Types of Rock
... Extrusive Rocks: forms when magma erupts onto the Earth’s surface (lava), cools quickly with very small or no crystals formed ...
... Extrusive Rocks: forms when magma erupts onto the Earth’s surface (lava), cools quickly with very small or no crystals formed ...
Unit 1: Geology
... making predictions, drawing conclusions based on evidence) ● Making evidence based claims to support the theory of Pangaea and continental drift ...
... making predictions, drawing conclusions based on evidence) ● Making evidence based claims to support the theory of Pangaea and continental drift ...
The Dynamic Earth Chapter 3
... A Global temperature regulator: • The oceans absorb and store energy from sunlight. • This regulates temps in the atmosphere. • The Worlds ocean absorbs over 50% of the radiation that reaches the surface. • Cities near the ocean have milder annual temps ...
... A Global temperature regulator: • The oceans absorb and store energy from sunlight. • This regulates temps in the atmosphere. • The Worlds ocean absorbs over 50% of the radiation that reaches the surface. • Cities near the ocean have milder annual temps ...
Lecture09
... atmosphere, is absorbed by the surface and radiated as infrared • CO2 is opaque to infrared and traps the infrared radiation, warming the Earth Current greenhouse gasses warm the Earth 23C • CO 2 is increasing due to man ...
... atmosphere, is absorbed by the surface and radiated as infrared • CO2 is opaque to infrared and traps the infrared radiation, warming the Earth Current greenhouse gasses warm the Earth 23C • CO 2 is increasing due to man ...
Constructive and Destructive Forces Notes and Activities
... naturally weaker than others, while others are more resistant (stronger). ...
... naturally weaker than others, while others are more resistant (stronger). ...
Document
... Superposition: youngest rocks superimposed on older rocks “Relative time” Dating by radioactive isotopes Half-life: time for ½ of unstable isotopes to decay “Absolute time” Uniformitarianism: Hutton (1795), Lyell (1830) “The same physical processes active in the environment today have been operating ...
... Superposition: youngest rocks superimposed on older rocks “Relative time” Dating by radioactive isotopes Half-life: time for ½ of unstable isotopes to decay “Absolute time” Uniformitarianism: Hutton (1795), Lyell (1830) “The same physical processes active in the environment today have been operating ...
Unit 2: Earth`s Systems
... Ocean currents regulate the climates on the lands they flow near. The Biosphere is is made up of the uppermost part of the geosphere, most of the hydrosphere, and the lower part of the atmosphere. Earth is a closed system, energy enters and leaves the system but matter does not. ...
... Ocean currents regulate the climates on the lands they flow near. The Biosphere is is made up of the uppermost part of the geosphere, most of the hydrosphere, and the lower part of the atmosphere. Earth is a closed system, energy enters and leaves the system but matter does not. ...
The Origin of Continents and Oceans
... Students will write and discuss ideas related to plate tectonics, as well as follow its progression through history(10D) ...
... Students will write and discuss ideas related to plate tectonics, as well as follow its progression through history(10D) ...
The ups and downs of sediments
... deviate from the terrestrial array. This would give a different signature to that typically found for ocean-island lavas. However, oceanic crust does not fit the bill as the source for ocean-island basalts either. Because of the way elements redistribute in the mantle during melting, the material th ...
... deviate from the terrestrial array. This would give a different signature to that typically found for ocean-island lavas. However, oceanic crust does not fit the bill as the source for ocean-island basalts either. Because of the way elements redistribute in the mantle during melting, the material th ...
IEA - Data Enhancement Project Questionnaire printing Study: SC2
... What fundamental assumption is made when the record found in the rocks is interpreted? A B C D E ...
... What fundamental assumption is made when the record found in the rocks is interpreted? A B C D E ...
Plate Tectonics
... continent which he called Pangaea (meaning "all lands"), and over time they have drifted apart into their current distribution. He believed that Pangaea was intact until about 300 million years ago, when it began to break up and drift apart. ...
... continent which he called Pangaea (meaning "all lands"), and over time they have drifted apart into their current distribution. He believed that Pangaea was intact until about 300 million years ago, when it began to break up and drift apart. ...
Sea-Floor Spreading - Catawba County Schools
... and then records the echoes of these sound waves. Sonar mapped midocean ridges. ...
... and then records the echoes of these sound waves. Sonar mapped midocean ridges. ...
Continental drift - La Salle Elementary School
... A. Highlights for Section 1 pages 55-59 Alfred Wegener (German scientist) proposed a theory: o Continental drift Earth was once a single landmass called Pangaea that has since broken up into large pieces that drifted apart. Evidence from fossils – preserved remains of ancient organisms support ...
... A. Highlights for Section 1 pages 55-59 Alfred Wegener (German scientist) proposed a theory: o Continental drift Earth was once a single landmass called Pangaea that has since broken up into large pieces that drifted apart. Evidence from fossils – preserved remains of ancient organisms support ...
Earth Science Unit Test #1 Study Guide
... o Brain POP Videos- Mountains, Volcanoes, Earthquakes, Earth’s Structure, Plate Tectonics ...
... o Brain POP Videos- Mountains, Volcanoes, Earthquakes, Earth’s Structure, Plate Tectonics ...
answers to review questions – chapter 33
... Name the four major geologic eras. What significant biological events characterise each of them? (pp. 769–777) Pre-Cambrian—origins of life Palaeozoic—ancient life Mesozoic—age of dinosaurs Cenozoic—the beginning of modern life Older Pre-Cambrian organisms were prokaryotes. Some of these prokaryotes ...
... Name the four major geologic eras. What significant biological events characterise each of them? (pp. 769–777) Pre-Cambrian—origins of life Palaeozoic—ancient life Mesozoic—age of dinosaurs Cenozoic—the beginning of modern life Older Pre-Cambrian organisms were prokaryotes. Some of these prokaryotes ...
ch7 answers to SG
... general, the asthenosphere transfers thermal energy to the surface by way of convection currents. Convection currents in the asthenosphere are dense solid rock sinking through less dense solid rock over a period of millennia, at a rate of a few centimeters per year. 30. If we could dig all the way t ...
... general, the asthenosphere transfers thermal energy to the surface by way of convection currents. Convection currents in the asthenosphere are dense solid rock sinking through less dense solid rock over a period of millennia, at a rate of a few centimeters per year. 30. If we could dig all the way t ...
Rev. 2013 Fast and Slow Changes to Earth`s Surface Volcano – Fast
... Helpful - when the lava spreads, cools and hardens the remaining surface becomes new land for the Earth. If it flows from underwater volcanoes the land formed will be an island. The new formed land tends to be a very rich or fertile soil for farmers. It is one way the Earth renews itself. Islands su ...
... Helpful - when the lava spreads, cools and hardens the remaining surface becomes new land for the Earth. If it flows from underwater volcanoes the land formed will be an island. The new formed land tends to be a very rich or fertile soil for farmers. It is one way the Earth renews itself. Islands su ...
- Maheshtala College
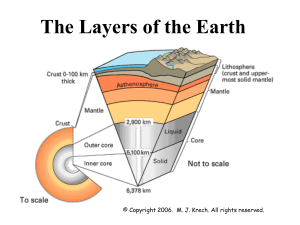
... The Earth is composed of four different layers. The crust is the layer that you live on, and it is the most widely studied and understood. The mantle is much hotter and has the ability to flow. The outer core and inner core are even hotter with pressures so great you would be squeezed into a ball sm ...
... The Earth is composed of four different layers. The crust is the layer that you live on, and it is the most widely studied and understood. The mantle is much hotter and has the ability to flow. The outer core and inner core are even hotter with pressures so great you would be squeezed into a ball sm ...
Age of the Earth

The age of the Earth is 4.54 ± 0.05 billion years (4.54 × 109 years ± 1%). This age is based on evidence from radiometric age dating of meteorite material and is consistent with the radiometric ages of the oldest-known terrestrial and lunar samples.Following the development of radiometric age dating in the early 20th century, measurements of lead in uranium-rich minerals showed that some were in excess of a billion years old.The oldest such minerals analyzed to date—small crystals of zircon from the Jack Hills of Western Australia—are at least 4.404 billion years old. Comparing the mass and luminosity of the Sun to those of other stars, it appears that the Solar System cannot be much older than those rocks. Calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions – the oldest known solid constituents within meteorites that are formed within the Solar System – are 4.567 billion years old, giving an age for the solar system and an upper limit for the age of Earth.It is hypothesised that the accretion of Earth began soon after the formation of the calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions and the meteorites. Because the exact amount of time this accretion process took is not yet known, and the predictions from different accretion models range from a few millions up to about 100 million years, the exact age of Earth is difficult to determine. It is also difficult to determine the exact age of the oldest rocks on Earth, exposed at the surface, as they are aggregates of minerals of possibly different ages.