Document
... The theory of plate tectonics states that the crust of the Earth is composed of moving plates. These plates move along the lithosphere (Earth’s crust and upper mantle) and the asthenosphere (the plastic-like layer beneath the lithosphere). This theory also says that these plates are always in motion ...
... The theory of plate tectonics states that the crust of the Earth is composed of moving plates. These plates move along the lithosphere (Earth’s crust and upper mantle) and the asthenosphere (the plastic-like layer beneath the lithosphere). This theory also says that these plates are always in motion ...
Plate Tectonics Unit Project
... 5.4.8.D.2: Major geological events, such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and mountain building, result from the motion of plates. Sea floor spreading, revealed in mapping of the MidAtlantic Ridge, and subduction zones are evidence for the theory of plate tectonics. ...
... 5.4.8.D.2: Major geological events, such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and mountain building, result from the motion of plates. Sea floor spreading, revealed in mapping of the MidAtlantic Ridge, and subduction zones are evidence for the theory of plate tectonics. ...
pHeT – Plate Tectonics
... a) Which type of crust has a higher temperature? ___________________________ b) Which type of crust has a higher composition of silica? ___________________________ c) Which type of crust has a higher composition of iron? ___________________________ d) Which type of crust is thicker? ________________ ...
... a) Which type of crust has a higher temperature? ___________________________ b) Which type of crust has a higher composition of silica? ___________________________ c) Which type of crust has a higher composition of iron? ___________________________ d) Which type of crust is thicker? ________________ ...
22.4 Plate Tectonics
... • Later on, geologists discovered fossils of species of landbased plants and animals on continents separated by large ...
... • Later on, geologists discovered fossils of species of landbased plants and animals on continents separated by large ...
plate boundaries
... The Earth’s crust is divided into _________________major plates, which are moved in various directions. Plates move at very _____________________ rates – from about _________ to _________ centimeters per year; At one time in geologic history the ____________________________ were ____________________ ...
... The Earth’s crust is divided into _________________major plates, which are moved in various directions. Plates move at very _____________________ rates – from about _________ to _________ centimeters per year; At one time in geologic history the ____________________________ were ____________________ ...
Subduction - Géosciences Montpellier
... first termed subduction by A. Amstutz in 1951 when discussing the evolution of alpine structures, allows nearly all oceanic lithosphere to be recycled into the mantle. By contrast, only the lower portion of the continental lithosphere (the lithospheric mantle) may, under certain conditions, be transp ...
... first termed subduction by A. Amstutz in 1951 when discussing the evolution of alpine structures, allows nearly all oceanic lithosphere to be recycled into the mantle. By contrast, only the lower portion of the continental lithosphere (the lithospheric mantle) may, under certain conditions, be transp ...
Mysteries of the mountains
... contributed not only to our knowledge of how mountain ranges are formed and vast plateaux elevated, but also to how the opening and closing of seaways between major land masses can change circulation patterns for both ocean currents and air masses, driving regional and perhaps global climate change. ...
... contributed not only to our knowledge of how mountain ranges are formed and vast plateaux elevated, but also to how the opening and closing of seaways between major land masses can change circulation patterns for both ocean currents and air masses, driving regional and perhaps global climate change. ...
2. Plate tectonics
... Explains many of Earth’s large-scale surface features and related phenomena Central idea of the theory Earth’s surface is broken up into some large pieces called tectonic plates Earth plate is composed of Crust and part of upper Mantle Ocean plates: 8-10 km thickness with dense rock ...
... Explains many of Earth’s large-scale surface features and related phenomena Central idea of the theory Earth’s surface is broken up into some large pieces called tectonic plates Earth plate is composed of Crust and part of upper Mantle Ocean plates: 8-10 km thickness with dense rock ...
Plate Tectonics Lab Activity The theory of plate tectonics states that
... 2. Name a specific location on the Earth where this kind of boundary activity takes place. ...
... 2. Name a specific location on the Earth where this kind of boundary activity takes place. ...
Doug - Cal State LA - Instructional Web Server
... • As new crust is formed, normal and reverse polarities are preserved in the rock record • 1963, Vine & Matthews observe magnetic anomalies in oceanic crust ...
... • As new crust is formed, normal and reverse polarities are preserved in the rock record • 1963, Vine & Matthews observe magnetic anomalies in oceanic crust ...
What are the causes of plate motion and what
... MOTION AND WHAT FEATURES DO THEY FORM? Plate tectonics is a scientific theory that describes the large-scale motions of Earth's lithosphere. The model builds on the concepts of continental drift, developed during the first few decades of the 20th century. The geoscientific community accepted the the ...
... MOTION AND WHAT FEATURES DO THEY FORM? Plate tectonics is a scientific theory that describes the large-scale motions of Earth's lithosphere. The model builds on the concepts of continental drift, developed during the first few decades of the 20th century. The geoscientific community accepted the the ...
to an introductory Plate Tectonics exercise for a
... Convergent – When plates come together. One plate will be subducted under the other. This forms features such as mountains, island arc systems, and ocean trenches. Divergent – When plates move apart. This creates spreading centers that show up as sea floor spreading zones in oceanic crust, and r ...
... Convergent – When plates come together. One plate will be subducted under the other. This forms features such as mountains, island arc systems, and ocean trenches. Divergent – When plates move apart. This creates spreading centers that show up as sea floor spreading zones in oceanic crust, and r ...
hal-insu.archives-ouvertes.fr - HAL
... motion of eastern Tibet and western Sichuan, south-eastward motion in northern Yunan and south to south-eastward motion in southern Yunan (Zhang et al. 2004; Gan et al. 2007; ArRajehi et al. 2010) (Figure 1c). Several strike-slip fault zones, which arrange from the convergent domain north of Tibet, ...
... motion of eastern Tibet and western Sichuan, south-eastward motion in northern Yunan and south to south-eastward motion in southern Yunan (Zhang et al. 2004; Gan et al. 2007; ArRajehi et al. 2010) (Figure 1c). Several strike-slip fault zones, which arrange from the convergent domain north of Tibet, ...
8-3 Subunit Test - Darlington Middle School
... other c. high folded mountains where two plates are pushing toward each other d. strike-slip faulting where two plates are sliding sideways past each other 11. (8-3.7/8) The fault seen in Figure 1 is classified as a… a. Lateral Fault b. Normal Fault c. Reverse Fault d. Strike-Slip Fault 12. (8-3.6) ...
... other c. high folded mountains where two plates are pushing toward each other d. strike-slip faulting where two plates are sliding sideways past each other 11. (8-3.7/8) The fault seen in Figure 1 is classified as a… a. Lateral Fault b. Normal Fault c. Reverse Fault d. Strike-Slip Fault 12. (8-3.6) ...
Chapter 10 Whole Notes
... Scientists have identified 15 major tectonic plates. These plate boundaries are defined by studying data from earthquakes. Tectonic plate boundaries may be in the middle of the ocean floor, around the edges of continents, or even within continents 3 Major Types of Plate Boundaries (1) Divergent Boun ...
... Scientists have identified 15 major tectonic plates. These plate boundaries are defined by studying data from earthquakes. Tectonic plate boundaries may be in the middle of the ocean floor, around the edges of continents, or even within continents 3 Major Types of Plate Boundaries (1) Divergent Boun ...
divergent boundary
... Basalt is much denser than the granite. Because of this the less dense continents ride on the denser oceanic plates. ...
... Basalt is much denser than the granite. Because of this the less dense continents ride on the denser oceanic plates. ...
Plate Tectonics - Welcome to Ms. Duff's Classroom!
... between the two plates, forcing the two plates apart and creating mid-oceanic mountain ridges as it cools and solidifies. At the mid-oceanic ridges new crust is created. But Earth’s crust is in balance, so that as new crustal material is created, old crust is “removed”. This happens at the trenches, ...
... between the two plates, forcing the two plates apart and creating mid-oceanic mountain ridges as it cools and solidifies. At the mid-oceanic ridges new crust is created. But Earth’s crust is in balance, so that as new crustal material is created, old crust is “removed”. This happens at the trenches, ...
file: RE Lab Plate Tect Maps v2
... Please do not consult a map of known plate boundaries while working on this exercise. The point is not to create a perfect map of what other scientists have deduced, but to see what you can deduce for yourself, and how much you can learn while doing so. I think you’ll be surprised at what you can fi ...
... Please do not consult a map of known plate boundaries while working on this exercise. The point is not to create a perfect map of what other scientists have deduced, but to see what you can deduce for yourself, and how much you can learn while doing so. I think you’ll be surprised at what you can fi ...
S6E5e. Recognize that lithospheric plates constantly move and
... alizations/es0807/es0807page01.cfm?chapter_no=visualization ...
... alizations/es0807/es0807page01.cfm?chapter_no=visualization ...
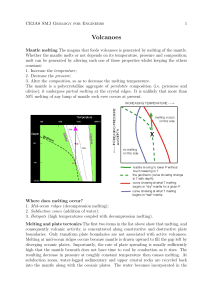
Volcanoes
... boundaries. Only transform plate boundaries are not associated with active volcanoes. Melting at mid-ocean ridges occurs because mantle is drawn upward to fill the gap left by diverging oceanic plates. Importantly, the rate of plate spreading is usually sufficiently high that the mantle beneath does ...
... boundaries. Only transform plate boundaries are not associated with active volcanoes. Melting at mid-ocean ridges occurs because mantle is drawn upward to fill the gap left by diverging oceanic plates. Importantly, the rate of plate spreading is usually sufficiently high that the mantle beneath does ...
What happens at the different plate boundaries?
... Collision boundaries happen when two plates of similar weight move together (i.e. two continental plates). This causes the material between them to buckle and rise up, forming fold mountains. The Himalayas are an example of a chain of fold mountains. They have been formed by the African plate collid ...
... Collision boundaries happen when two plates of similar weight move together (i.e. two continental plates). This causes the material between them to buckle and rise up, forming fold mountains. The Himalayas are an example of a chain of fold mountains. They have been formed by the African plate collid ...
22. Stratigraphy and Tectonic Interpretations of Multichannel
... er trench slope and named it the chain-saw mechanism. The normal fault system of the graben thus still appears to be active even after subduction beneath the inner slope. Tensional events have occurred in the upper portion of the subduction plate as far as 100 km landward from the trench axis (Yoshi ...
... er trench slope and named it the chain-saw mechanism. The normal fault system of the graben thus still appears to be active even after subduction beneath the inner slope. Tensional events have occurred in the upper portion of the subduction plate as far as 100 km landward from the trench axis (Yoshi ...
Plate Tectonics - NewPath Learning
... Alfred Wegener’s theory of continental drift was convincing; however, he could not explain how continental drift occurred. A number of discoveries throughout the 20th century led to a completely new theory, known as plate tectonics. This theory was first proposed in the early 1960’s. As explained ab ...
... Alfred Wegener’s theory of continental drift was convincing; however, he could not explain how continental drift occurred. A number of discoveries throughout the 20th century led to a completely new theory, known as plate tectonics. This theory was first proposed in the early 1960’s. As explained ab ...
Oceanic trench
The oceanic trenches are hemispheric-scale long but narrow topographic depressions of the sea floor. They are also the deepest parts of the ocean floor. Oceanic trenches are a distinctive morphological feature of convergent plate boundaries, along which lithospheric plates move towards each other at rates that vary from a few mm to over ten cm per year. A trench marks the position at which the flexed, subducting slab begins to descend beneath another lithospheric slab. Trenches are generally parallel to a volcanic island arc, and about 200 km (120 mi) from a volcanic arc. Oceanic trenches typically extend 3 to 4 km (1.9 to 2.5 mi) below the level of the surrounding oceanic floor. The greatest ocean depth to be sounded is in the Challenger Deep of the Mariana Trench, at a depth of 11,034 m (36,201 ft) below sea level. Oceanic lithosphere moves into trenches at a global rate of about 3 km2/yr.