PLATE TECTONICS - New Jersey City University
... Apparent motion of north magnetic pole through time – Split in path – indicates continents split apart ...
... Apparent motion of north magnetic pole through time – Split in path – indicates continents split apart ...
Daily Warm-Ups #61-80
... Warm-Up #69 1. Complete the chart (3 facts about each of layer of Earth) Earth’s Layers Crust Mantle Outer Core Inner Core 3. What is the lithosphere? Warm-Up #70 1. Compare and contrast the lithosphere and asthenosphere. 2. How is the mantle heated? Draw a diagram to show this heating process. 3. ...
... Warm-Up #69 1. Complete the chart (3 facts about each of layer of Earth) Earth’s Layers Crust Mantle Outer Core Inner Core 3. What is the lithosphere? Warm-Up #70 1. Compare and contrast the lithosphere and asthenosphere. 2. How is the mantle heated? Draw a diagram to show this heating process. 3. ...
PT Answers
... Plate Tectonics Lab. SQ: 1. Eurasian & Indo-Australian; 2. No. America and Eurasia or So. America & Africa; 3. Eurasian & Pacific; 4. There are many along the Mid-Atlantic Ridge; 5. Divergent = ridges and rift valleys; 6. Pacific and No. American = transform-sliding; 7. The Atlantic Ocean is getting ...
... Plate Tectonics Lab. SQ: 1. Eurasian & Indo-Australian; 2. No. America and Eurasia or So. America & Africa; 3. Eurasian & Pacific; 4. There are many along the Mid-Atlantic Ridge; 5. Divergent = ridges and rift valleys; 6. Pacific and No. American = transform-sliding; 7. The Atlantic Ocean is getting ...
Journey to the centre Examining the crust
... Identical rocks and fossils dating from this time have been found in West Africa and eastern South America. This tells AFRICA ...
... Identical rocks and fossils dating from this time have been found in West Africa and eastern South America. This tells AFRICA ...
Constructing the Costa Rica-Nicaragua
... this happens, the mantle flow rates are very fast. This flow pattern cannot occur in a 2D model which can only represent a tectonic plate of infinite length, and hence with no edges. Have you experienced any problems while constructing these models? ...
... this happens, the mantle flow rates are very fast. This flow pattern cannot occur in a 2D model which can only represent a tectonic plate of infinite length, and hence with no edges. Have you experienced any problems while constructing these models? ...
Background Information
... Convergent – Convergent plate boundaries form when two tectonic plates come together and collide with each other. These boundaries can have different results depending on whether they form in continental crust or oceanic crust. ...
... Convergent – Convergent plate boundaries form when two tectonic plates come together and collide with each other. These boundaries can have different results depending on whether they form in continental crust or oceanic crust. ...
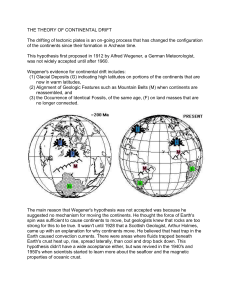
the theory of continental drift
... The main reason that Wegener's hypothesis was not accepted was because he suggested no mechanism for moving the continents. He thought the force of Earth's spin was sufficient to cause continents to move, but geologists knew that rocks are too strong for this to be true. It wasn't until 1928 that a ...
... The main reason that Wegener's hypothesis was not accepted was because he suggested no mechanism for moving the continents. He thought the force of Earth's spin was sufficient to cause continents to move, but geologists knew that rocks are too strong for this to be true. It wasn't until 1928 that a ...
CHAPTER 19 - PLATE TECTONICS
... boundaries. Plate convergence causes intense deformation and uplift of rocks creating mountain belts in a process called orogenesis. Orogenies may occur as a result of arc-continent convergence or continent-continent convergence. Brief discussion of migrating plate boundaries, plate size, and a summ ...
... boundaries. Plate convergence causes intense deformation and uplift of rocks creating mountain belts in a process called orogenesis. Orogenies may occur as a result of arc-continent convergence or continent-continent convergence. Brief discussion of migrating plate boundaries, plate size, and a summ ...
Shoe Box Model of Ocean Floor Spreading
... Styrofoam Model: Put the rough edges of two pieces of styrofoam together. Slowly slide the two pieces of styrofoam past each other in opposite directions. 1. This is a model of a ________________________ plate boundary. 2. Why do the rough edges of the styrofoam make a good model of a plate boundary ...
... Styrofoam Model: Put the rough edges of two pieces of styrofoam together. Slowly slide the two pieces of styrofoam past each other in opposite directions. 1. This is a model of a ________________________ plate boundary. 2. Why do the rough edges of the styrofoam make a good model of a plate boundary ...
oceanic crust - Science by Shaw
... – End at abyssal plain at depth of about 5 km – Lie upon oceanic crust ...
... – End at abyssal plain at depth of about 5 km – Lie upon oceanic crust ...
mantleplumes template.indd
... This proliferation of models can be viewed as “a sign of a hypothesis in trouble” (Foulger, 2003a). What seems certain is that a Hawaii-style model for plate motion over a deeplyrooted and fixed plume is now untenable as an explanation for both the NAIP and Iceland. It appears possible to interpret ...
... This proliferation of models can be viewed as “a sign of a hypothesis in trouble” (Foulger, 2003a). What seems certain is that a Hawaii-style model for plate motion over a deeplyrooted and fixed plume is now untenable as an explanation for both the NAIP and Iceland. It appears possible to interpret ...
Plate Tectonics and Sea Floor Spreading
... Altogether there are about 12 plates that make up the surface of the earth. Many of the continents have their own plate. For example there is a North American plate, which includes all of North America and extends out into the ocean on both sides. Europe and Asia share a plate, the Eurasian Plate. T ...
... Altogether there are about 12 plates that make up the surface of the earth. Many of the continents have their own plate. For example there is a North American plate, which includes all of North America and extends out into the ocean on both sides. Europe and Asia share a plate, the Eurasian Plate. T ...
Continental drift and a theory of convection
... To understand what has been discovered about the Earth consider some of the methods employed. On land, geologists have long studied surface rocks, They early resolved the problems of palaeontology, stratigraphy, and structure. They developed a precise relative time-scale, unrivalled in other science ...
... To understand what has been discovered about the Earth consider some of the methods employed. On land, geologists have long studied surface rocks, They early resolved the problems of palaeontology, stratigraphy, and structure. They developed a precise relative time-scale, unrivalled in other science ...
Dismantling the Deep Earth: Geochemical
... -Radiogenic isotopes (e.g., 87Sr/86Sr) and some trace element ratios (e.g., Nb/U) are little changed between solid and melt. -Lavas erupted at hotspots reveal significant isotopic and trace element heterogeneity. Therefore: the solid mantle sources of these lavas are heterogeneous. http://cache.eb.c ...
... -Radiogenic isotopes (e.g., 87Sr/86Sr) and some trace element ratios (e.g., Nb/U) are little changed between solid and melt. -Lavas erupted at hotspots reveal significant isotopic and trace element heterogeneity. Therefore: the solid mantle sources of these lavas are heterogeneous. http://cache.eb.c ...
Sample
... Our knowledge concerning the structure of Earth’s interior is based on the study of seismology. Thus we are able to define the major layers of Earth, including the inner core, outer core, mantle, and crust. The uppermost layer of Earth is known as the lithosphere, which is relatively strong and rigi ...
... Our knowledge concerning the structure of Earth’s interior is based on the study of seismology. Thus we are able to define the major layers of Earth, including the inner core, outer core, mantle, and crust. The uppermost layer of Earth is known as the lithosphere, which is relatively strong and rigi ...
Chapter 14: The Internal Processes
... a) Basically, where material is added, crust will sink, but it will rise when material is removed. b) Variety of causes result in isostatic reactions. (1) For example, deposition of sediment or accumulation of glacial ice vs. erosion as ice sheet melts or large body of water drains. C. Continental D ...
... a) Basically, where material is added, crust will sink, but it will rise when material is removed. b) Variety of causes result in isostatic reactions. (1) For example, deposition of sediment or accumulation of glacial ice vs. erosion as ice sheet melts or large body of water drains. C. Continental D ...
Geology 111 - A3 - Global geology at the turn of the century
... and had since been pushed apart. He pursued his theory with an almost religious zeal - combing the libraries for evidence to support it - largely ignoring the evidence that did not support it. He relied heavily on the matching geological patterns - sedimentary strata in South America matching those ...
... and had since been pushed apart. He pursued his theory with an almost religious zeal - combing the libraries for evidence to support it - largely ignoring the evidence that did not support it. He relied heavily on the matching geological patterns - sedimentary strata in South America matching those ...
Mantle plume
A mantle plume is a mechanism proposed in 1971 to explain volcanic regions of the earth that were not thought to be explicable by the then-new theory of plate tectonics. Some such volcanic regions lie far from tectonic plate boundaries, for example, Hawaii. Others represent unusually large-volume volcanism, whether on plate boundaries, e.g. Iceland, or basalt floods such as the Deccan or Siberian traps.A mantle plume is posited to exist where hot rock nucleates at the core-mantle boundary and rises through the Earth's mantle becoming a diapir in the Earth's crust. The currently active volcanic centers are known as ""hot spots"". In particular, the concept that mantle plumes are fixed relative to one another, and anchored at the core-mantle boundary, was thought to provide a natural explanation for the time-progressive chains of older volcanoes seen extending out from some such hot spots, such as the Hawaiian–Emperor seamount chain.The hypothesis of mantle plumes from depth is not universally accepted as explaining all such volcanism. It has required progressive hypothesis-elaboration leading to variant propositions such as mini-plumes and pulsing plumes. Another hypothesis for unusual volcanic regions is the ""Plate model"". This proposes shallower, passive leakage of magma from the mantle onto the Earth's surface where extension of the lithosphere permits it, attributing most volcanism to plate tectonic processes, with volcanoes far from plate boundaries resulting from intraplate extension.