Central Nervous System
... Refractory period – short period of time after an action potential when a threshold stimulus will NOT trigger another action potential. a.Limits frequency b.Ensures the impulse is only transmitted in one direction – down the axon. ...
... Refractory period – short period of time after an action potential when a threshold stimulus will NOT trigger another action potential. a.Limits frequency b.Ensures the impulse is only transmitted in one direction – down the axon. ...
Nervous System Worksheet
... A. The collective name for a range of diseases affecting the nerves. B. Another name for a nerve cell. C. The small sac that contains the genetic material of each cell in the body, including the nerve cell. _____ 4. What is a myelin sheath? A. The protective coating that encloses a nerve cable (axon ...
... A. The collective name for a range of diseases affecting the nerves. B. Another name for a nerve cell. C. The small sac that contains the genetic material of each cell in the body, including the nerve cell. _____ 4. What is a myelin sheath? A. The protective coating that encloses a nerve cable (axon ...
The Nervous System Neurons A. Definition 1. Basic cells of the
... 1. A change in the environment that may cause an organism to respond B. Sensory Receptors 1. Collect and transmit information about the outside world a. Five senses ...
... 1. A change in the environment that may cause an organism to respond B. Sensory Receptors 1. Collect and transmit information about the outside world a. Five senses ...
CHAPTER 10: NERVOUS SYSTEM I OBJECTIVES 1. Name the two
... List, and discuss the structure and function of the four types of neuroglial cells in the CNS. Astrocyte- star shaped, nourishes neurons and provide structural support Oligodendrocyte- Looks like an eyeball, produces myelin Microglia- Looks like a spider, Phagocytosis Ependyma, epithelial like layer ...
... List, and discuss the structure and function of the four types of neuroglial cells in the CNS. Astrocyte- star shaped, nourishes neurons and provide structural support Oligodendrocyte- Looks like an eyeball, produces myelin Microglia- Looks like a spider, Phagocytosis Ependyma, epithelial like layer ...
10-1
... 25. This neurotransmitter is produced in quite a few areas of the brain, including the substantia nigra and the ventral tegmental area. It is also a neurohormone released by the hypothalamus. Its principle hormonal role is to inhibit the release of prolactin from the anterior lobe of the pituitary. ...
... 25. This neurotransmitter is produced in quite a few areas of the brain, including the substantia nigra and the ventral tegmental area. It is also a neurohormone released by the hypothalamus. Its principle hormonal role is to inhibit the release of prolactin from the anterior lobe of the pituitary. ...
Nervous System Intro
... • Sensory receptors detect a change outside or inside the body • Monitor internal, external and environmental factors • Light and sound, temperature, oxygen concentration ...
... • Sensory receptors detect a change outside or inside the body • Monitor internal, external and environmental factors • Light and sound, temperature, oxygen concentration ...
Nervous System Vocabulary KEY Afferent Neurons: (Sensory
... the tissue fluid & they do so very rapidly. This outflow of positive ions from the cell restores the electrical conditions at the membrane to the polarized or resting state, an event called repolarization. Until repolarization occurs, a neuron cannot conduct another impulse. 29. Saltatory Conduction ...
... the tissue fluid & they do so very rapidly. This outflow of positive ions from the cell restores the electrical conditions at the membrane to the polarized or resting state, an event called repolarization. Until repolarization occurs, a neuron cannot conduct another impulse. 29. Saltatory Conduction ...
Nervous System
... – Neurons only possess one – mm to m in length. Where could an axon a meter in length be found? ...
... – Neurons only possess one – mm to m in length. Where could an axon a meter in length be found? ...
Nervous System - Mohawk Medicinals
... Action potentials are produced sequentially in adjacent membrane Refractory period prevents backflow of conduction ...
... Action potentials are produced sequentially in adjacent membrane Refractory period prevents backflow of conduction ...
ppt of nervous system slides
... Action potentials are produced sequentially in adjacent membrane Refractory period prevents backflow of conduction ...
... Action potentials are produced sequentially in adjacent membrane Refractory period prevents backflow of conduction ...
Chapter 2
... for segregation of molecules involved in cellular processes (smooth); lipid molecules are made here (smooth) Golgi apparatus – wraps around products of a secretory cell (secretion = ...
... for segregation of molecules involved in cellular processes (smooth); lipid molecules are made here (smooth) Golgi apparatus – wraps around products of a secretory cell (secretion = ...
Nervous System
... neurons, sometimes over a considerable distance. In the neurons that make up the nerves running from the spinal cord to your toes, the axons can be as long as three feet! ...
... neurons, sometimes over a considerable distance. In the neurons that make up the nerves running from the spinal cord to your toes, the axons can be as long as three feet! ...
General Neurophysiology
... Transported retrogradely in nerve cells Released from the nerve cell body Taken up by the terminals of neiboring neurons ...
... Transported retrogradely in nerve cells Released from the nerve cell body Taken up by the terminals of neiboring neurons ...
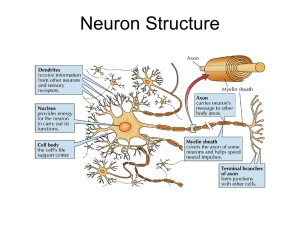
What is a neuron?
... Dendrites (receive) Cell Body (process) Axon (send) Axon Terminals (transfer) ...
... Dendrites (receive) Cell Body (process) Axon (send) Axon Terminals (transfer) ...
Nervous Tissue rawan turky
... 2. Myelinated nerve fiber: No Neurolemma as fibers in white matter. 3. Myelinated nerve fiber with Neurolemma as the peripheral somatic nerves outside the spinal cord. 4. Nerve fiber which are covered with Neurolemma but no with myelin sheath as the post ganglionic fibers. Rawan turky ...
... 2. Myelinated nerve fiber: No Neurolemma as fibers in white matter. 3. Myelinated nerve fiber with Neurolemma as the peripheral somatic nerves outside the spinal cord. 4. Nerve fiber which are covered with Neurolemma but no with myelin sheath as the post ganglionic fibers. Rawan turky ...
CHAPTER 28 Nervous Systems
... An action potential is a nerve signal – It is an electrical change in the plasma membrane voltage from the resting potential to a maximum level and back to the resting potential ...
... An action potential is a nerve signal – It is an electrical change in the plasma membrane voltage from the resting potential to a maximum level and back to the resting potential ...
Chapter 2
... • Action potential occurs when the membrane potential rapidly shifts from -70 to +40 mV – Ion channels open in the membrane, allowing sodium ions to enter the axon – Sodium entry shifts the membrane potential toward a positive value – Potential is restored when other channels open, allowing potassiu ...
... • Action potential occurs when the membrane potential rapidly shifts from -70 to +40 mV – Ion channels open in the membrane, allowing sodium ions to enter the axon – Sodium entry shifts the membrane potential toward a positive value – Potential is restored when other channels open, allowing potassiu ...
Study Guide for Chapter 7 - Neuron Function Be familiar with the
... (transmembrane) potential, microglia, motor neuron, multipolar neuron, oligodendrocyte, peripheral nerve, peripheral nervous system (PNS), polarized, postsynaptic cell, repolarization, resting membrane potential, Schwann cell, sensory neuron, Na+/K+ ATPase pump, synapse, synaptic end bulb (or bouton ...
... (transmembrane) potential, microglia, motor neuron, multipolar neuron, oligodendrocyte, peripheral nerve, peripheral nervous system (PNS), polarized, postsynaptic cell, repolarization, resting membrane potential, Schwann cell, sensory neuron, Na+/K+ ATPase pump, synapse, synaptic end bulb (or bouton ...
Central Nervous System
... • Neuron cell bodies and axons are insulated from their surroundings by processes of glial cells: - satellite cells surround cell bodies in peripheral ganglia - every peripheral axon (unmyelinated or myelinated) is covered by Schwann cells or neurolemmocytes - plasmalemma of an axon is called axolem ...
... • Neuron cell bodies and axons are insulated from their surroundings by processes of glial cells: - satellite cells surround cell bodies in peripheral ganglia - every peripheral axon (unmyelinated or myelinated) is covered by Schwann cells or neurolemmocytes - plasmalemma of an axon is called axolem ...
nervous system worksheet
... A. Synapse B. Axon C. Myelin sheath D. Nerve impulse E. Sense receptor F. Response; G. Reflex H. Cell body I. Dendrite J. Nerve K. Neurotransmitter L. Axon terminal Term ...
... A. Synapse B. Axon C. Myelin sheath D. Nerve impulse E. Sense receptor F. Response; G. Reflex H. Cell body I. Dendrite J. Nerve K. Neurotransmitter L. Axon terminal Term ...
Chapter 8 Study Guide: The Nervous System
... – Neurons conduct impulses, whereas glial cells are for support ...
... – Neurons conduct impulses, whereas glial cells are for support ...
Nervous System Cells
... • Neurons can be classified according to the direction in which they conduct impulses • Afferent neurons – transmit to the spinal cord or brain • Efferent neurons – transmit away from the brain or spinal cord ...
... • Neurons can be classified according to the direction in which they conduct impulses • Afferent neurons – transmit to the spinal cord or brain • Efferent neurons – transmit away from the brain or spinal cord ...
Node of Ranvier

The nodes of Ranvier also known as myelin sheath gaps, are the gaps (approximately 1 micrometer in length) formed between the myelin sheaths generated by different cells. A myelin sheath is a many-layered coating, largely composed of a fatty substance called myelin, that wraps around the axon of a neuron and very efficiently insulates it. At nodes of Ranvier, the axonal membrane is uninsulated and, therefore, capable of generating electrical activity.