crust and eventually erup ...
Investigation 6: What Happens When Plates Collide? Investigation
... 18. Which plate is overriding and which plate is subducting in the U.S. Pacific Northwest at the convergent plate boundary? Support your answer with evidence from the GIS map. (Hint: Where are the volcanoes located?) ...
... 18. Which plate is overriding and which plate is subducting in the U.S. Pacific Northwest at the convergent plate boundary? Support your answer with evidence from the GIS map. (Hint: Where are the volcanoes located?) ...
Tectonic–climatic interaction

Tectonic–climatic interaction is the interrelationship between tectonic processes and the climate system. The tectonic processes in question include orogenesis, volcanism, and erosion, while relevant climatic processes include atmospheric circulation, orographic lift, monsoon circulation and the rain shadow effect. As the geological record of past climate changes over millions of years is sparse and poorly resolved, many questions remain unresolved regarding the nature of tectonic-climate interaction, although it is an area of active research by geologists and palaeoclimatologists.