Cenozoic magmatism in the western Ross Embayment:
... [2] Major continental rifts are usually associated with either short-lived large igneous provinces of continental flood basalts, or long-lasting alkaline magmatic provinces such as the Basin and Range of North America and the East African Rift. In both conditions, a connection between lithospheric e ...
... [2] Major continental rifts are usually associated with either short-lived large igneous provinces of continental flood basalts, or long-lasting alkaline magmatic provinces such as the Basin and Range of North America and the East African Rift. In both conditions, a connection between lithospheric e ...
Continents On The Move
... lithosphere and the destruction of old lithosphere. The oldest sea-floor rocks on Earth are only about 200 million years old, because oceanic crust continuously recycles into the mantle at subduction zones (Figure 3). Rocks as old as about 4 billion years are found on continents, because subduction ...
... lithosphere and the destruction of old lithosphere. The oldest sea-floor rocks on Earth are only about 200 million years old, because oceanic crust continuously recycles into the mantle at subduction zones (Figure 3). Rocks as old as about 4 billion years are found on continents, because subduction ...
tectonics teachers notes
... Discuss the human response to the Bam earthquake. 92,000 tents and 200,000 blankets were supplied to help keep people warm. Other aid in the form of 56,000 items of clothing, 51,000 oil heaters and 400,000 ready meals, plus bread, rice, sugar and other food was supplied. Later a 250-bed emergency ho ...
... Discuss the human response to the Bam earthquake. 92,000 tents and 200,000 blankets were supplied to help keep people warm. Other aid in the form of 56,000 items of clothing, 51,000 oil heaters and 400,000 ready meals, plus bread, rice, sugar and other food was supplied. Later a 250-bed emergency ho ...
Main menu
... When an oceanic plate and a continental plate collide, the oceanic plate is forced underneath the continental plate. The oceanic plate melts in the magma. This is called subduction. The continental plate forms fold mountains. ...
... When an oceanic plate and a continental plate collide, the oceanic plate is forced underneath the continental plate. The oceanic plate melts in the magma. This is called subduction. The continental plate forms fold mountains. ...
Introduction - San Jose State University
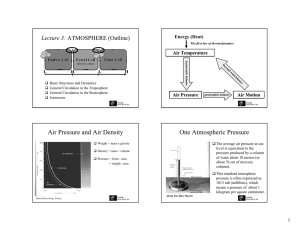
... T - Temperature (K) For moist air one can use the virtual temperature; Tv=T(1+0.61r) r- water vapor mixing ratio Virtual temperatures allows for the use of R for dry air in ideal gas law. ...
... T - Temperature (K) For moist air one can use the virtual temperature; Tv=T(1+0.61r) r- water vapor mixing ratio Virtual temperatures allows for the use of R for dry air in ideal gas law. ...
Chapter 10 Resource: Forces Shaping Earth
... Volcanoes can form when plates of Earth’s lithosphere sink into the mantle at subduction zones. These are referred to as subduction volcanoes. The deeper the plates sink, the hotter they become. Eventually the plates begin to melt, becoming magma. Because this newly formed magma is less dense than t ...
... Volcanoes can form when plates of Earth’s lithosphere sink into the mantle at subduction zones. These are referred to as subduction volcanoes. The deeper the plates sink, the hotter they become. Eventually the plates begin to melt, becoming magma. Because this newly formed magma is less dense than t ...
Plate Tectonics - Hobbs Municipal Schools
... Explain to the students that along the plate boundaries there are fault zones where the earth slips. ...
... Explain to the students that along the plate boundaries there are fault zones where the earth slips. ...
Tectonics of the Indonesian Region
... trench lies along the east side of northeasternmost Sulawesi and the Sangir island arc that trends from there to south-central Mindanao. This Sangir subduction system is imbricate in the north with respect to the Mindanao-northeast Halmahera Benioff zone, and convergent in the south with respect to ...
... trench lies along the east side of northeasternmost Sulawesi and the Sangir island arc that trends from there to south-central Mindanao. This Sangir subduction system is imbricate in the north with respect to the Mindanao-northeast Halmahera Benioff zone, and convergent in the south with respect to ...
Trace element and isotope geochemistry of gabbro
... Relics of igneous textures, mineral and bulk-rock compositional variations indicate a comagmatic origin for the gabbro-derived granulites. They can be generally recognized as cumulitic rocks with negligible amounts of residual trapped liquid, on the basis of low SiO2/A1203 ratios (Kempton and Harmon ...
... Relics of igneous textures, mineral and bulk-rock compositional variations indicate a comagmatic origin for the gabbro-derived granulites. They can be generally recognized as cumulitic rocks with negligible amounts of residual trapped liquid, on the basis of low SiO2/A1203 ratios (Kempton and Harmon ...
File
... • Volcanoes are often located near tectonic plate boundaries where plates are either colliding or separating from one another. • The majority of the world’s active volcanoes on land are located along tectonic plate boundaries that surround the Pacific Ocean. ...
... • Volcanoes are often located near tectonic plate boundaries where plates are either colliding or separating from one another. • The majority of the world’s active volcanoes on land are located along tectonic plate boundaries that surround the Pacific Ocean. ...
1st Sem (unit I)
... The Mantle: The portion of the interior beyond the crust is called the mantle. It is separated from the crust by a boundary, called Moho’s discontinuity. The mantle is about 2900 km thick. It is divided into two sections: the upper mantle and the Lower mantle. These are separated by another boundary ...
... The Mantle: The portion of the interior beyond the crust is called the mantle. It is separated from the crust by a boundary, called Moho’s discontinuity. The mantle is about 2900 km thick. It is divided into two sections: the upper mantle and the Lower mantle. These are separated by another boundary ...
Introduction to Oceanography 112
... The exact pattern of motion in the mantle isn’t well-defined yet. However there is little disagreement that it moves very slowly in some way. The motion is thought to be convective. Convection is vertical motion (motion against gravity) driven by differences in temperature where hot material lies be ...
... The exact pattern of motion in the mantle isn’t well-defined yet. However there is little disagreement that it moves very slowly in some way. The motion is thought to be convective. Convection is vertical motion (motion against gravity) driven by differences in temperature where hot material lies be ...
Activity 4
... the continent grows larger at its edge. Continents also grow as the igneous rock of volcanoes and batholiths are added to the continent above the subduction zone, as described above.The growth of a continent along its edge in these ways is called continental accretion.This has been going on through ...
... the continent grows larger at its edge. Continents also grow as the igneous rock of volcanoes and batholiths are added to the continent above the subduction zone, as described above.The growth of a continent along its edge in these ways is called continental accretion.This has been going on through ...
Chapter 4
... Tectonic plates are composed of the crust and the upper most mantle that functions as a brittle solid. These plates can be composed of oceanic crust, continental crust or a mixture of both. The Oceanic Crust is thinner and normally underlies the world’s oceans, while the Continental Crust is thicker ...
... Tectonic plates are composed of the crust and the upper most mantle that functions as a brittle solid. These plates can be composed of oceanic crust, continental crust or a mixture of both. The Oceanic Crust is thinner and normally underlies the world’s oceans, while the Continental Crust is thicker ...
Percolating Through Volcanic Subsurface Rocks, Seawater is
... (“submersibles”) in areas where faults and fractures how reactions change as physical and chemical have exposed rocks on the seafloor that were once conditions are varied, and they help scientists dein the deep subsurface. The disadvantage of this termine how the chemistry of the fluid and the rock ...
... (“submersibles”) in areas where faults and fractures how reactions change as physical and chemical have exposed rocks on the seafloor that were once conditions are varied, and they help scientists dein the deep subsurface. The disadvantage of this termine how the chemistry of the fluid and the rock ...
Growth of Archean continental crust in oceanic
... Understanding the origin of the continental crust is one of the key objectives of earth sciences because as a land species we owe our existence to continents. In addition, change in the volume of the continental crust and distribution of continents on Earth’s surface have profound effects on major g ...
... Understanding the origin of the continental crust is one of the key objectives of earth sciences because as a land species we owe our existence to continents. In addition, change in the volume of the continental crust and distribution of continents on Earth’s surface have profound effects on major g ...
09_Testbank
... 56) How fast do plates move on Earth? A) a few centimeters per year B) a few millimeters per century C) a few kilometers per century D) quite fast, but only during earthquakes E) about 1 mile per hour Answer: A 57) How long, approximately, do geologists estimate it takes for the entire seafloor to ...
... 56) How fast do plates move on Earth? A) a few centimeters per year B) a few millimeters per century C) a few kilometers per century D) quite fast, but only during earthquakes E) about 1 mile per hour Answer: A 57) How long, approximately, do geologists estimate it takes for the entire seafloor to ...
Tectonic–climatic interaction

Tectonic–climatic interaction is the interrelationship between tectonic processes and the climate system. The tectonic processes in question include orogenesis, volcanism, and erosion, while relevant climatic processes include atmospheric circulation, orographic lift, monsoon circulation and the rain shadow effect. As the geological record of past climate changes over millions of years is sparse and poorly resolved, many questions remain unresolved regarding the nature of tectonic-climate interaction, although it is an area of active research by geologists and palaeoclimatologists.