Chapter 1
... b. Organizing—the process of deciding where decisions will be made, who will perform what jobs and tasks, and who will report to whom in the company. 1. By organizing effectively, managers can better coordinate human, material, and information resources. c. Leading—involves communicating with and mo ...
... b. Organizing—the process of deciding where decisions will be made, who will perform what jobs and tasks, and who will report to whom in the company. 1. By organizing effectively, managers can better coordinate human, material, and information resources. c. Leading—involves communicating with and mo ...
Definitions MCHB Leadership Competencies
... DEFINITION MCH Leadership Competency 5: Communication Communication is the verbal, nonverbal, and written sharing of information. The communication process consists of a sender who encodes and presents the message and the receiver(s) who receives and decodes the message. Communication involves both ...
... DEFINITION MCH Leadership Competency 5: Communication Communication is the verbal, nonverbal, and written sharing of information. The communication process consists of a sender who encodes and presents the message and the receiver(s) who receives and decodes the message. Communication involves both ...
TCF-59 - Exemplar Global
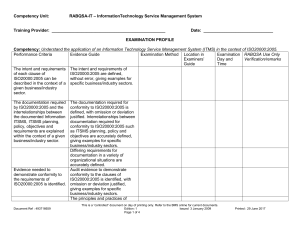
... documented ITSMS and documented ITSMS and service management information assets included in the processes belonging to an scope of the ITSMS is accurately organization, its customers defined, giving examples for and suppliers is explained. specific business/industry sectors. ...
... documented ITSMS and documented ITSMS and service management information assets included in the processes belonging to an scope of the ITSMS is accurately organization, its customers defined, giving examples for and suppliers is explained. specific business/industry sectors. ...
Chapter 9 Succession Management Learning Objectives
... focus on duties, skills, job experience, and responsibilities required to perform the job Not adequate since ...
... focus on duties, skills, job experience, and responsibilities required to perform the job Not adequate since ...
Competency Framework for Non-Profit Organizations: an
... Every organization is as good as the people who work for that organization (Drucker 1993). An NPO thrives on motivation that is predominantly intrinsic and to some extent extrinsic. But a below average compensation may deteriorate personal motivation and values (Kaplan 2001) owing to an individual’s ...
... Every organization is as good as the people who work for that organization (Drucker 1993). An NPO thrives on motivation that is predominantly intrinsic and to some extent extrinsic. But a below average compensation may deteriorate personal motivation and values (Kaplan 2001) owing to an individual’s ...
hodges Succession Planning Presentation
... Assessing current organizational culture may determine how it needs to change in the future. Allows you to develop a set of cultural related leadership criteria and development approaches. ...
... Assessing current organizational culture may determine how it needs to change in the future. Allows you to develop a set of cultural related leadership criteria and development approaches. ...
PowerPoint model of a poster paper, which you may use to prepare
... objectives and priorities, the strategies and the responsibilities of the maintenance activities and by implementing them through planning, control and supervision the improvement methods taking into consideration several economical aspects of the organisation. Maintenance management competencies re ...
... objectives and priorities, the strategies and the responsibilities of the maintenance activities and by implementing them through planning, control and supervision the improvement methods taking into consideration several economical aspects of the organisation. Maintenance management competencies re ...
Competency_Mapping - Eclat HR Management Trendz
... Behaviour Indicators Based upon what outstanding individuals actually do • The competency definitions are based upon outstanding current performance in the organization. These competencies do not reflect someone's management theory or an academic idea of what it takes to do the job well, but rather ...
... Behaviour Indicators Based upon what outstanding individuals actually do • The competency definitions are based upon outstanding current performance in the organization. These competencies do not reflect someone's management theory or an academic idea of what it takes to do the job well, but rather ...
The development of career competencies in the
... Career competences are not static, they need to be renewed taking into consideration a person’s career goals and plans of actions needed to achieve them. This is determined by boundaryless career development process which is continuing and its success is determined by individual’s personal character ...
... Career competences are not static, they need to be renewed taking into consideration a person’s career goals and plans of actions needed to achieve them. This is determined by boundaryless career development process which is continuing and its success is determined by individual’s personal character ...