Molecular Gas in the Large Magellanic Cloud
... Magellanic Cloud (LMC). The observations were conducted at the Mopra Telescope as part of the Magellanic Mopra Assessment (MAGMA) project, which has obtained high resolution (45′′ ) maps of the ...
... Magellanic Cloud (LMC). The observations were conducted at the Mopra Telescope as part of the Magellanic Mopra Assessment (MAGMA) project, which has obtained high resolution (45′′ ) maps of the ...
Galaxy Assembly through Mergers
... another challenge, even though, given their massive nature, they may be responsible for the high mass end of the mass function. Understanding the latter in the local universe, dubbed dry mergers, constitutes the basis of this work. With the availability of large dedicated surveys such as the Sloan D ...
... another challenge, even though, given their massive nature, they may be responsible for the high mass end of the mass function. Understanding the latter in the local universe, dubbed dry mergers, constitutes the basis of this work. With the availability of large dedicated surveys such as the Sloan D ...
Niraj D. Welikala Thesis - D-Scholarship@Pitt
... The role of star formation in galaxies is clearly a fundamental component of their evolution, although it is becoming clear that galaxy environments may also play a significant role. To explore the relationship between environment and star formation in galaxies, I use the photometric information con ...
... The role of star formation in galaxies is clearly a fundamental component of their evolution, although it is becoming clear that galaxy environments may also play a significant role. To explore the relationship between environment and star formation in galaxies, I use the photometric information con ...
The VIMOS Ultra-Deep Survey (VUDS): Fast Increase in the Fraction
... (Stark et al. 2010; 2011; Pentericci et al. 2011) are based on a hybrid photometric-spectroscopic technique: the denominator of the fraction (i.e., the total number of star–forming galaxies at those redshifts) is only constrained by photometry, and thus its determination relies on the strong assumpt ...
... (Stark et al. 2010; 2011; Pentericci et al. 2011) are based on a hybrid photometric-spectroscopic technique: the denominator of the fraction (i.e., the total number of star–forming galaxies at those redshifts) is only constrained by photometry, and thus its determination relies on the strong assumpt ...
... Secular evolution is not confined to barred and oval galaxies. Bars can selfdestruct by building up the central mass concentration, so secular evolution may have happened even if no bar is seen today. Global spiral structure also makes galaxies evolve, albeit more slowly than do bars. These processe ...
The correlation between galaxy morphology and star
... acquisition of three photometric bands. In contrast, the SED selection is observationally much more expensive because it requires a large number of photometric bands to yield robust photometric redshifts as well as robust measures of the stellar population properties, i.e. stellar mass, star–formati ...
... acquisition of three photometric bands. In contrast, the SED selection is observationally much more expensive because it requires a large number of photometric bands to yield robust photometric redshifts as well as robust measures of the stellar population properties, i.e. stellar mass, star–formati ...
THE UV-OPTICAL COLOR MAGNITUDE DIAGRAM. II. PHYSICAL
... derived from the SDSS spectroscopic sample to measure the distribution of galaxies in the local universe (z < 0:25) and their physical properties as a function of specific star formation rate (SFR /M? ) and stellar mass (M? ). Throughout this study our emphasis is on the properties of galaxies on an ...
... derived from the SDSS spectroscopic sample to measure the distribution of galaxies in the local universe (z < 0:25) and their physical properties as a function of specific star formation rate (SFR /M? ) and stellar mass (M? ). Throughout this study our emphasis is on the properties of galaxies on an ...
environmental effects on galaxy evolution in nearby clusters
... The environmental effects on galaxy evolution in nearby clusters are investigated using a multiwavelength dataset. The present analysis is focused on the properties of three (Abell 1367, Virgo and Coma) among the best studied clusters in the local Universe. Due to the variety of their environmental ...
... The environmental effects on galaxy evolution in nearby clusters are investigated using a multiwavelength dataset. The present analysis is focused on the properties of three (Abell 1367, Virgo and Coma) among the best studied clusters in the local Universe. Due to the variety of their environmental ...
The most metal-poor galaxies
... no HII regions and very low surface brightness, the only available spectroscopic method hitherto, has been to study individual bright stars which are within reach in nearby galaxies only. In more distant galaxies, individual stars are not observable and the metallicity has to be inferred from either ...
... no HII regions and very low surface brightness, the only available spectroscopic method hitherto, has been to study individual bright stars which are within reach in nearby galaxies only. In more distant galaxies, individual stars are not observable and the metallicity has to be inferred from either ...
PhD thesis
... 1 Massive star formation 1.1 Massive star formation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.1.1 Observational massive star-forming features . . . . . . 1.2 Ionized gas . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.2.1 Thermal emission from ionized gas . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.2. ...
... 1 Massive star formation 1.1 Massive star formation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.1.1 Observational massive star-forming features . . . . . . 1.2 Ionized gas . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.2.1 Thermal emission from ionized gas . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.2. ...
Preliminary Talk Abstract Book - MoCA
... of baryons in relatively small dark matter halos (1010 to1012 M⊙ ) is probably the most crucial process to produce realistic galaxies. ...
... of baryons in relatively small dark matter halos (1010 to1012 M⊙ ) is probably the most crucial process to produce realistic galaxies. ...
Infrared Astronomy
... 1. Introduction – the discovery and use of infrared ............................................................................... 1 1.1 Herschel and his discovery of infrared ................................................................................... 1 1.2 Black body radiation – the first ...
... 1. Introduction – the discovery and use of infrared ............................................................................... 1 1.1 Herschel and his discovery of infrared ................................................................................... 1 1.2 Black body radiation – the first ...
Mid-infrared Properties of Seyfert Galaxies: the IRAS 12um Sample
... Study in more detail the “20μm peakers” decomposing their SED to the various dust components SHAO - Oct 2010 ...
... Study in more detail the “20μm peakers” decomposing their SED to the various dust components SHAO - Oct 2010 ...
Mapping the Pathways of Galaxy Transformation Across Time and
... University of Arizona, Steward Observatory ...
... University of Arizona, Steward Observatory ...
The visibility of Lyman Alpha Emitters: constraining reionization
... GADGET-2 to obtain the physical properties of z ≃ 5.7 galaxies, (b) a dust model that took into account the entire star formation history of each galaxy to calculate its dust enrichment and, (c) a RT code (CRASH) to obtain the ionization fields to calculate the IGM Lyα transmission for each galaxy, ...
... GADGET-2 to obtain the physical properties of z ≃ 5.7 galaxies, (b) a dust model that took into account the entire star formation history of each galaxy to calculate its dust enrichment and, (c) a RT code (CRASH) to obtain the ionization fields to calculate the IGM Lyα transmission for each galaxy, ...
Galaxies - hwchemistry
... distant galaxy, astronomers rush to observe it. – Studies show that type Ia supernovae—caused by the collapse of a white dwarf—all reach about the same absolute magnitude at maximum. – By searching for Cepheids and other distance indicators in nearby galaxies where type Ia supernovae have occurred, ...
... distant galaxy, astronomers rush to observe it. – Studies show that type Ia supernovae—caused by the collapse of a white dwarf—all reach about the same absolute magnitude at maximum. – By searching for Cepheids and other distance indicators in nearby galaxies where type Ia supernovae have occurred, ...
Star Formation in the Milky Way and Nearby Galaxies Further
... The past decade has witnessed an unprecedented stream of new observational information on star formation on all scales, thanks in no small part to new facilities such as the Galaxy Evolution Explorer (GALEX), the Spitzer Space Telescope, and the Herschel Space Observatory; the introduction of powerf ...
... The past decade has witnessed an unprecedented stream of new observational information on star formation on all scales, thanks in no small part to new facilities such as the Galaxy Evolution Explorer (GALEX), the Spitzer Space Telescope, and the Herschel Space Observatory; the introduction of powerf ...
Chapter 5 The Evolutionary Paths Of Nearby Galaxies
... To investigate whether the quenching is due to AGN feedback or environmental effects, I divide the sample according to nuclear activity and Hi content (Figure 5.1, top row, central and right panel, respectively), as described in Chapter 2. For M∗ & 1010 M⊙ , AGN-host spirals are uniformly distribute ...
... To investigate whether the quenching is due to AGN feedback or environmental effects, I divide the sample according to nuclear activity and Hi content (Figure 5.1, top row, central and right panel, respectively), as described in Chapter 2. For M∗ & 1010 M⊙ , AGN-host spirals are uniformly distribute ...
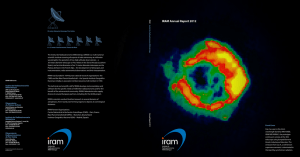
IRAM Annual Report 2012
... processes in the interstellar medium (ISM). As ISM regions are often characterized by a high diversity of molecular species, identifying the spectral signature and diagnosing their chemical properties is becoming a challenge in itself. The majority of interstellar molecules have been detected at mil ...
... processes in the interstellar medium (ISM). As ISM regions are often characterized by a high diversity of molecular species, identifying the spectral signature and diagnosing their chemical properties is becoming a challenge in itself. The majority of interstellar molecules have been detected at mil ...
T3-Cosmic Star Formation History
... of the complex evolutionary phases of individual galaxy subpopulations. The modern version of this technique relies on some basic properties of stellar populations and dusty starburst galaxies: 1. The UV-continuum emission in all but the oldest galaxies is dominated by short-lived massive stars. The ...
... of the complex evolutionary phases of individual galaxy subpopulations. The modern version of this technique relies on some basic properties of stellar populations and dusty starburst galaxies: 1. The UV-continuum emission in all but the oldest galaxies is dominated by short-lived massive stars. The ...
The Multitude of Molecular Hydrogen Knots in the Helix Nebula 1
... the central star appeared slightly more amorphous in their structure with less well defined rims. The culmination of these optical observations appear to support the theory that these knots were initially formed earlier by instabilities at the ionization front or perhaps by the interaction of the fa ...
... the central star appeared slightly more amorphous in their structure with less well defined rims. The culmination of these optical observations appear to support the theory that these knots were initially formed earlier by instabilities at the ionization front or perhaps by the interaction of the fa ...
IRAM Annual Report 2011
... number abundance of 6 10-5 as found in other ULIRGs. The water line is found to be strong only in the red velocity component, with an intensity ratio I(H2O)/I(CO) ~0.5, suggesting a strong local FIR radiation field, possibly from an active nuclear component. The authors also report the highest redsh ...
... number abundance of 6 10-5 as found in other ULIRGs. The water line is found to be strong only in the red velocity component, with an intensity ratio I(H2O)/I(CO) ~0.5, suggesting a strong local FIR radiation field, possibly from an active nuclear component. The authors also report the highest redsh ...
Observational evidence for AGN feedback in early
... strength of the Balmer lines that is at least what expected by recombination theory. From the fit to the stellar continuum and absorption features, we measure the line-of-sight velocity dispersions. From subtraction of the emission-line spectrum from the observed one, we get the clean absorption lin ...
... strength of the Balmer lines that is at least what expected by recombination theory. From the fit to the stellar continuum and absorption features, we measure the line-of-sight velocity dispersions. From subtraction of the emission-line spectrum from the observed one, we get the clean absorption lin ...
ROSAT Ian R. Stevens* and David K. Strickland*
... superimposed on the Digitized Sky Survey image. The X-ray contours are from the longer 6.2-ks observation only. As noted by Turner et al. (1993), there are several point sources in the vicinity of the nucleus of NGC 1365. In addition to a strong central point source there is also low-surface-brightn ...
... superimposed on the Digitized Sky Survey image. The X-ray contours are from the longer 6.2-ks observation only. As noted by Turner et al. (1993), there are several point sources in the vicinity of the nucleus of NGC 1365. In addition to a strong central point source there is also low-surface-brightn ...
Megamaser
A megamaser is a type of astrophysical maser, which is a naturally occurring source of stimulated spectral line emission. Megamasers are distinguished from astrophysical masers by their large isotropic luminosity. Megamasers have typical luminosities of 103 solar luminosities (L☉), which is 100 million times brighter than masers in the Milky Way, hence the prefix mega. Likewise, the term kilomaser is used to describe masers outside the Milky Way that have luminosities of order L☉, or thousands of times stronger than the average maser in the Milky Way, gigamaser is used to describe masers billions of times stronger than the average maser in the Milky Way, and extragalactic maser encompasses all masers found outside the Milky Way. Most known extragalactic masers are megamasers, and the majority of megamasers are hydroxyl (OH) megamasers, meaning the spectral line being amplified is one due to a transition in the hydroxyl molecule. There are known megamasers for three other molecules: water (H2O), formaldehyde (H2CO), and methine (CH).Water megamasers were the first type of megamaser discovered. The first water megamaser was found in 1979 in NGC 4945, a galaxy in the nearby Centaurus A/M83 Group. The first hydroxyl megamaser was found in 1982 in Arp 220, which is the nearest ultraluminous infrared galaxy to the Milky Way. All subsequent OH megamasers that have been discovered are also in luminous infrared galaxies, and there are a small number of OH kilomasers hosted in galaxies with lower infrared luminosities. Most luminous infrared galaxies have recently merged or interacted with another galaxy, and are undergoing a burst of star formation. Many of the characteristics of the emission in hydroxyl megamasers are distinct from that of hydroxyl masers within the Milky Way, including the amplification of background radiation and the ratio of hydroxyl lines at different frequencies. The population inversion in hydroxyl molecules is produced by far infrared radiation that results from absorption and re-emission of light from forming stars by surrounding interstellar dust. Zeeman splitting of hydroxyl megamaser lines may be used to measure magnetic fields in the masing regions, and this application represents the first detection of Zeeman splitting in a galaxy other than the Milky Way.Water megamasers and kilomasers are found primarily associated with active galactic nuclei, while galactic and weaker extragalactic water masers are found in star forming regions. Despite different environments, the circumstances that produce extragalactic water masers do not seem to be very different from those that produce galactic water masers. Observations of water megamasers have been used to make accurate measurements of distances to galaxies in order to provide constraints on the Hubble constant.