Conserved BK Channel-Protein Interactions Reveal Signals
... BKAPs were identified from chick membrane/cytoskeletal and cytoplasmic fractions using BK co-IP, 2-D gel electrophoresis, and LC-MS/MS analysis. This procedure involved the removal of non-specific binding proteins, and isolation of BKAPs with controls using non-immunoprecipitated matrix assays and i ...
... BKAPs were identified from chick membrane/cytoskeletal and cytoplasmic fractions using BK co-IP, 2-D gel electrophoresis, and LC-MS/MS analysis. This procedure involved the removal of non-specific binding proteins, and isolation of BKAPs with controls using non-immunoprecipitated matrix assays and i ...
Identification of cAMP-dependent phosphorylated proteins involved
... other than a core polypeptide of Complex III of a mitochondrial electron transport chain. That is, RISP may form part of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore complex, and the phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of this protein may be involved in the regulation of the mitochondrial permea ...
... other than a core polypeptide of Complex III of a mitochondrial electron transport chain. That is, RISP may form part of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore complex, and the phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of this protein may be involved in the regulation of the mitochondrial permea ...
non-RD - Crop Genetics Innovation
... are abundant in a handful of subfamilies that contain many of the known PRRs. Collectively these PRR subfamilies do not form a distinct clade and are instead scattered among numerous receptor and cytoplasmic kinase clades involved in a wide range of biological functions (Figure 2). Thus, the phyloge ...
... are abundant in a handful of subfamilies that contain many of the known PRRs. Collectively these PRR subfamilies do not form a distinct clade and are instead scattered among numerous receptor and cytoplasmic kinase clades involved in a wide range of biological functions (Figure 2). Thus, the phyloge ...
FUNCTIONS OF PLASMA PROTEINS
... separation into albumin, fibrinogen, alpha, beta and gamma globulins Paper electrophoresis Ultracentrifugation Affinity chromatography Fractional precipitation method Immune electrophoresis ...
... separation into albumin, fibrinogen, alpha, beta and gamma globulins Paper electrophoresis Ultracentrifugation Affinity chromatography Fractional precipitation method Immune electrophoresis ...
The Sense of Smell
... Olfactory receptors respond to several different odor-causing chemicals When bound to ligand these proteins initiate a G protein mechanism, which uses cAMP as a second messenger cAMP opens Na+ and Ca2+ channels, causing depolarization of the receptor membrane triggers an action potential ...
... Olfactory receptors respond to several different odor-causing chemicals When bound to ligand these proteins initiate a G protein mechanism, which uses cAMP as a second messenger cAMP opens Na+ and Ca2+ channels, causing depolarization of the receptor membrane triggers an action potential ...
Protein Analysis-Determination of Protein Concentration
... tyrosine and tryptophan. The general method is just to take a solution of your protein, stick it into a spectrophotometer, and read the A280. If you have pure protein, you then have a measure of the protein concentration. However, not only does protein absorb at 280 nm, but many other compounds also ...
... tyrosine and tryptophan. The general method is just to take a solution of your protein, stick it into a spectrophotometer, and read the A280. If you have pure protein, you then have a measure of the protein concentration. However, not only does protein absorb at 280 nm, but many other compounds also ...
2. Fredriksson, R., et al., The G-protein
... and the βγ dimer [24]. Both the GTP bound α-subunit and the released βγ-dimer can mediate the stimulation or inhibition of effector proteins such as enzymes and ion channels [e.g, adenylate cyclase, guanylyl cyclase, phospholipase C, mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), Ca+2, and K+ channels]. ...
... and the βγ dimer [24]. Both the GTP bound α-subunit and the released βγ-dimer can mediate the stimulation or inhibition of effector proteins such as enzymes and ion channels [e.g, adenylate cyclase, guanylyl cyclase, phospholipase C, mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), Ca+2, and K+ channels]. ...
Notes
... Clefts / pockets (Prediction of ligand binding sites) – For ~85% of ligand-binding proteins, the largest cleft is the ligandbinding site – For additional ~10% of ligand-binding proteins, the second largest cleft is the ligand-binding site ...
... Clefts / pockets (Prediction of ligand binding sites) – For ~85% of ligand-binding proteins, the largest cleft is the ligandbinding site – For additional ~10% of ligand-binding proteins, the second largest cleft is the ligand-binding site ...
Gene Section ARNT (aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... NADP(H): oxidoreductase ( NQO1). Transcriptional activation of these genes depends upon prior binding of AHR to xenobiotic ligands, including 2,3,7,8tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (dioxin) and benzo(a)pyrene. The AHR/ARNT dimer and ARNT itself can also impact signaling by the eostrogen receptor. The HI ...
... NADP(H): oxidoreductase ( NQO1). Transcriptional activation of these genes depends upon prior binding of AHR to xenobiotic ligands, including 2,3,7,8tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (dioxin) and benzo(a)pyrene. The AHR/ARNT dimer and ARNT itself can also impact signaling by the eostrogen receptor. The HI ...
Translation - Santa Susana High School
... – energy from GTP is used in the formation of the unit ...
... – energy from GTP is used in the formation of the unit ...
A novel protein transport system involved in the biogenesis of
... Studies in E. coli have identi¢ed two operons, tatABCD and tatE, coding for components of the Tat pathway (Fig. 1). Strains with in-frame deletions in tatB, in tatC, or in a combination of both tatA and tatE, are completely defective in the translocation of precursor proteins with twin-arginine sign ...
... Studies in E. coli have identi¢ed two operons, tatABCD and tatE, coding for components of the Tat pathway (Fig. 1). Strains with in-frame deletions in tatB, in tatC, or in a combination of both tatA and tatE, are completely defective in the translocation of precursor proteins with twin-arginine sign ...
MEICPS: substitution mutations to engineer intracellular protein
... (SPI) is calculated by summing all the DSP values corresponding to their respective structural environment. Thus, for each ...
... (SPI) is calculated by summing all the DSP values corresponding to their respective structural environment. Thus, for each ...
1 - chem.msu.su
... those we have described. Some proteins have consensus sequences recognized by several different protein kinases, each of which can phosphorylate the protein and alter its enzymatic activity. For example, glycogen synthase is inactivated by cAMP-dependent phosphorylation of specific Ser residues, and ...
... those we have described. Some proteins have consensus sequences recognized by several different protein kinases, each of which can phosphorylate the protein and alter its enzymatic activity. For example, glycogen synthase is inactivated by cAMP-dependent phosphorylation of specific Ser residues, and ...
Mutational analysis of the early f orespore/mother
... to sense the activating signal or, presumably, to transduce it to the catalytic domain inside the cell. The N-terminal end of SpoIIGA, predicted to contain only 6 or 7 aa, stands out by the conservation of some of these residues (Y4, D6, V7) in the SpoIIGA homologue found in the sporulating bacteriu ...
... to sense the activating signal or, presumably, to transduce it to the catalytic domain inside the cell. The N-terminal end of SpoIIGA, predicted to contain only 6 or 7 aa, stands out by the conservation of some of these residues (Y4, D6, V7) in the SpoIIGA homologue found in the sporulating bacteriu ...
Quorum Sensing as a Potential Antimicrobial Target
... Quorum sensing in bacterial pathogenesis QS is involved in expression of virulence genes in various bacteria, indicating the possible role of quorum sensing as a drug target. Several QS system mutant bacteria show the heavily reduced pathogenicity. Pseudomonas aeruginosa mutant in synthesis o ...
... Quorum sensing in bacterial pathogenesis QS is involved in expression of virulence genes in various bacteria, indicating the possible role of quorum sensing as a drug target. Several QS system mutant bacteria show the heavily reduced pathogenicity. Pseudomonas aeruginosa mutant in synthesis o ...
Chapter 7: Proteins
... Proteins stimulate the release of CCK Pancreas release the protein splitting enzymes: trypsin, chymotrypsin, and carboxypeptidase into the duodenum The enzymes will break peptones into smaller peptides and amino acids Peptides and amino acids are ready for absorption ...
... Proteins stimulate the release of CCK Pancreas release the protein splitting enzymes: trypsin, chymotrypsin, and carboxypeptidase into the duodenum The enzymes will break peptones into smaller peptides and amino acids Peptides and amino acids are ready for absorption ...
Protein Structure - Particle Sciences
... interactions between one-another, while aromatic groups such as those of phenylalanine and tryosine often stack together. Acidic or basic amino acid side-chains will generally be exposed on the surface of the protein as they are hydrophilic. The formation of disulfide bridges by oxidation of the sul ...
... interactions between one-another, while aromatic groups such as those of phenylalanine and tryosine often stack together. Acidic or basic amino acid side-chains will generally be exposed on the surface of the protein as they are hydrophilic. The formation of disulfide bridges by oxidation of the sul ...
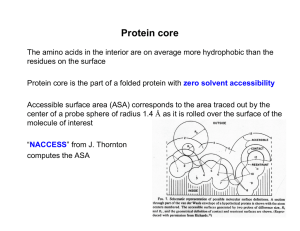
Protein core - Acsu.buffalo.edu
... Thermal stability influences the average lifespan of a protein molecules since proteolysis likely occurs while the protein is in an unfolded state ...
... Thermal stability influences the average lifespan of a protein molecules since proteolysis likely occurs while the protein is in an unfolded state ...
MCB Lecture 3 – Gene Regulation
... o An inducible gene is normally off, but can be turned on. What is a repressible gene? o A repressible gene is always on, but can be turned off. What are constitutive genes? o Constitutive genes are those that stay more or less constant because they are the housekeeping genes of the cell. What are t ...
... o An inducible gene is normally off, but can be turned on. What is a repressible gene? o A repressible gene is always on, but can be turned off. What are constitutive genes? o Constitutive genes are those that stay more or less constant because they are the housekeeping genes of the cell. What are t ...
as a PDF
... Haemophilus influenzae were to be determined [7] with the long-range goal of using protein structure to facilitate the assignment of function. Structural genomics refers to the large-scale, highthroughput determination of three-dimensional structures of biological macromolecules. A major goal of suc ...
... Haemophilus influenzae were to be determined [7] with the long-range goal of using protein structure to facilitate the assignment of function. Structural genomics refers to the large-scale, highthroughput determination of three-dimensional structures of biological macromolecules. A major goal of suc ...
amino acids
... • A compact and globular structural unit of a protein is often called as a domain (i.e. pearls on a string) • The size of a domain ranges from 30 to 400 amino acid residues. • Different proteins can have a similar or the same domain. • Domain is a structural working unit of a protein for the common ...
... • A compact and globular structural unit of a protein is often called as a domain (i.e. pearls on a string) • The size of a domain ranges from 30 to 400 amino acid residues. • Different proteins can have a similar or the same domain. • Domain is a structural working unit of a protein for the common ...
Non-Invasive Optical Biosensor for Probing Cell Signaling
... measures an averaged response of a large population of cells located at the light incident area. Although cells undergo micromotion at the single cell level, the large populations of cells examined give rise to a net-zero DMR response in average. Furthermore, it is known that intracellular macromole ...
... measures an averaged response of a large population of cells located at the light incident area. Although cells undergo micromotion at the single cell level, the large populations of cells examined give rise to a net-zero DMR response in average. Furthermore, it is known that intracellular macromole ...
Proteins: Classification and Types
... Although all forms of proteins can be digested and used as a source of energy and as a building material by different organisms, there are certain forms which are meant for storage only and they are not used for other purposes. This includes the proteins legumins (legumes), zein (maize), hordein (oa ...
... Although all forms of proteins can be digested and used as a source of energy and as a building material by different organisms, there are certain forms which are meant for storage only and they are not used for other purposes. This includes the proteins legumins (legumes), zein (maize), hordein (oa ...
Mapping allosteric connections from the receptor G proteins
... conformation. Heptahelical receptors in the cell membrane activate G proteins by catalyzing GTP for GDP exchange on G␣, leading to the activation of downstream effector proteins by G␣(GTP) and G␥. The signal is terminated upon the hydrolysis of GTP to GDP by G␣ and its reassociation with G␥ (1). N ...
... conformation. Heptahelical receptors in the cell membrane activate G proteins by catalyzing GTP for GDP exchange on G␣, leading to the activation of downstream effector proteins by G␣(GTP) and G␥. The signal is terminated upon the hydrolysis of GTP to GDP by G␣ and its reassociation with G␥ (1). N ...
Three-Dimensional Structure of the Muscle Fatty-Acid
... N-terminus and at the regions defined by Gly 25 to Arg 31, Asp 78 to Val 82, and Gly 100 to His 102. As expected from the overall lower temperature factors, the interactions between molecule I1 and its symmetry-related partners are more extensive with 25 protein-protein contacts within 3.5 A. For mo ...
... N-terminus and at the regions defined by Gly 25 to Arg 31, Asp 78 to Val 82, and Gly 100 to His 102. As expected from the overall lower temperature factors, the interactions between molecule I1 and its symmetry-related partners are more extensive with 25 protein-protein contacts within 3.5 A. For mo ...
G protein–coupled receptor

G protein–coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptor, and G protein–linked receptors (GPLR), constitute a large protein family of receptors that sense molecules outside the cell and activate inside signal transduction pathways and, ultimately, cellular responses. Coupling with G proteins, they are called seven-transmembrane receptors because they pass through the cell membrane seven times.G protein–coupled receptors are found only in eukaryotes, including yeast, choanoflagellates, and animals. The ligands that bind and activate these receptors include light-sensitive compounds, odors, pheromones, hormones, and neurotransmitters, and vary in size from small molecules to peptides to large proteins. G protein–coupled receptors are involved in many diseases, and are also the target of approximately 40% of all modern medicinal drugs. Two of the United States's top five selling drugs (Hydrocodone and Lisinopril) act by targeting a G protein–coupled receptor. The 2012 Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to Brian Kobilka and Robert Lefkowitz for their work that was ""crucial for understanding how G protein–coupled receptors function."". There have been at least seven other Nobel Prizes awarded for some aspect of G protein–mediated signaling.There are two principal signal transduction pathways involving the G protein–coupled receptors: the cAMP signal pathway and the phosphatidylinositol signal pathway. When a ligand binds to the GPCR it causes a conformational change in the GPCR, which allows it to act as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF). The GPCR can then activate an associated G protein by exchanging its bound GDP for a GTP. The G protein's α subunit, together with the bound GTP, can then dissociate from the β and γ subunits to further affect intracellular signaling proteins or target functional proteins directly depending on the α subunit type (Gαs, Gαi/o, Gαq/11, Gα12/13).